Market news & analysis.
Catch up on the latest in the market and get the latest market reviews.

USD hits 30-year high in 2024: What does it mean for the markets

A Traders Guide To Today's Federal Funds Rate Decision

Forex Trading Week Ahead Analysis: 10th June

5 Signs That Indicate It’s Time to Change Your Trading Strategy

How to Protect Yourself From Market Reversals?

US Inflation Outlook for 2025

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 3rd March

How to Trade the ECB Rate Decision

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 24th February

How to Subscribe to Trading Signals on MetaTrader

Guide to Trump Coin: Everything Traders Must Know

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 17th February
Advanced Technical Analysis with MT5 Indicators

When to Trade a Forex Cross Pair?

How Can Traders Use GDP to Find Opportunities?
Can Positive Reevaluation Improve Your Trading Performance?
Can You Add Scripts to MetaTrader 4?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 10th February

How to Avoid Being Influenced by Recency Bias

DeepSeek's Disruption of Global Financial Markets: What You Need to Know

Why You Should Set (And Stick To) A Maximum Trading Loss
How to Change The Volume of a Trade in MetaTrader
How To Create Templates In MT5
Mastering Chart Types in MetaTrader 5

Trading Opportunities in the MSCI Emerging Markets Index

What Happens When a Central Bank Cuts Interest Rates?

A Comprehensive Guide to Using Demo Accounts + Top Tips

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 3rd February

Why European Central Bank Cut Interest Rates Again?

Fed Cuts Interest Rates: Recession or Just a Soft Landing?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 20th January

Treasury Bonds vs. Treasury Notes vs. Treasury Bills

What is WTI Crude Oil: A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding the Benchmark

Impact of Fed Rate Cuts on Oil Prices

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 13th January

Where Interest Rates Might Go In 2025?

Top Cryptocurrency Forecasts for 2025

Bitcoin Price Prediction For 2025: What to Expect?

Forex Markets in 2025: Top Predictions

Oil Prices in 2025: What Do The Experts Say?

Emerging Market Currencies to Watch

Should You Trade Forex During Christmas and New Year?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 9th December

Will Gold Climb Higher in 2025?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 16th December

Is The US Recession Coming in 2025?

Is the BOJ Interest Rate Hike Coming Soon?

What are Corporate Bonds?

What is next for FTSE 100?

Copper Trading: Capitalizing on Global Demand

What is a Treasury Bond?

Treasury Notes: Navigating Mid-Term US Debt Investments

Platinum Trading: Opportunities in Precious Metals

How to Trade The MSCI World Index
Advance-Decline Line: How to Use The Market Breadth Indicator
Simple Moving Average (SMA)

Crypto Staking - What it is And How it Works
What is Position Trading?

Global Markets Stumble as Oil Prices Surge on Mideast Tensions

Bullish and Bearish Harami Candlestick Pattern

McClellan Summation Index: A Deep Dive

Top Trend Following Strategies

Yield Farming in Crypto: What Is It and How Does It Work?

Beginner's Guide to Quantitative Trading

Crypto Day Trading: Top Strategies

How Does The Arms Index (TRIN) Analyzes Market Sentiment

How to Use Put/Call Ratio to Gauge Market Sentiment

Rate of Change (ROC) Indicator Explained

Strategies for Trading Volatile Forex Pairs

Why Use Custom Moving Averages To Tailor Your Strategy

Buy and Hold: The Long-Term Trading Strategy
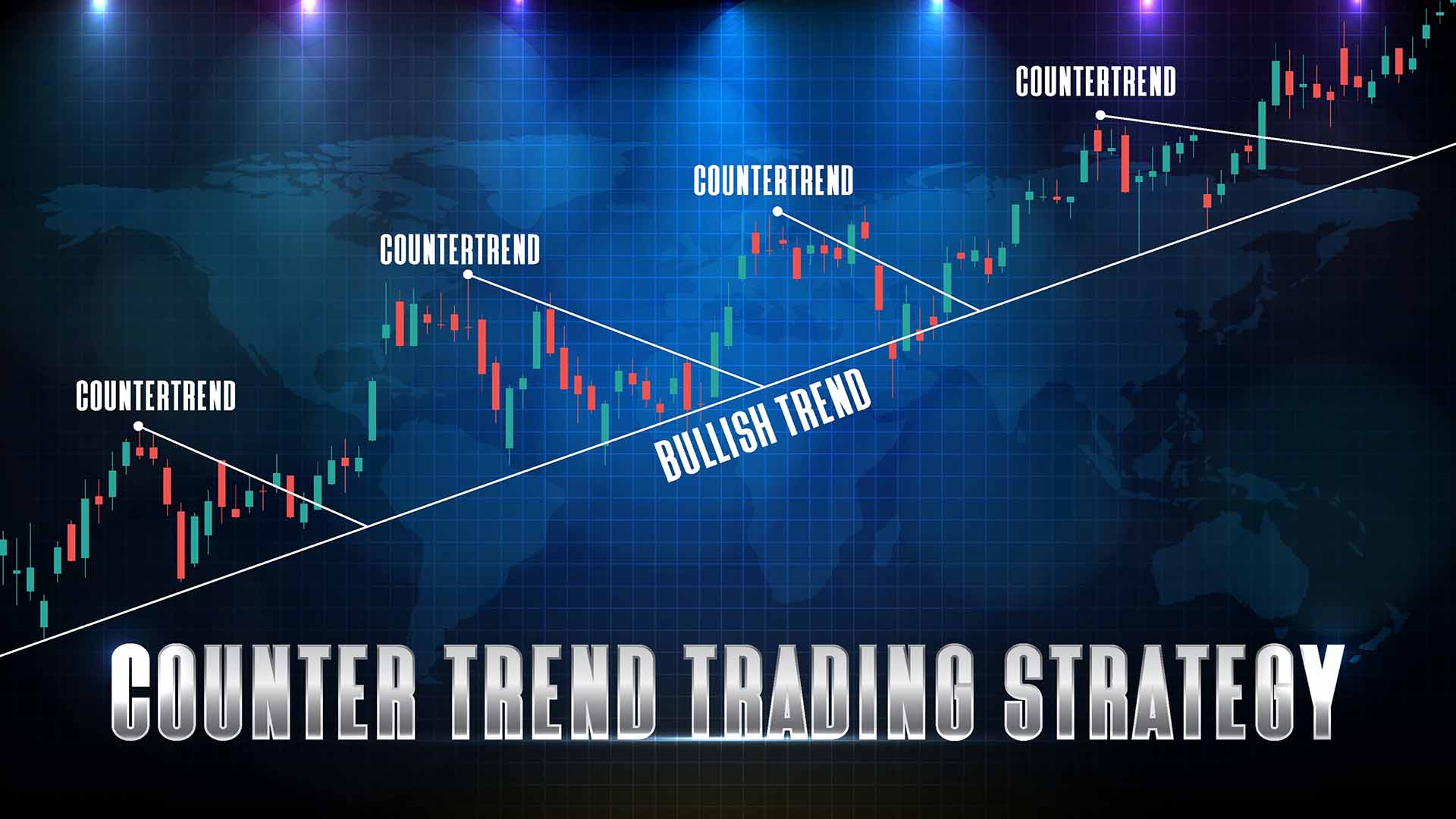
Counter-Trend Trading: Strategies and Tips

How to Use HODLing: The Long-Term Crypto Strategy
Protective Put Strategy: The Complete Guide
What is High-Frequency Trading (HFT) And How Does it Work?

