Moving Average:
The Complete Guide
Moving Average is used in Forex trading to compare the current currency pair pricing and where it stands with respect to the current average pair prices. It sends buy and sell signals whenever the currency pair price moves closer to the Moving Average line. Traders can use this as a signal for a market reversal trend. Since Moving Averages are used to identify trend directions, they can help you exit the market as soon as a downtrend is about to occur and push you to enter the market before an uptrend. The impact of short-term price movements and fluctuations are offset with the Moving Average, so we get smooth currency pair price data.
What is a Moving Average?
The Moving Average is a technical indicator that represents the average closing currency pair price in the market over a defined period. It indicates the market momentum and analyses data through a series of currency pair prices.
How do you calculate the Moving Average?
The Moving Average can be calculated by adding currency pair prices over a specific period and dividing them by that same number. This is also known as the Simple Moving Average (SMA).
SMA Formula:
Summation of all the currency pair prices/Time over which the data were considered
For example, let’s assume a 5-day SMA chart of USD/EUR gives the closing price of 1,1.2,1.5,1,1.3 = 6
Number of time periods: 5
Computation: 6/5 = 1.2
Hence, the SMA is 1.2
The 50-day Moving Average is a common choice for most traders. Similarly, the 200-day Moving Average is also considered to be a solid indicator of market trend reversals.
What is a Moving Average crossover?
A Moving Average crossover occurs whenever a fast MA (short period Movin g Average) crosses over a slow MA (longer period Moving Average). This indicates a trend reversal as a long period MA provides them with a strong support level.
Moving Averages you should know about:
-
Exponential Moving Average:
The Exponential Moving Average or EMA is widely used to generate accurate MA prices. It weighs the recent currency pair prices more than the older ones. This is so that it is more responsive to the latest data prices and sensitive to the current market volatility.
EMA Formula:
EMA (today) = [value of the currency pair today*(smoothing)]+{EMA of yesterday*[1–(smoothing)]}
Note: smoothing is a number derived by an algorithm that removes noise from the data set. It can also be known as the weight you give to the data set to ensure that current prices are given more importance.
Formula to derive smoothing = [2/(total number of observations+1)]
Yesterday’s EMA can be written as the SMA until that day. Suppose you want to use five days as the total number of observations for the EMA. To derive yesterday’s EMA, you can use the SMA until the 5th day. Considering our previous example of SMA, yesterday’s EMA will be 1.2.
We can also assume that the closing price of USD/EUR is 2.
The smoothing will be = [2/(5+1)] = 0.33.
Finally, you can calculate the current EMA as (2*0.33)+1.2*(1-0.33)=1.21
Hence, the EMA is 1.21.
-
Double Exponential Moving Average:
The Double Exponential Moving Average (DEMA) allocates even greater weight on the recent currency pair prices and gives more accurate results. This helps short-term traders spot trend reversals at the earliest possible time. The DEMA involves the least deviation. This makes it more sensitive to volatility in the market by using two EMAs instead of one.
DEMA Formula:
2*EMA(ɳ)–EMA of EMA(ɳ)
Where EMA(ɳ)=EMA of a specific period
-
Triple Exponential Moving Average :
The Triple Exponential Moving Average (TEMA) reduces the lag of EMA. The difference between DEMA and TEMA is that the latter uses an EMA smoothed thrice as the original EMA. Hence, the TEMA stays closer to the currency pair prices than the DEMA.
TEMA Formula:
(3*first EMA)–(3*second EMA)+third EMA
Where first EMA = EMA of the specific time
Second EMA = EMA of the first EMA
Third EMA = EMA of the second EMA
-
Weighted Moving Average:
Traders use Weighted Moving Average (WMA) to speculate on market trend directions. Less weight is given on past currency pair prices, and more is given to the recent ones. Each point in the data is multiplied by a factor. Whenever prices move above the WMA, it signals an uptrend. However, when the prices are below the WMA, it indicates a downtrend.
WMA Formula:
(currency pair price 1*w1+currency pair price 2*w2+….+currency pair price ɳ*wɳ)/[ɳ*(ɳ+1)]/2
Where currency pair price 1,2,…ɳ= currency pair’s closing price that day
W1, w2,…wɳ = the weight allocated to each currency pair price
How do you use a Moving Average in Forex?
