Seasonal trading in forex allows traders to leverage recurring patterns and trends observed during specific times of the year. By aligning trades with historical seasonal tendencies and economic cycles, traders can improve their chances of capturing predictable price movements.
In this article, we will understand seasonal trading in depth.
What is seasonal trading?
Seasonal trading is a trading strategy that takes advantage of predictable patterns/trends during certain times of the year as a season. Several factors, such as holidays, weather, business cycles, consumer behavior, and more, influence these patterns.
Certain sectors or commodities are more prone to seasonal trends. For instance, agricultural commodities like wheat or corn may experience price changes depending on the planting and harvest seasons. Meanwhile, forex may be affected by the end of the calendar year since many institutional traders close their books and reduce their trading activity as the year ends. Around Christmas and New Year, trading volumes typically decrease, which can cause more erratic movements in currency pairs during and right after the holiday season.
Factors to consider with seasonal trading
Quarterly earnings reports
Quarterly earnings reports cause significant volatility in currency pairs and stocks tied to the companies whose reports are out. Traders can consider opening more positions in the earning season, when there is increased trading volume and the opportunity to gain in the short term increases based on earnings surprises or disappointments (during short trades).
Interest rate cycles
Interest rate cycles impact currency values by affecting capital flows. The central bank’s decision to increase or decrease rates can strengthen or weaken a currency. Traders can anticipate these changes within a broad economic cycle and place trades accordingly.
Geopolitical events
Geopolitical events, such as crises, elections, or policy changes, cause sudden and significant price shifts. These events can disrupt normal trading patterns and create opportunities or risks for traders based on the nature and location of the geopolitical event.
Weather impact analysis
Weather patterns affect agricultural commodities and energy prices, influencing related currency pairs. For example, a harsh winter might boost energy prices, while droughts could impact crop yields. These factors make weather forecasts an important consideration in seasonal trading strategies.
Top strategies for seasonal trading
Holiday effect strategy
The holiday effect strategy refers to the time period around major holidays, such as Christmas and New Year when most traders go on vacation and stop trading in the forex market. This leads to less liquidity and volatility in the market, making forex prices less susceptible to changes.
Traders can purchase currency pairs before holidays such as Christmas and even Thanksgiving while expecting a rise in prices due to increased consumer spending and positive market sentiment during and after the holiday period.
Seasonal trend analysis
Seasonal trend analysis is a trading strategy that focuses on identifying and trading currency pairs based on recurring patterns as per historical data.
Traders analyze the past performance of a currency pair during specific times of the year to predict future price movements. For example, retail stocks may see a boost before the holiday season, while certain commodities may follow harvest cycles, impacting related currencies similarly.
Economic calendar trading
Economic calendar trading refers to planning trades around key economic events scheduled throughout the year.
These reports include but are not limited to NFP reports, GDP reports, interest rate announcements, employment data releases, and more. Traders predict market reactions to these events and place orders accordingly to gain from the volatility after such announcements.
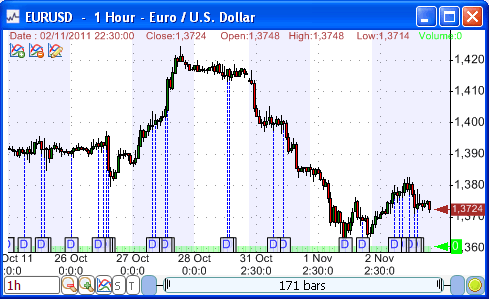
*This is an example only to enhance a consumer's understanding of the strategy being described above and is not to be taken as Blueberry Markets providing personal advice.
Step-wise guide to seasonal trade
1. Research and data collection
Gather historical data on currency pairs, focusing on past price movements, trends, and key dates. Include data on economic events, holidays, and geopolitical events.
2. Analyze seasonal trends
Identify recurring patterns or trends in the historical data. Look for periods where certain currency pairs tend to strengthen or weaken consistently.
3. Monitor economic indicators
Track key economic indicators like interest rates, GDP, employment figures, and inflation. Use an economic calendar to stay updated on upcoming events impacting currency movements.
4. Develop a trading plan
Based on the analysis, create a detailed trading plan. Define entry and exit points, position sizes, risk management strategies, and contingency plans.
4. Backtest the strategy
Test the trading plan against historical data to see how it would have performed in past seasons. Adjust the strategy based on the backtesting results.
5. Execute trades
Implement the trading plan in the live market. Enter trades according to the seasonal patterns and economic indicators identified.
6. Monitor performance
Review trades regularly to ensure they align with the trading plan. Track key metrics like gain/loss, win rate, and drawdowns.
7. Review and adjust
After the trading season, evaluate the overall performance. Identify what worked well and what did not. Then, adjust the strategy based on these findings for future seasons.
Top 5 tips for seasonal trading in forex
-
Keep track of market sentiment and investor behavior using sentiment indicators and news analysis. Sentiment can influence whether a seasonal trend will hold or deviate
-
Combine seasonal analysis with technical indicators such as moving averages, RSI, or trend lines. Technical tools can provide additional confirmation and improve the trade timings
-
Be mindful of liquidity levels throughout the year. During certain periods, like major holidays or end-of-year, liquidity can drop, leading to increased volatility and wider spreads
-
Use forecasts and reports from reputable sources that analyze seasonal trends and economic conditions. These can provide insights and validation for trading decisions
-
Be ready for deviations from expected seasonal trends due to unforeseen events or changing market conditions. Have contingency plans in place for such scenarios
Balancing the risk and advantage of seasonal trading in forex
Seasonal trading provides traders with clear entry and exit points during specific time periods based on predictable market movements. However, this approach carries risks, as unexpected events or shifting market conditions can disrupt these patterns. Therefore, while seasonal trading can improve trading returns, it requires vigilant risk management and the flexibility to adapt to unforeseen changes.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.