Dollar Retreats Ahead of US Jobs Report Looms

Straddle Options Strategy: Meaning, Examples and Benefits

Technical Indicator Composites: The Complete Guide
What is a Covered Call Options Strategy?
What is a Take-Profit Order?

How to Build Your Own Crypto Trading Strategy

How to Create a Crypto Trading Journal

How to Use Fundamental Analysis for Crypto Trading
How to Use Rounding Top Pattern to Identify Bearish Signals

Seasonal Trading: The Complete Guide
Butterfly Pattern Trading: A Comprehensive Guide

Diamond Trading Pattern: Comprehensive Guide for Traders

Guide to Rounding Bottom Pattern

How to Use Dark Cloud Cover to Identify Trading Signals

How to Use Technical Analysis for Commodities Trading
M Trading Pattern: Master Double Top Strategy

Runaway Gap: Identifying and Trading Trends

Top Indicators for Swing Trading

Trading the Engulfing Pattern: Bullish & Bearish
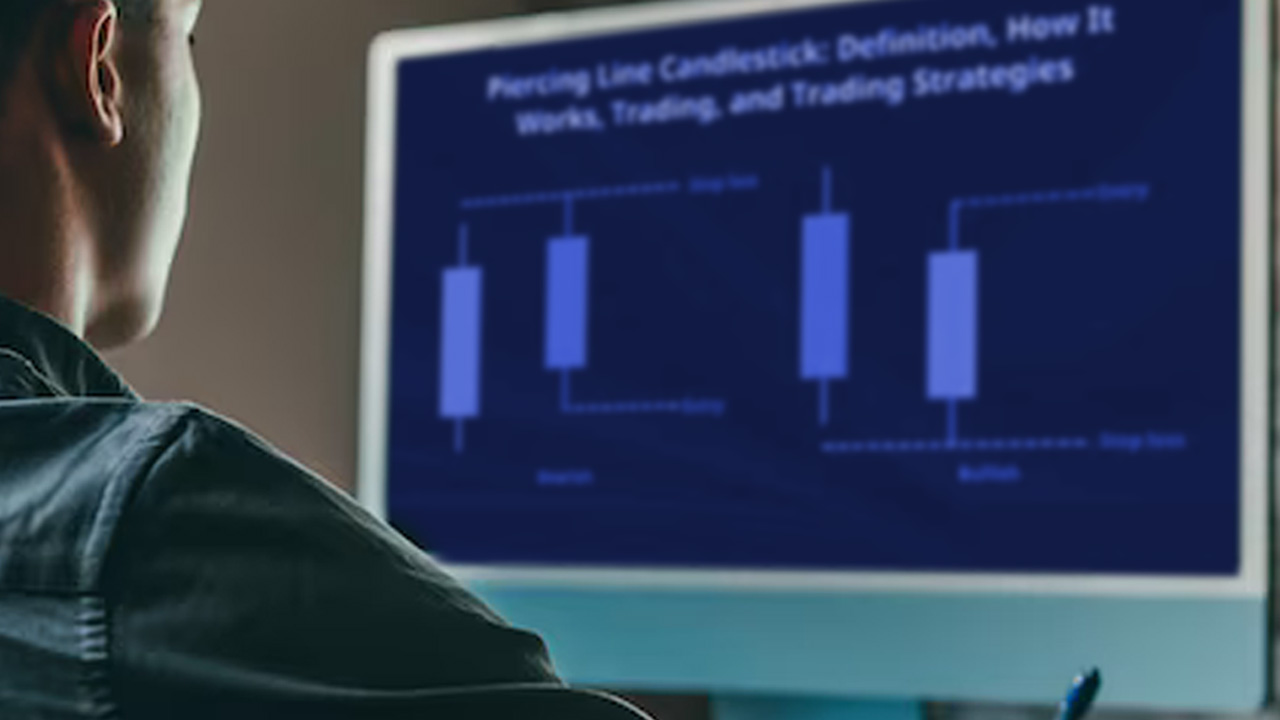
Trading the Piercing Line Pattern: A Quick Guide
W Pattern Trading: Mastering the Double Bottom Strategy

Dollar to Fluctuate as Investors Weigh Rate Cut Chances

Forex and AI: How is AI Changing the Forex Market in 2024?

Gold Prices Falling After a Period of Strong Growth

Questions to Ask When Trading Trends

Top Ways to Minimize Missed Trades

USD to Range-Bound Amidst Central Bank Speculation

Top Market Breadth Indicators

Trading Wedge Pattern: A Comprehensive Guide

Forex Trading Week Ahead: 16th September
Custom Oscillators To Personalizing Your Trading

Forex Cycles Analysis: Timing Market Movements

Forex Trading Week Ahead: 9th September

Exploring Exotic Forex Pairs: Opportunities and Risks

Trading the Russell 2000: Everything You Should Know

Pairs Trading: How to Use it For Hedging

Commitment of Traders: What are COT Reports & How to Read them
Exhaustion Gap: How to Trade the Final Push

Understanding Common Gap in Trading

British Pound Reversal

Forex Trading Week Ahead: 26th August

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 26th August

How to trade GBP/JPY

Gold Makes New Highs

Forex Weekly Trading Ideas: 19th August

Forex Weekly Trading Ideas: 19th August (1)

Why are retail traders wrong?

GBP Rallies Despite Unemployment Claims Shock

Forex Weekly Trading Ideas: 12th August

Japanese Markets to Rebound After its Biggest Drop in August's First Week

Top Market Predictions for Q3 2024

Gold Trends for Q3 2024: What to Expect?

Navigating the EURUSD Ahead of ECB's Interest Rate Decision

Correction or Recession?