Using MAs in confluence with other price action patterns is recommended to generate the most accurate figures. Here are the top three methods in which MAs can be used in the Forex market:
-
Support and resistance:
The most common MAs that traders use are the 10-day MA, 20-day MA, 50-day MA, 100-day MA, and 200-day MA. These MAs can be used as resistance and support levels in a market. Some MAs carry more weight than others, like the 10-day, 20-day, and 50-day MA. Since they are more commonly used, the market reacts in its favour as more traders use the same level to enter or exit the market. Hence, they could act as the support and resistance levels.
-
Trend analysis:
Different MAs can be combined together to interpret the trend in the market. For example, you can combine the 10-day MA and 20-day MA to identify a trend. Let us assume that the AUD/USD daily chart shows buying opportunities when the 10-day MA is above the 20-day MA. Since the 10-day MA is following the currency pair prices more closely, it signals the market being in an uptrend when it is higher than the 20-day MA. However, once the 10-day MA is below the 20-day MA, it sends traders a signal for selling opportunities due to the downtrend.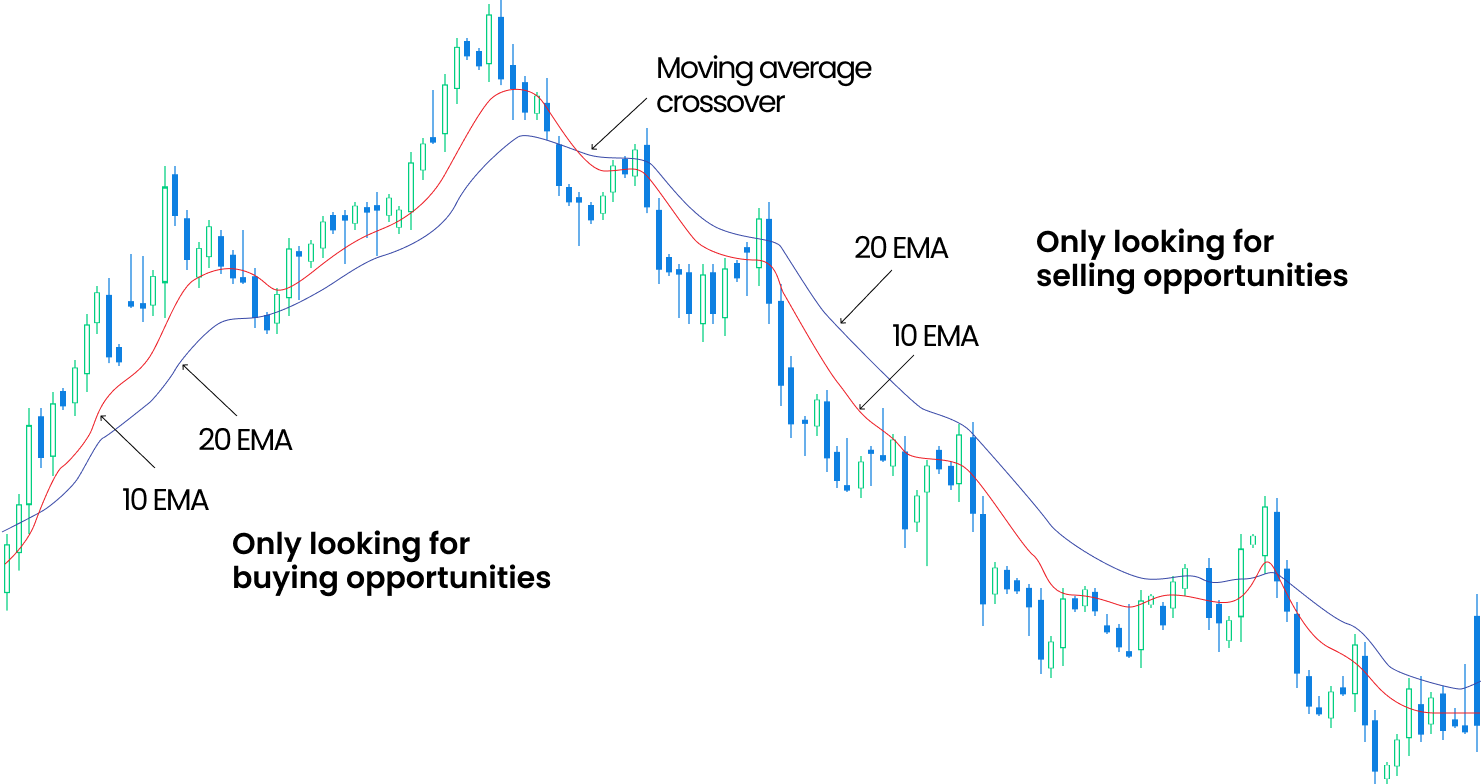
-
Overextended markets:
MAs also help identify overextended markets. Moving averages allow traders to trade a trend just in time. Once a market moves away from the MA price, price action traders usually wait for the currency pair price trend to normalise and return to the MA level before thinking about exiting the market.