Weekly Forex Trading Ideas- 5th August

What a week to be a forex trader

How to Use Technical Analysis When Trading Crypto

How to Use The Umbrella Pattern Trading
Dragon Pattern Trading: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Use The Megaphone Trading Pattern

Forex Weekly Trading Ideas: 29th July

Managing Emotions in High-Stakes Trading

How to Overcome the Fear of Losing Your Gains

Weekly Forex Trading Ideas: 29th July
Harmonic Trading Patterns

How To Trade USD/CAD: 24th July

Triangle Pattern Trading: Master Technical Analysis

How to Read Crypto Charts?

How to Create a Trading Strategy
Can You Set Up Expert Advisors In Metatrader 4?

Forex Weekly Trading Ideas: 22nd July

How To Trade CoT Reports

How to Place a Trade on MT5

Forex Weekly Trading Ideas: 15th July
How to Achieve Consistent Wins in Forex Trading

Why Trading With Data Matters

Weekly Forex Trading Ideas: 8th July

Top Indicators for Crypto Trading

Gold Finds Support Amid Rising Risk Events

Effective Risk Management in Crypto Trading

Cryptocurrency Trading Psychology: Everything Traders Should Know

How to Setup the Perfect Trading Routine?

How to Handle Trading Slumps

How to Set a Trailing Stop-Loss on MT5?

How to Choose Optimal Time Frames for Crypto Trading

Should You Trade Cryptocurrency on The Weekends?

How to Change Time Frames on MT5
How to Install Expert Advisors on MT5

Don't Trade EUR/AUD Until You See This

How Do Oil Prices Affect the Stock Market?
What Is Implied Volatility & Factors Affecting it?
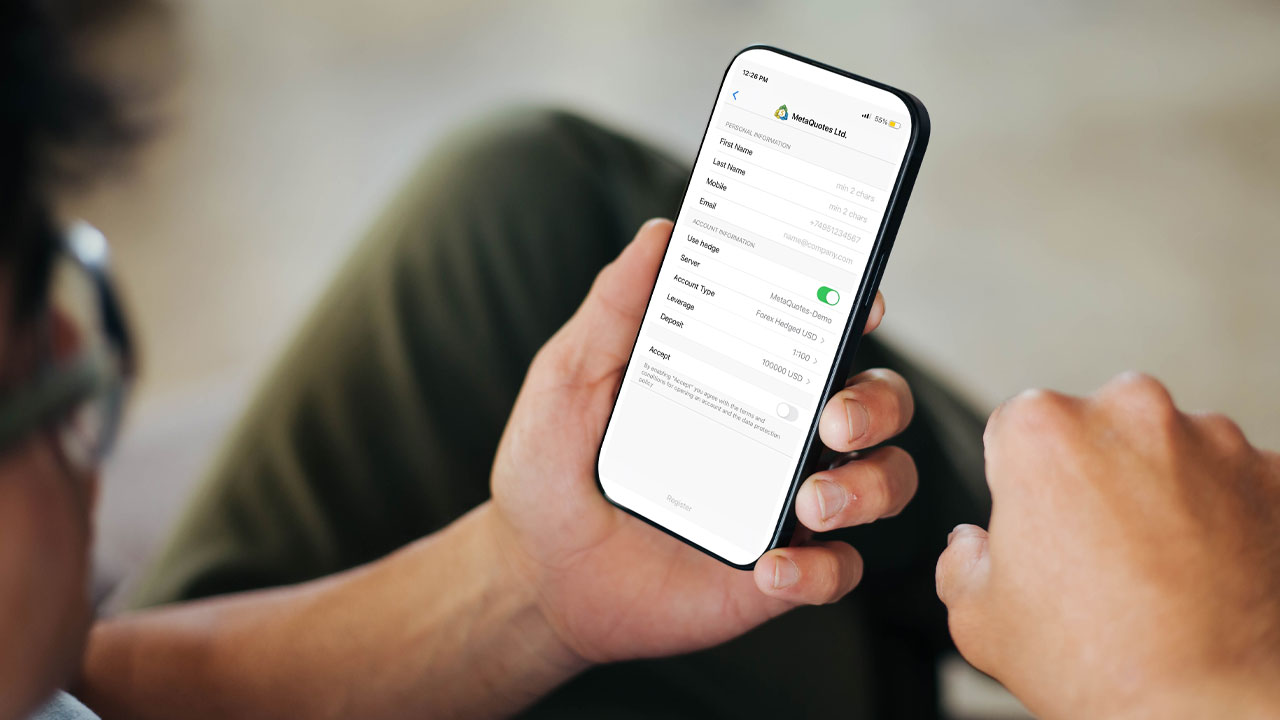
How to Create a Demo Account on MT5

Weekly Forex Trading Ideas: 24th June

How CoT Reports Could Predict a CAD Rally

Weekly Forex Trading Analysis: 17th June-21st June

Benefits and Risks of investing in the Tokyo Stock Exchange from Vietnam

How To Use MetaTrader 5 Mobile App

How to Use a Risk-Reward Calculator
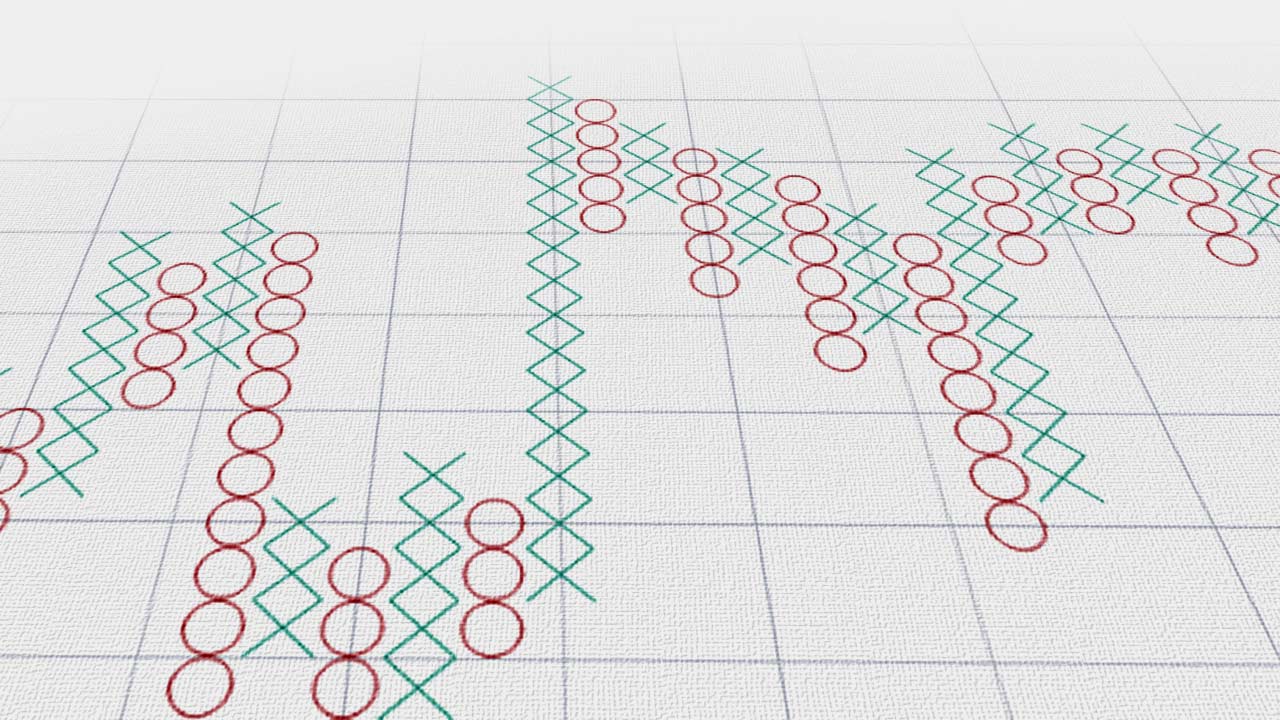
How to Trade With Point-and-Figure (P&F) Charts?
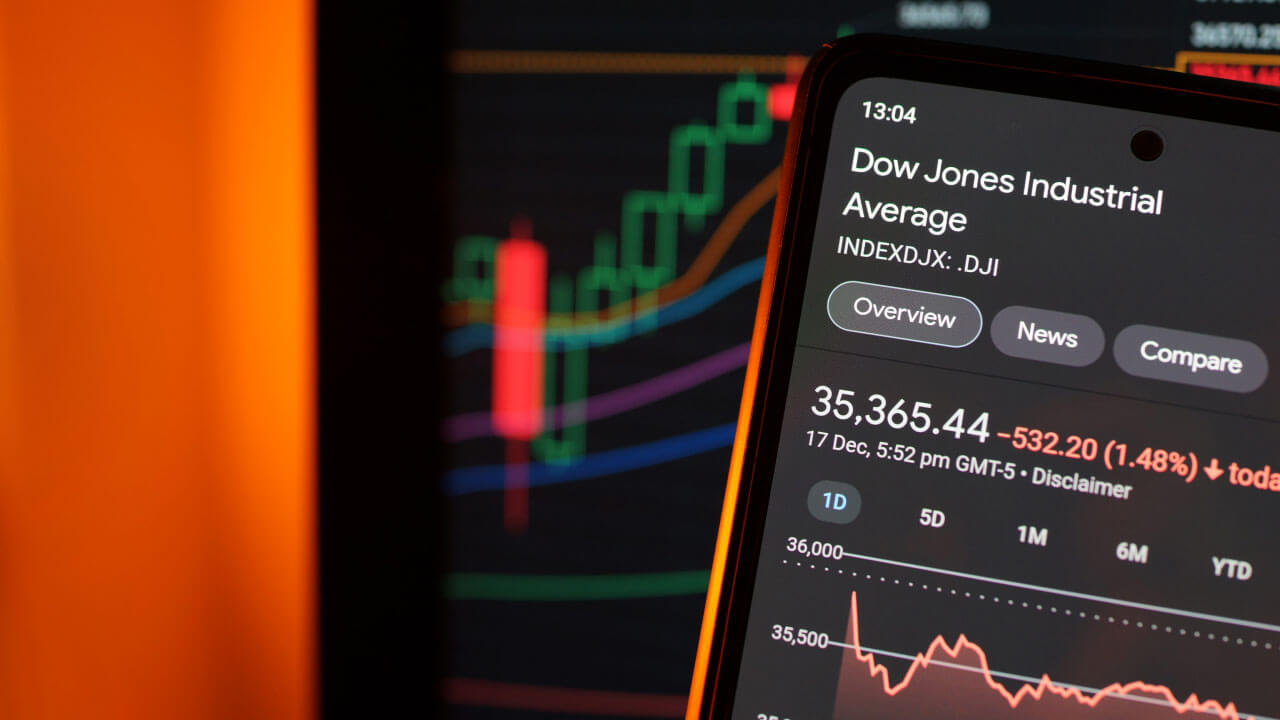
Understanding the Dow Jones Index: A Beginner's Guide

ECB Poised to Cut Interest Rates

How to Keep Trading Overconfidence in Check
How To Find A Trading Style That Suits You

How Forex Brokers Manage Risks

Forex Trading Week Ahead: 3rd June

How to Use Pivot Points for Range Trading
How to Trade With Guppy Multiple Moving Average (GMMA)

Donald Trump Found Guilty- FX Unchanged

Why Silver is the Undervalued Commodity
5 Exit Strategies To Consider in Forex Trading

EUR/USD Price Forecast 2024: What to Expect

Trading Cryptocurrencies with MetaTrader 5
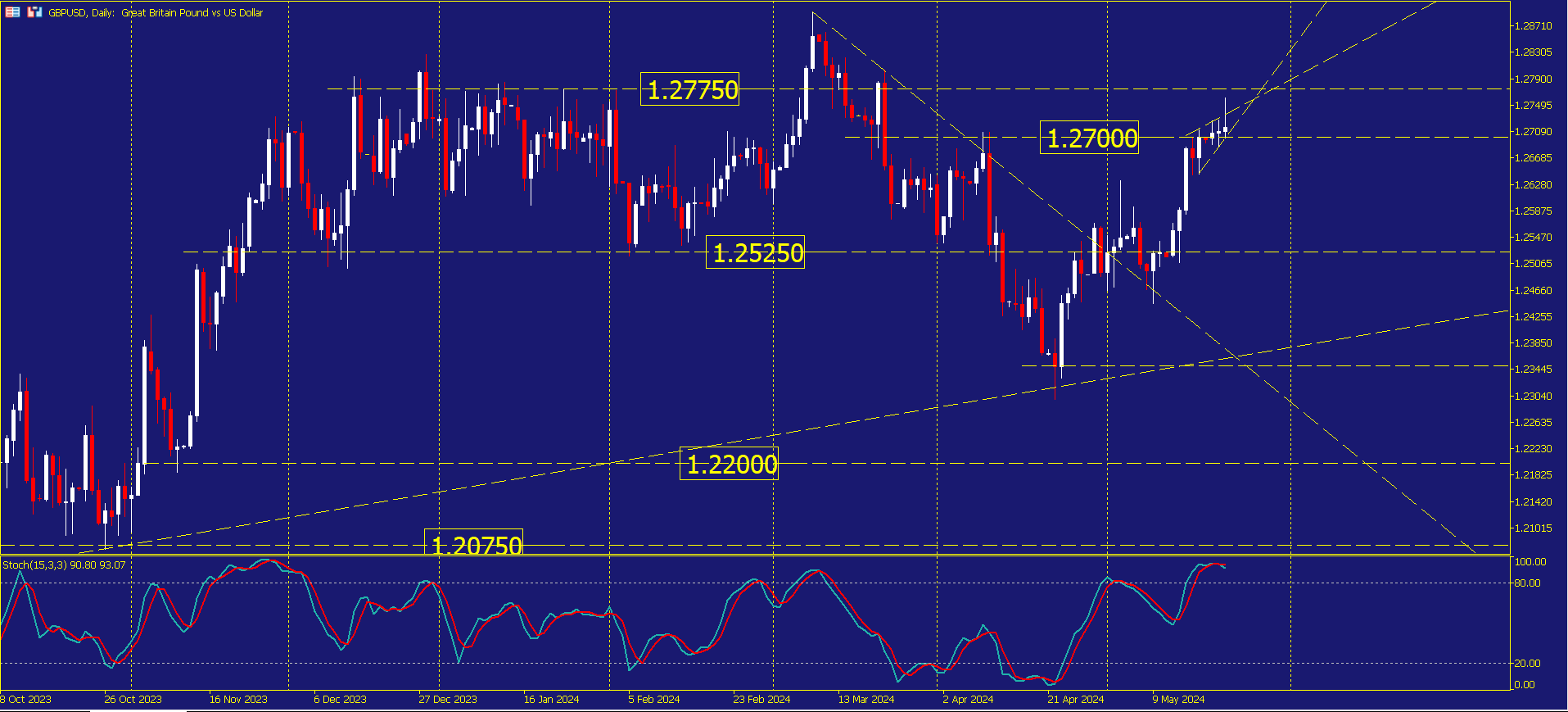
GBP/USD Spikes as UK Inflation Declines to 2.3%