Top Moving Average trading indicators
-
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD):
The MACD chart portrays the difference between a 26-day EMA and a 12-day EMA. It also plots a 9-day EMA as an overlay. With respect to the zero lines, a positive or negative relationship is identified. This relationship indicates the market trend and direction.
Traders usually enter the market when the MACD crosses the signal line from below. However, when there is a downtrend, and the MACD is below the zero line, traders usually go short as soon as MACD crosses the signal line from below. To mitigate risk, traders use stop-loss orders below the recent low swing for long positions and above the recent swing high for short positions.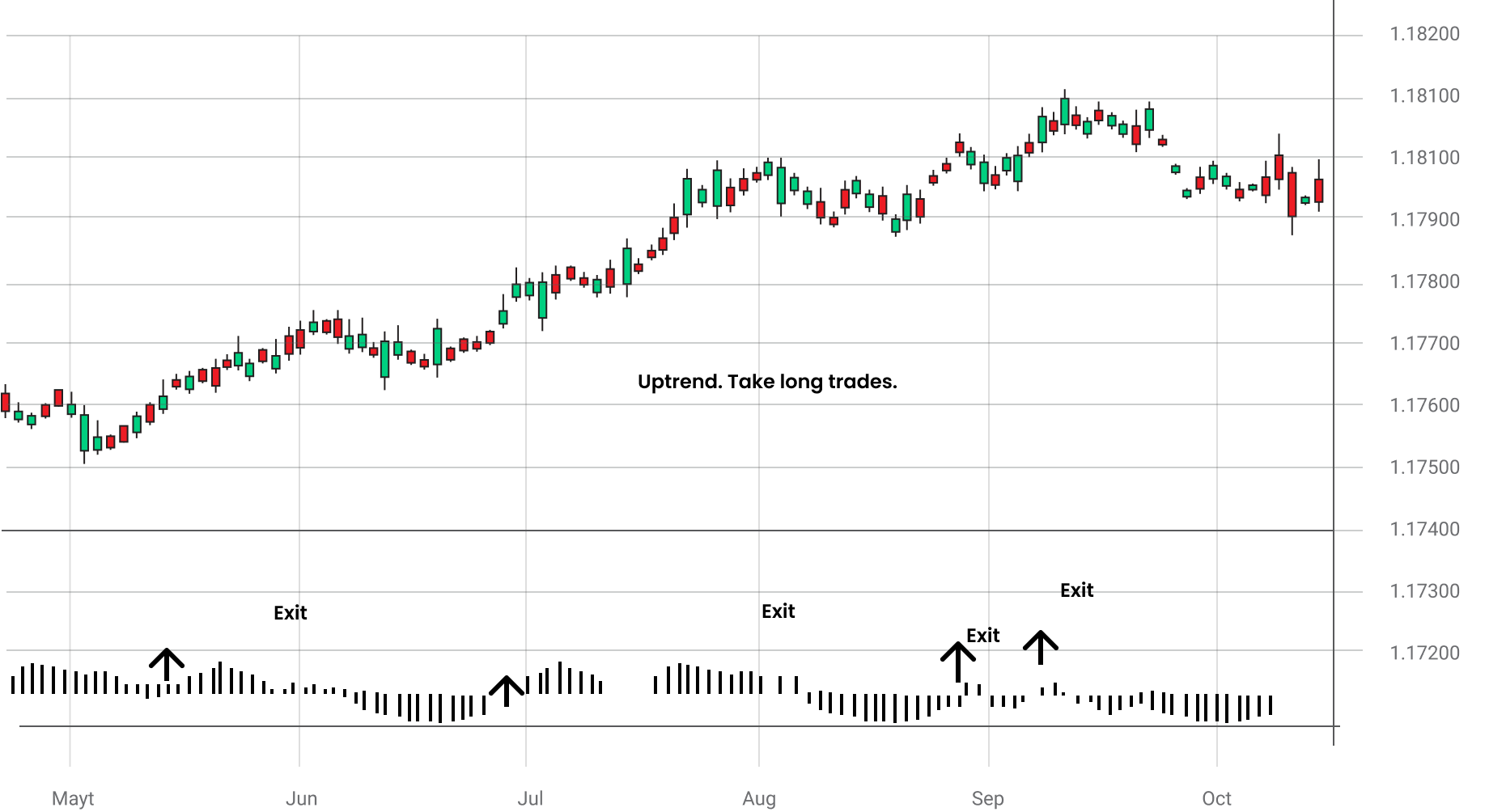
-
Moving Average envelope:
The MA envelope uses envelopes based on percentages placed below and above the MA. Envelopes are most common between 10 to 100 days, and the percentage used for envelopes is from 1 to 10%. The percentage set changes daily, depending on market volatility. It is recommended to trade when you see a strong directional bias to the currency pair price.
A strong downtrend signals traders to go short when the price reaches the MA and drops further. A stop-loss order can be placed above the recent swing high for short positions and vice versa for long positions.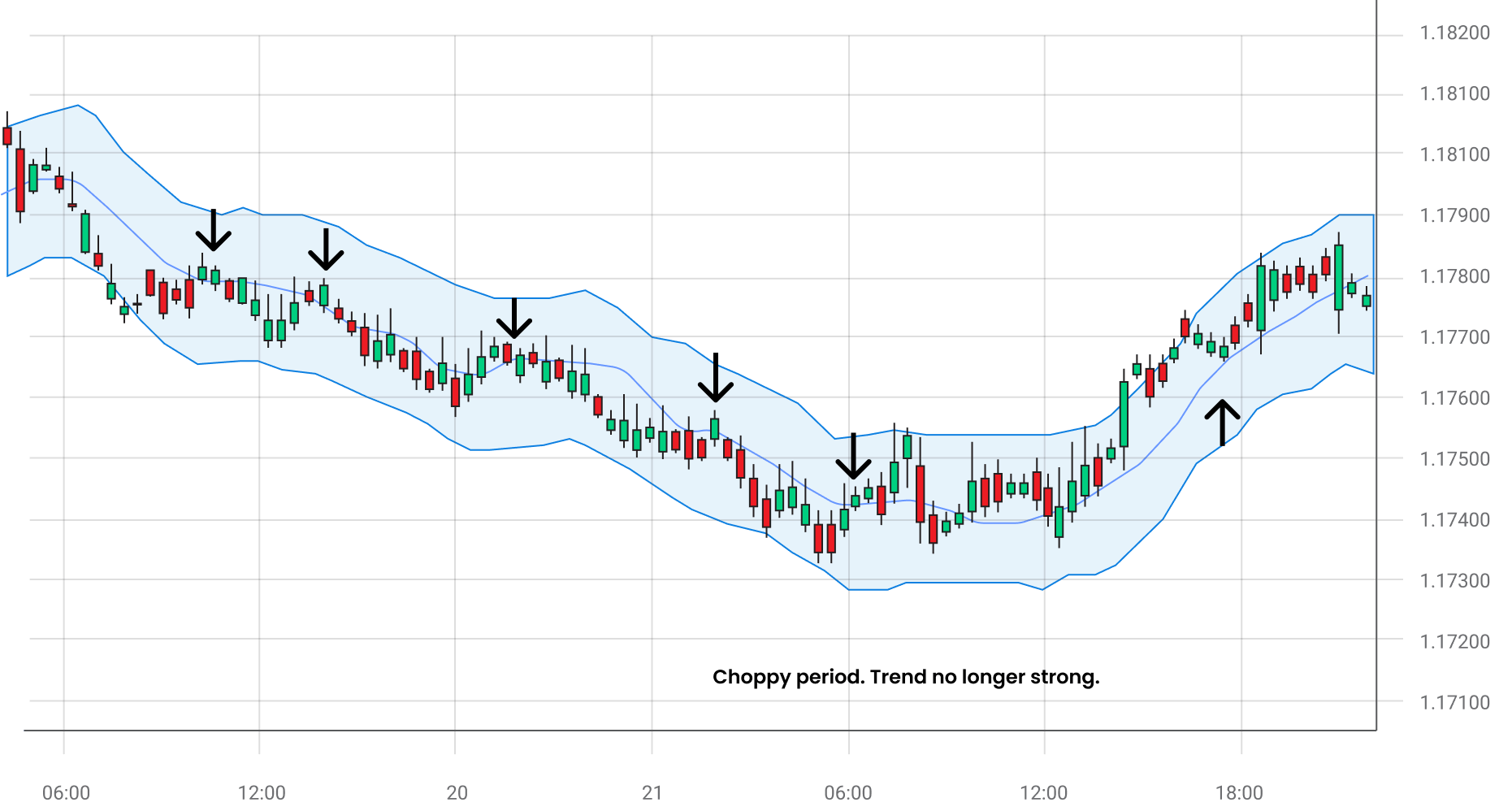
-
Moving Average ribbon:
The MA ribbon is commonly used in a trend reversal. You can formulate the ribbon based on a series of 8-day to 15-day EMAs plotted in the same chart. The