GBPUSD A Key Pair to Watch This Week for Forex Traders

What is a Floating Exchange Rate?
How to Backtest a Trading Strategy?

How to Trade the EUR/CHF

How to Trade GBP/CAD?

US CPI: A Market Letdown and Its Implications
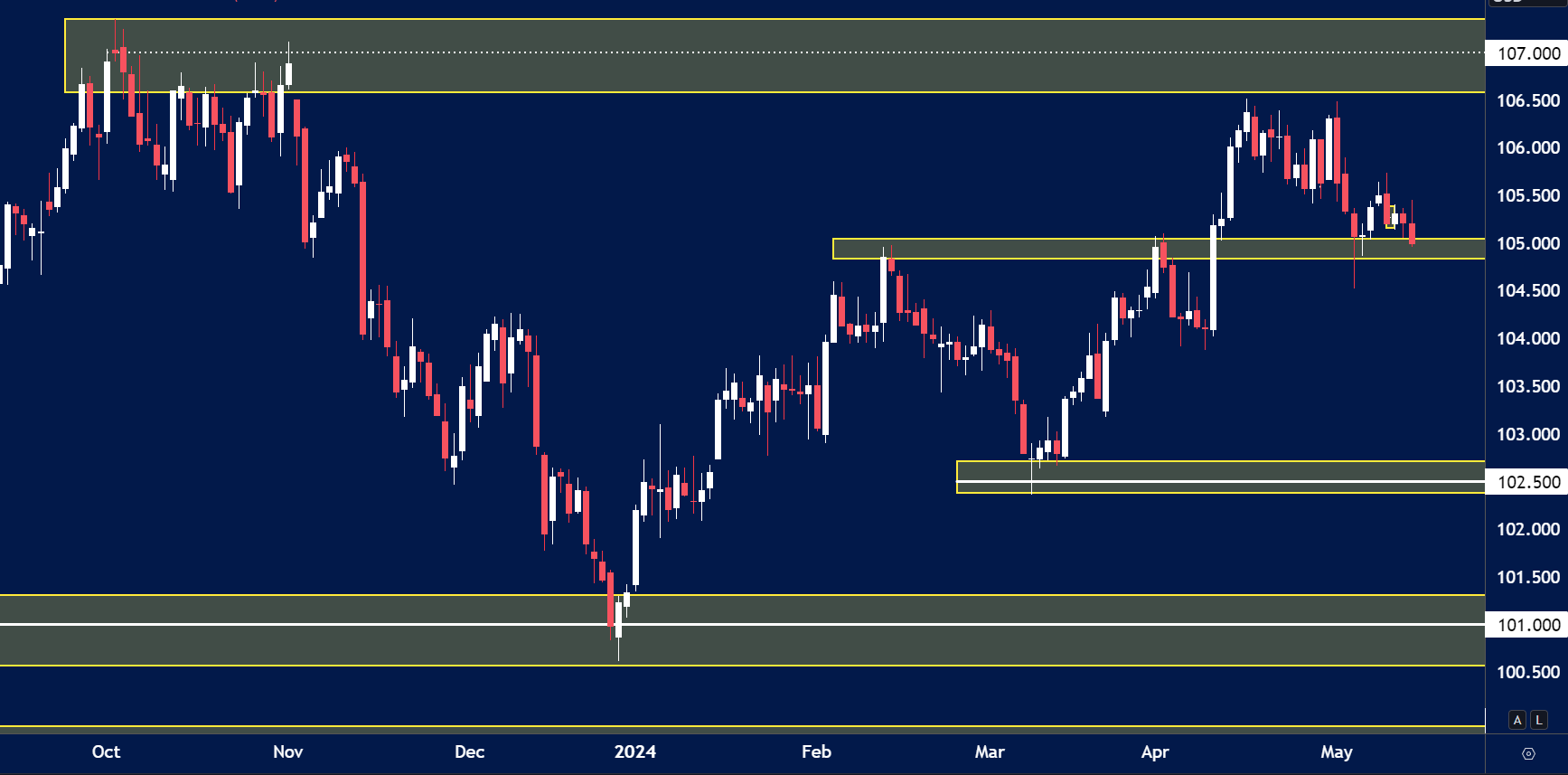
Insights Ahead of US CPI Release

Sell In May and Go Away

How do Bank Holidays Affect Trading Prices?

How Does The FOMC Affect The Market?

How to Trade AUD/JPY

How to Bounce Back From a Blown Trading Account
How to Use The Dragonfly Doji Candlestick Pattern?

To Trade or Fade USDCAD?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 29th April

What is the ICT trading strategy?

What is a Lot in Forex?