MA ribbon indicates the trend’s strength and direction. The steeper the MA angle with higher separation, the stronger the trend.
When the MAs come close and form a thick line, it is wise to move in favour of the trend. The stop-loss can be placed below the lowest point of the trending range if you are buying and vice versa if you are selling.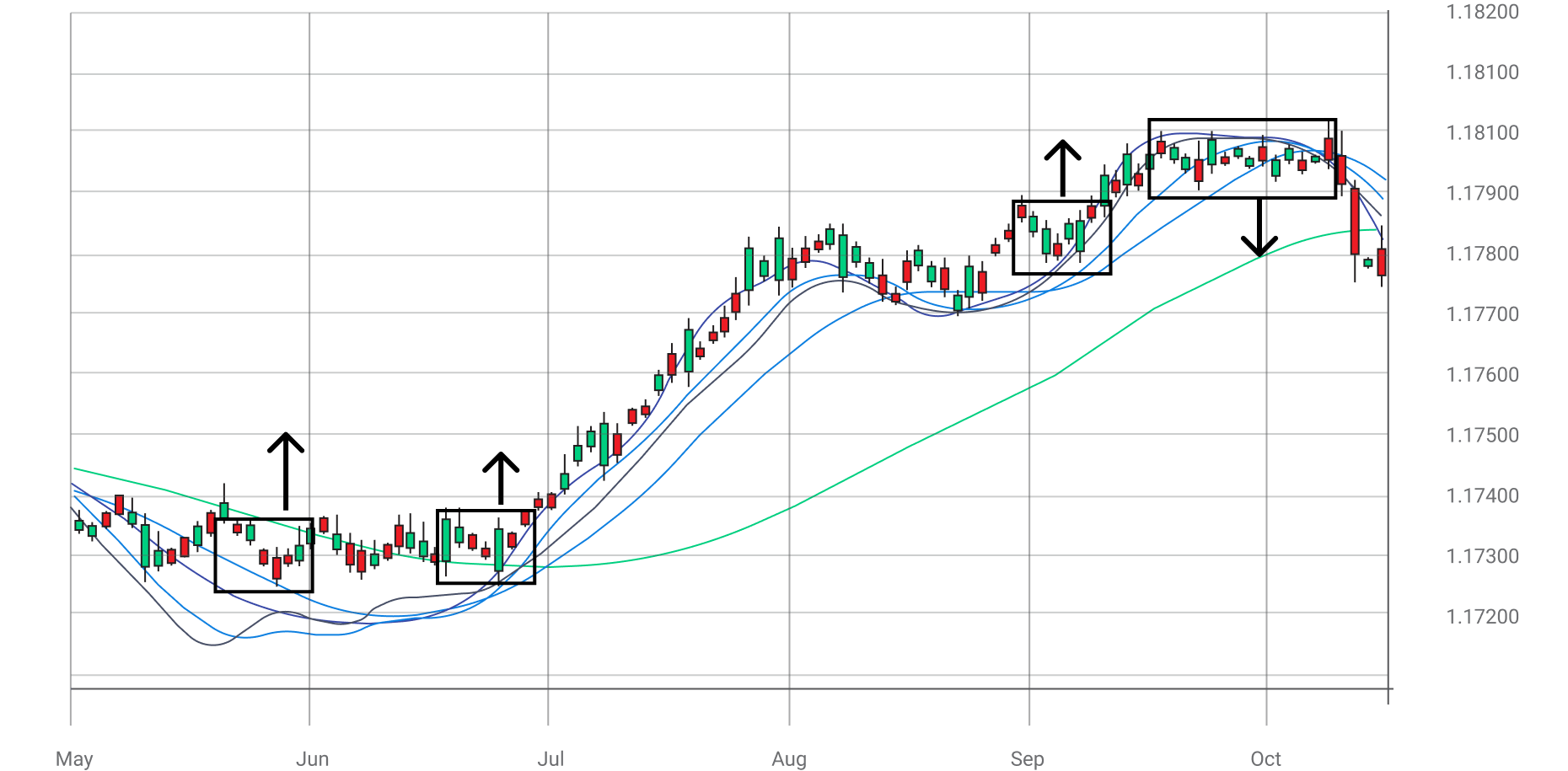
Read more about MA trading indicators here.
Maximise your trades with Moving Averages
Moving Average plays an important role in sending exit and entry signals to traders. With different Forex strategies and MA indicators combined, you can make the most out of your trades.
Blueberry Markets has an industry-standard trading platform that comes with tools and charts you can use together with your chosen MA indicators and strategies.
Sign up for a live trading account today to get started.
Recommended Topics
-
Top Pivot Point Strategies
Pivot point analysis can predict not only price movements but also help time entries and exits correctly to develop a risk management strategy.
-
How to Use The Bill Williams Indicator
Bill Williams Indicator is helpful in analysing trending markets, reversals and momentum.
-
How to Use Relative Vigor Index in Forex
The Relative Vigor Index (RVI) is a technical analysis indicator that helps measure a trend’s strength in forex trading.
-
Technical Trading Strategies for Day Traders
Technical trading strategies for day traders include technical analysis tools to identify short-term trading opportunities in the market.
-
How to Use The Force Index Indicator in Forex?
The Force Index indicator combines the currency pair’s price and volume to determine the power of bulls and bears in the market.
-
The Ultimate Guide to Trading Trends in Forex
Trading trends in forex provides you with opportunities to identify the strong market direction and enter an order accordingly.
-
MT5 Indicators Every Trader Should Know
MT5 is a forex and stock trading platform that enables traders to place automatic orders.
-
What is Volume Trading Strategy
Volume trading in forex is all about trading currency pairs with high buying or selling pressure.
-
Top Low Spread Scalping Strategies For Forex Traders
Scalping strategies allow traders to leverage on the small price changes in the forex market to turn the trends in their favour.
-
What is Forex Currency Swap?
Forex currency swap helps reduce foreign borrowing costs and mitigate exchange rate risks.
-
What is Forex Spot Trading
With forex spot trading, one can make significant short-term profits by trading at prevailing prices.
-
How to Short Sell a Currency
Short selling enables traders to place lucrative forex orders even in a falling market.
-
How to Use The Chaikin Money Flow Indicator
The Chaikin Money Flow indicator provides future market direction by analysing the strength of the market trend and underlying buying or selling pressures.
-
What is Momentum Trading? Top Momentum Trading Strategies
Momentum trading leverages market volatility to the trader’s advantage by identifying the strength of the market’s current trend.
-
How to Trade With VWAP Indicator in Forex
The Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) helps eliminate any unwanted price fluctuations during the trading period.
-
5 Top ADX Trading Strategies
The Average Directional Movement Index (ADX) strategy measures the forex market’s overall strength.
-
How to Identify a Trend in the Forex Market
Identifying market trends in forex is also helpful in understanding if your trading strategy is going as per plan and where you can improve.
-
Forex Trading Robots: How Do They Work?
Forex trading robots make multitasking possible by processing multiple conditions like order entries/exits and entering stop loss orders automatically.
-
What Are Momentum Indicators in Forex
Momentum indicators measure how strong the price change is in the currency pairs.
-
How to Use Gator Oscillator For Forex Trading
Gator Oscillator helps in identifying a trending or consolidating market.
-
What is The Exponential Moving Average
Exponential Moving Average (EMA) helps in understanding the market’s trend direction.