USDJPY: Can Price Go Any Higher?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 22nd April
Difference Between Trading on Demo Accounts and Live Accounts

Reasons Why New Traders Give up Too Early

GBPUSD Traders Be Aware

The Complete Guide to Global Financial Regulatory Bodies

How to Overcome Trading Anxiety

Top Financial Regulatory Bodies in Europe

USDCAD Outlook Amidst Diverging Central Bank Policies

How to Prepare Your Taxes as a Forex Trader in 2024

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 15th April

Keeping an Eye on USDCHF Amidst Central Bank Moves and Economic Data

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 8th April

Gold Rallies Amidst Rising US Bond Yields: A Technical Outlook
5 Ways to Start Forex Trading As a Beginner

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 1st April

Understanding Japan's Stance on JPY Weakening

WTI Crude Oil Set to Trade to $100.00?

Navigating the Forex Markets: A Quieter Week Ahead

How To Trade GBPUSD Fundamentals

USD In Focus Ahead Of Fed Announcement

Optimizing MT4 and MT5 Performance with VPS: Configuration Tips and Tricks

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 18th March

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Making Forex Deposits

How to Transition from a Demo Account to a Live Account

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 18th March 2025

Why Do Forex Brokers Charge Commission Fees?

Top Gap Trading Strategies

Demo Accounts: Setting Goals and Establishing Rules
Exploring the Recent Plunge of USDJPY: Is Further Decline Imminent?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 11th March

How to Trade Inside Days

Passive vs Active Trading: What's the Difference?

Is EURUSD Bullish In 2024?
What are Speed Resistance Lines?

What is The Aroon Indicator?
Yield Curve: What it is and How to Use it

How to Trade USD/MXN Currency Pair

How to Use The Slow Stochastic Oscillator for Day Trading
What Are Price Charts (And How to Use Them?)

What is the Linear Regression Slope?

How to Trade with CCI Indicator

How to Start Trading on MetaTrader 4 with Robots

How Does Supply and Demand Affect Markets?
What is the Raff Channel Indicator?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 4th March

Bitcoin Soars as New ETFs Drive Record Trades

Tips For Trading Gold

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 26th February

What is an Emerging Market?

AUDJPY In Focus Ahead Of RBA Meeting Minutes

What to do With Big Wins as a Forex Trader?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 19th Feb | Technical Analysis
5 Key Strategies for Advanced Technical Analysis

What is the Hidden Divergence Trading Strategy?

What is the 5-3-1 Trading Strategy in Forex?

How to Set Realistic Trading Goals

How to Learn From Your Trading Mistakes With Technical Analysis

Will Gold Prices Fall Further?

Five Trading Strategies For a Highly Volatile Market

How to Build Flexibility in Forex Trading
How to Check Your Trade History in MT5?

What Does it Take to Cultivate a Winning Attitude for Forex Trading

Why Forex Traders Should Use a Risk Calculator

How to Combine Trading Strategies

How and When to Buy or Sell in Forex Trading

How to Trade Low Volatility Markets?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 12th Feb | EURUSD | GBPUSD | SILVER
Have Traders Spotted This Forex Breakout?
A Blueprint to Consistency in Forex Trading

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 5th February | Technical Analysis

USD Index Key Levels

Don't Trade GBP/AUD Until You See This

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 27th January

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 29th Jan | Technical Analysis

Three-Bar Reversal Pattern For Day Trading

What is the Retail Sales Index?

A Forex Trader's Guide to Federal Reserve Bank

How to Trade the EUR/JPY Currency Pair?

How Trading Competitions Work?

The Year Ahead: Top Crypto Predictions for 2024

What Are Competitive Spreads?

EURJPY What Next? | Price Action Trading
Is This The NEXT Trending Forex Pair?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 22nd Jan | Technical Analysis
How to Download Historical Data on MT4

What is the Consumer Sentiment Index?

Will This Market Crash?

JPY Forecast For 2024

Understanding the Link Between Trade and Capital Flows

Where Is The Bitcoin Price Heading Now?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 15th Jan | Technical Analysis

Price Action Trading In Forex
Top Triangle Chart Patterns

Gold Price Forecast For 2024

How Does The Bank of England Impact The Forex Market?

What is Leverage in Forex?

How To Predict Forex Movements?
What is The Tick Volume Indicator?

Forex Traders Alert! EURGBP Technical Analysis

How Setting The Right Position Sizing Can Save Traders?
Trading Biases vs Predictions: What's The Difference?

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 8th Jan | Technical Analysis
Master Trading The Range In Forex | In The Trading Zone

Forex Economic Calendar 2024: What to Watch

Popular Stocks to Start Your 2024 Out Strong

Forex Week Ahead Analysis: 2nd Jan | Technical Analysis

How to Avoid Stop-Loss Hunting?

Helpful Tips For Forex Trading Newbies

How to Trade AUD/USD?
How to Use a Forex Demo Account for Practice?

How to Manage Currency Exposure in Your Portfolio?
Trading with MetaTrader's Forex Volume Indicator
What is Drawdown in Forex Trading?

Forex Predictions 2024: Trends Shaping the Future of Forex Markets

How to Trade the Impact of Politics on Forex Markets?

Why Does the BoJ Intervene in the Forex Markets?

Top Tips to Resume Trading After The 2023 Christmas Break

Top Trading Strategies For GBP/USD

What Higher Oil Prices in 2024 Could Mean For The Markets?
What is Golden Cross Trading?

How To Find Better Forex Trading Levels

2024 Economy And Stock Market Predictions

How to Trade a Short Squeeze?

How Bond Yields Affect Currency Movements in Forex?

How to attract Clients to your Introducing Brokers (IBs) Business through Social Media?

How to Invest in Crypto Without Buying Crypto?

How To Set A Stop-Loss Based On Price Volatility?

Is Forex Trading Halal or Haram?

How To Cautiously Trade Cryptocurrencies?
How To Be A Better Forex Trader | In The Trading Zone

Top 8 Questions Introducing Brokers Need to Ask When Selecting a Broker
What is The Marubozu Candlestick Pattern?

What is The Petrodollar?

How to Know When to Close a Trade

What is the Risk-Reward Ratio?

How To Use Currency Strength Vs Weakness In Forex Trading

What is an Introducing Broker (IB)?

How to Calculate Lot Size in Forex?

How Do Unemployment Rates Affect The Forex Market?

4 Big Mistakes Traders Make When Setting Stops
Choosing Forex Pairs: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Study Your Losses to Realize Gains?
Scalping vs. Position Trading: Which is Right for You?

Understanding the Relationship Between Oil and Currency

Risk On Returns In The Forex Markets

What The Israel-Palestine Conflict Means For Forex Markets?

How Does Inflation Affect The Interest Rates?

Online Trading vs Offline Trading: What's the Difference?
When to Move from Demo to Live Forex Trading Account?

How to Read and Leverage The Forex Economic Calendar

What Are Trading Signals & How Do They Work?

Forex Trading and Taxes: What You Need to Know

Understanding Supply and Demand in Forex Trading
What is the FRA40 index?