-
Top Forex Volatility Indicators
Forex volatility defines the risk an investor takes in the market. The higher the volatility, the greater the risk and the higher the potential returns.
-
How to Use Forex Market Sentiment Indicators
Sentiment indicators in the forex market indicate extremely volatile market conditions.
-
How to Use The Hanging Man Candlestick Pattern For Forex Trading
The Hanging Man Candlestick pattern provides downtrend reversal signals, which helps traders place sell or short orders to profit off falling markets.
-
How to Add MT4 Indicators
MetaTrader 4 comes with several built-in and custom indicators to boost your trading strategy.
-
Top MACD Trading Strategies
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) strategies enable traders to measure market momentum and trend strength.
-
Top Indicators for MT4
MT4 indicators help analyse forecasted currency pair prices and place exit or entry orders accordingly.
-
How to Trade Bullish and Bearish Divergences
Bullish and bearish divergences enable you to trade market reversals.
-
Top Support and Resistance Indicators
Support and Resistance indicators identify price points on the forex chart where the markets can potentially reverse.
-
What is The Donchian Channel Indicator
The Donchian Channel indicator can determine volatility and potential breakout signals in the market.
-
How to Install MT4: A Beginner's Guide
MetaTrader 4 (MT4) is a powerful forex trading platform with a user-friendly interface and advanced analytical tools for automating trading.
-
What are Trendlines in Forex Trading?
Trendlines in forex provide clear market signals for placing long or short orders.
-
Market Order vs Limit Order
Market and Limit orders help execute automatic trading transactions, as per your trading preferences.
-
Bearish and Bullish Markets
In the trading world, it is essential to be aware of the bull and bear market trends because they define the direction of the market
-
How to Read Trading Charts
Trading forex live charts can help identify ongoing market trends, which can help you place successful traders.
-
Top Reversal Patterns For Forex Trading
Reversal patterns provide traders with price levels at which the market can potentially reverse.
-
How to Find The Best Forex Trading Signals
Forex trading signals are important market triggers that provide traders with ideal entry and exit price levels in the market.
-
Top Forex Trading Strategies That Actually Work
Trading in forex, you will come across several forex trading strategies -- some more complex than the others. It is immensely crucial to start forex trading with the right strategy.
-
Scalping vs Swing Trading: What’s the Difference?
Every forex trader has a different purpose, objective, time constraints, and investment capital. The right forex trading style for you depends on your main trading goals and requirements.
-
What are Volume Indicators
Volume in the forex market can be used to determine the upcoming market trends. Volume indicators are forex trading indicators that can identify if the volume for a particular currency pair is high or low, providing traders with market continuation and reversal signals
-
Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern
The Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern can identify bearish market reversals and provide traders with ideal price levels to short or exit the trade.
-
Top Trading Chart Patterns
Predicting future currency pair prices help in confirming market continuation and reversal signals.
-
What is Slippage in Forex Trading?
Slippages occur when a currency pair order is executed at a price different from the set market order price.
-
Buy limit vs Sell Stop Orders in Forex
Placing buy limit and sell stop orders help employ a price control strategy on forex trades. Let's take a look at buy limit vs sell stop orders.
-
The Best Time Frame For Forex Trading
A time frame is a designated time period where forex trading takes place. Time frames can be measured in minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years.
-
Top Technical Indicators in Forex
Technical indicators are a market direction signal based on the current and historical price movement of a currency pair that provides traders with future price expectations
-
Top Continuation Patterns
A continuation pattern indicates if the current market trend is going to continue in the same direction or not
-
How to Ace Divergence Trading in Forex
The forex market is all about timing your trades well. Divergences give traders a market reversal signal right before a price trend changes
-
How To Trade Forex With Japanese Candlesticks?
A Japanese Candlestick is a technical analysis tool used to analyze the currency pair’s price movement in the forex market.
-
Top Momentum Indicators To Analyse Trend Strength
Momentum indicators are technical analysis tools that determine in which direction the market is headed and how strong or weak the ongoing trend is
-
Types of Moving Averages Every Trader Should Know
Moving Average is a technical indicator which averages out currency pair prices in a specific time period in order to accurately identify market trend reversals and support-resistance levels.
-
8 Popular Intraday Trading Indicators
Intraday Trading Indicators help place successful short-term trade orders in the forex market.