How Central Banks Impact the Forex Market?

How to Maintain Forex Trading Discipline and Patience?

How to Read And Understand Forex Trading Quotes
What is Multi-Asset Trading?
A Beginner's Guide to Hedging

How to Use a Trading Journal?

Top Strategies to Trade The Euro/British Pound

Forex Trading Hours: What is The Right Time to Trade?

The Forex Trader's Guide to USD/JPY Pair

Major Economic Reports That Affect the British Pound

The Impact of BOJ on the Forex Market

How to Create an AI Trading Bot With ChatGPT?

Benefits And Risks of Using AI in Trading

How to Switch Forex Brokers?

How to Trade the Euro/British Pound?

How to Trade the EUR/AUD Currency Pairs?

How to Trade the Japanese Yen?

FTSE 100 vs FTSE 250: What’s The Difference?
Risks Associated With Candlestick Chart Patterns

Stop-Loss Strategy For Day Trading

Five Questions to Ask Your Forex Broker
Hedging vs Speculation: Top Differences

How to Use ChatGPT for Algorithmic Trading?

How To Analyze A Forex Chart: AUDJPY In Focus

The Correlation Between Commodities And Inflation

What is the NAS100 Index?

Risk Management Strategies for Active Traders

Risks of Automated Trading Systems
How to Make the Most of Your Brokerage Account
How Does GDP Affect Forex Trading?
How to Read a Balance Sheet For Trading?
What Are the Factors Affecting USD/CAD?

How Oil Impacts The Canadian Dollar?
CFDs vs Futures: What Are The Differences?

What is Forex VPS Hosting: A Comprehensive Guide

How to Trade Crypto CFDs?

How Does CPI Affect the Stock Market?

How Does NFP Affect the Price of Gold?

Seasonal Market patterns For EUR/USD

Top Differences Between Hedging and Stop-loss

What is the Ideal Setup for Trading?

Top Industries in FRA40 Index

The Complete Guide to Euro Stoxx 50 Index

What is DAX 30 Index?

What is OPEC, and How Does it Influence Oil Prices?

How Will AI Impact Trading

How Can Oil Prices Affect Stock Prices?

How to Use ChatGPT For Trading?

Top AI Tools for Trading

How Does GDP Affect the Stock Market?

Forex Economic Calendar for 2023

What is Core PCE and How Does it Affect the Forex Market?

Top Economic News Events for Forex Trading
What is Volatility Index (VIX) And How Do You Trade It?

S&P 500 Index

How Does The Recession Affect The Stock Market?
What is ADP National Employment Report?

What is the Shanghai Index?

How Does Inflation Affect the Forex Market?
How To Get The News Feed In MT4?
How To Set Up MetaTrader? Step-By-Step Instruction

Can You Use MetaTrader 4 Without A Broker?
How to Copy a Trade on MT4?

Is MetaTrader 4 Good For Beginners?

How to Add Templates to MT4?
Type of Orders in Metatrader
How To Speed Up MT4?
Understanding the Fear and Greed Index: A Comprehensive Guide for Forex Traders

How Do You Set Price Alerts With MetaTrader 4?

How Does MetaTrader 4 Work?
How to Add Commodities to MT4?

How to Add Indices to MT4?

Understanding the Japanese Stock Market: Insights for Vietnamese Investors
How to Use MetaTrader 4

Dos and Don'ts of Forex Trading in Vietnam
What is Nikkei 225?

Managing Risk When Investing in the Tokyo Stock Exchange from Vietnam
How to Open a Trading Account to Invest in the Tokyo Stock Exchange from Vietnam

Top Industries to Invest in on the Tokyo Stock Exchange for Vietnamese Investors

Common Mistakes When Exchanging Foreign Currency to Vietnamese Dong

Tips on Exchange Rate When Exchanging Foreign Currency to Vietnamese Dong

What traders need to know about fees when exchanging foreign currency to Vietnamese dong

5 Guides for Exchanging Foreign Currency to Vietnamese Dong Without Getting Scammed

The Ultimate Guide to The Tokyo Stock Exchange

Exchanging Foreign Currency to Vietnamese Dong: Pros And Cons
Basic Functions of MT4

Customizing MT4 Interface: Tips and Tricks

Top 10 Essential MT4 Indicators for Technical Analysis
The Advantages of Using MT4 for Forex Trading
A Comprehensive Guide to MT4 Trading for Beginners
How to Optimize MT4 Trading Experience

What is Purchasing Manager's Index?

15 Strongest Currencies in The World

A Beginner's Guide to Exchanging Foreign Currency to Vietnamese Dong
Buying The Dip: What Does it Mean?

Popular Trading Tools for New Traders

Gold Price Forecast for 2023

Forex Chart Of The Day: Is Gold Heading To $1800.00?
How to Open a MetaTrader 5 Account

Automated Trading vs Manual Trading

Top Factors That Affect Gold Prices

How to Become a Part-Time Forex Trader

Top Forex Trends For 2023

The Ultimate CFD Day Trading Guide

Cryptocurrencies to Focus on in 2023
What is Grid Trading?

Russian Ruble Financial Crisis 2022: What to Expect?

How Do Interest Rates Affect The Stock Market?

What is a Ranging Market?
How to Use RSI for Intraday Trading
How to Trade With MetaTrader Webtrader

How to Build a Diversified Portfolio

Top Forex Forecasting Techniques

What is Dow Jones?

What is Overtrading (And How to Avoid it)

How to Master The Psychology of Forex Trading

Major Forex Market Hours and Trading Sessions

How to Choose a CFD Trading Platform

How to Overcome Fear When Trading

The Most Volatile Currency Pairs (& How to Trade Them)

What is Carry Trade in Forex?

How to Trade Forex News: Forex News Trading Strategy

Why Do Traders Lose Money in Intraday Trading
What is Consolidation in the Stock Market?

Forex Words and Jargons Every Trader Should Know
What Are Market Reversals And How to Spot Them?
MetaTrader 4: Top Tips and Tricks

Hawkish vs Dovish: How Do They Affect The Forex Market

Cryptocurrency vs Forex Market: What’s The Difference?

Top Silver Trading Strategies To Get Ahead
What Are The Key Drivers of The Forex Market

Questions to Ask When Planning Trade Exits
7 Popular Indices Trading Strategies

Non-Farm Payrolls and Forex: Everything You Need to Know

How The Russia-Ukraine Crisis is Impacting the Forex Market

Top CFD Trading Strategies For Beginners

Trading Gold CFDs: Here’s Everything You Need to Know

How to Use the USDX for Forex Trading

What is Margin Call in Forex (And How Do You Avoid One)

How to Trade Oil CFDs
How Does an Index CFD Work?

10 Important Rules for CFD Trading
15 Most Popular Forex Chart Patterns

How to Find Out Which Forex Broker Is Legit

Index Trading Explained: How to Trade Indices

Silver Trading: A Beginner's Guide to Trading in Silver

Top 10 Tips for Bitcoin and Crypto Trading

Short Selling Stocks: What does Shorting a Stock Mean?

16 Effective Day Trading Strategies for Beginners

Oil Trading: How to Trade Oil Spot Prices, Options, and Futures

Get Started with Cryptocurrency CFDs: Everything You Need to Know

Forex 101: Terms And Jargon That You Need To Understand

CFDs vs Stocks: Which is a Better Investment?

How to Start Oil Trading in 5 Simple Steps

Top Economic Indicators Traders Should Watch

Forex Trading Strategies That Actually Work
How to Use Trailing Stop-Loss in Forex: 3 Powerful Techniques

How to Trade Commodities: A Complete Guide

Top 5 Moving Average Trading Indicators

What is Bitcoin and How Do You Trade It?
Types of Forex Charts (And How to Read Them)
How to Trade Gold: Top Gold Trading Strategies and Tips

FOREX Chart Of The Day: How To Identify A Market To Trade

Top 10 Trading Indicators Every Forex Trader Should Know

A Guide to Multiple Timeframe Analysis

Top Benefits of Trading CFDs

How to Start Day Trading Gold

A Beginner's Guide to Contract for Differences (CFDs)
6 Forex Exit Indicators: When to Exit Your Trade and Take a Profit

How Interest Rates Affect Forex Trading

Why Forex Traders Need Quantitative Tightening

Why A Forex Trading Plan Matters (And How To Build One)
Trend Trading In Forex: How To Effectively Use This Strategy
What Is Algorithmic Trading

Spoofing In Forex Trading Blueberry Markets

Monetary And Fiscal Policies In Forex
How To Profit From Double Candlestick Patterns
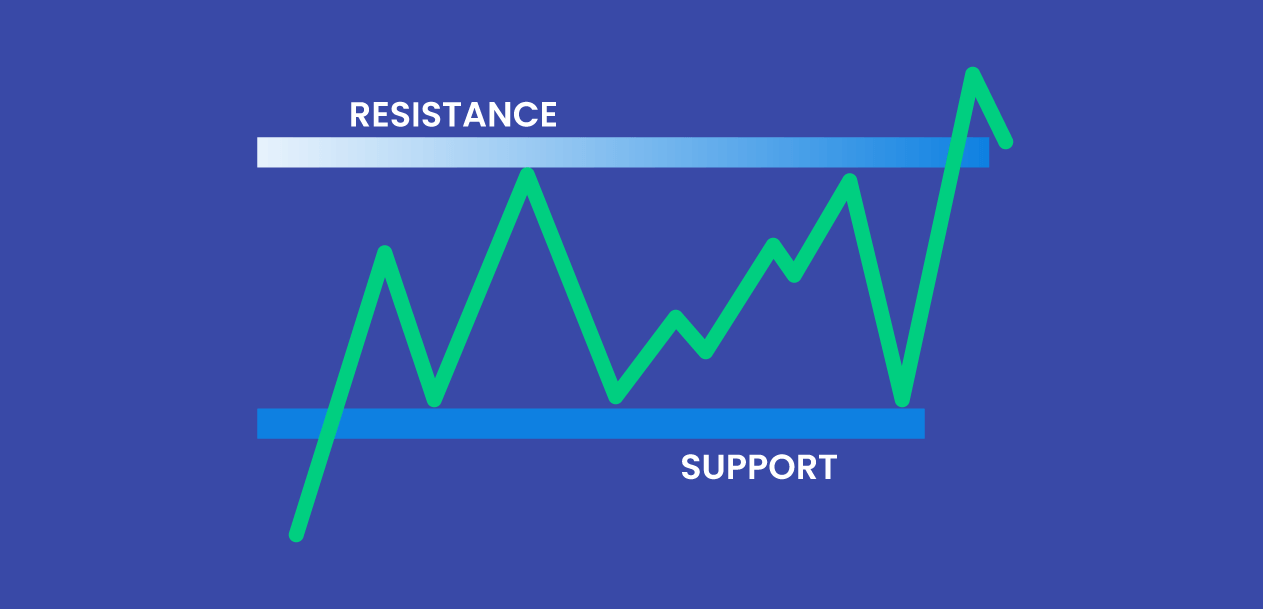

Forex Trading Using Support And Resistance Levels

How to Use a VPS For Forex?

Can Bitcoin Eventually Become (Or Replace) The US Dollar As A Reserve Currency?

Exploring Binary Options Trading

Three Powerful Strategies You Can Use In Forex Trading

Binni Ong On The Past, Present, And Future Of Forex

Trading With The RSI Indicator

It's always a good time to make your money work for you

Choosing Your Forex Broker

The Best Time To Trade Forex

The Pip And Its Usage In Forex

The Basics Of A Fundamental Analysis

The Basics Of Opening A Forex Account
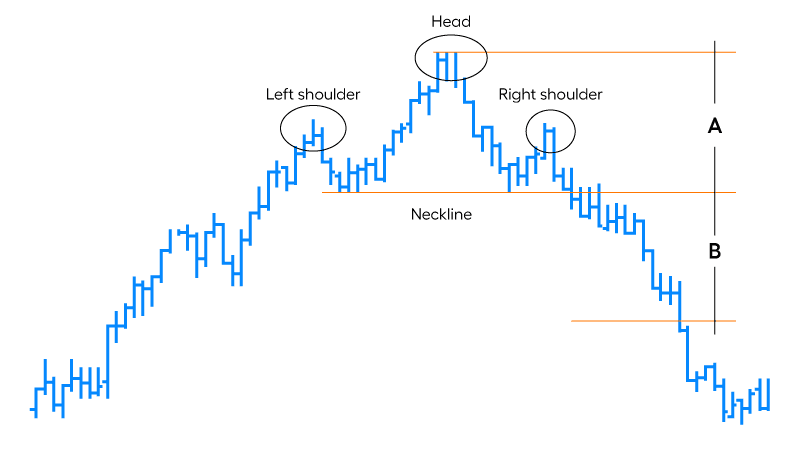
How To Trade With The Head And Shoulders Pattern

Forex: Its History And Futures
The Basics Of Swing Trading

Forex 101: What You Need To Know Before Placing Your First Trade

Forex 101: How To Make A Forex Trading Plan
Divergence Trading and How to Navigate Around It
How To Use The RSI Indicator Forex Trading
How To Spot Trend In The FOREX Market
Trading with the Head and Shoulders Pattern

Pivot Points and Why They Matter

The Key to Making It as a Retail Trader