-
What is the Tweezer Candlestick Formation?
The Tweezer Candlestick formation is a reversal pattern that indicates either a market top (strong uptrend) or market bottom (strong downtrend)
-
Average Directional Index
The ADX is a strength indicator that measures how strong or weak a particular market trend is.
-
How to Use Elliott Wave Theory For Forex Trading?
The Elliott Wave Theory analyses a currency pair’s long-term price movement in the forex market.
-
What are Pivot Points in Forex
Pivot Points help traders identify market reversals. With Pivot Points, traders can predict the support and resistance levels of a currency pair to make entry and exit decisions.
-
Keltner Channel
Keltner Channel is a technical indicator that provides traders with strong continuation signals and trend directions by assessing a currency pair's price volatility.
-
Leading vs Lagging Indicators
Leading and lagging indicators help traders measure the future and current performance of a currency pair, respectively. These indicators can help make successful trading decisions.
-
What is Relative Strength Index?
Relative Strength Index (RSI) helps traders understand how frequently the currency pair prices change in the forex market to predict the future market prices.
-
Wide Ranging Bars
Wide Ranging Bars are strong momentum indicators that help traders understand the market direction and identify ideal entry and exit points.
-
Harmonic Price Patterns in Forex
Harmonic Price Patterns allow traders to predict future price movements and trend reversals to make ideal entry and exit decisions in the Forex market.
-
Double tops and bottoms
Double Tops and Double Bottoms chart patterns help traders identify solid bullish and bearish trend reversals in the Forex market, and in turn, find the ideal market entry and exit points.
-
Falling and Rising Wedges
When you are trading currency pairs in the Forex market, it is essential to know when the market can possibly reverse. The Falling and Rising Wedges pattern help identify market reversal signals and accurate market entry and exit points.
-
Forex Scalping Strategy
Scalping refers to trading currency pairs in the Forex market based on real-time analysis. With Forex scalping, you hold a position for a very short period and close once you see a profit opportunity.
-
Symmetrical Triangle Pattern
Symmetrical Triangle Patterns help identify market breakdowns (price fall) and breakouts (price rise), and in turn, help you plot the entry and exit prices for profitable Forex trading.
-
Introduction to Technical Analysis in Forex
Technical analysis in Forex trading provides you with significant market trends, reversals and fluctuations and in turn helps you long and short term trades.
-
Trading breakouts and fakeouts
Breakout and fakeout trading enable traders to take positions in rising and falling markets.
-
Fundamental Analysis in Forex Trading Explained
Fundamental analysis in Forex trading is one of the several methods you can use to determine the relative security and intrinsic value of a nation’s currency.
-
8 Top Commodity Trading Strategies
Commodity trading is one of the best ways to diversify your portfolio and protect yourself from losses incurred due to inflation.
-
What is a Doji Candlestick?
The Doji Candlestick is a pattern used in technical analyses of trend reversals in a market.
-
What is Volatility Index (VIX) and How Do You Trade It?
One of the most popular trading markets in the world, the foreign exchange market allows investors to make quick money by trading currencies.
-
Forex Profit Calculator
On average, a Forex trader can make anywhere between 5 to 15% of the initial amount they invested in the market.
-
Understanding markets gaps and slippage
The foreign exchange rate reveals valuable details about particular currencies a trader wishes to trade-in.
-
What is a pip in forex?
When trading in the Forex market, you need to have a close eye on two currencies at the same time. PIP helps you denote the change in a currency pair’s value.
-
Introduction to Order Types in Forex
Forex has different order types which allow traders to automate entering and exiting positions.
-
Using orders to manage risk
Forex risk management includes a robust set of rules and regulations that protect you against Forex's negative impacts.
-
Managing risk in 7 steps
Risk management in Forex is essential to individuals, groups of individuals, and organizations since it enables them to implement measures that help mitigate Forex risk and its negative impact.
-
Bullish and Bearish Flag Patterns
Blueberry Markets discusses why it is essential to study the bullish and bearish flag patterns in Forex. Learn more.
Advanced
Master risk management and
become an expert forex trader.
Move on to the advanced course.
Guide to Forex
Trading indicators.
Enter your details to get a copy of our
free eBook

Start a risk free
demo account
News & Analysis
Catch up on what you might
have missed in the market.

