Forex forecasting helps traders make informed trading decisions based on predicted exchange rate values. These techniques use the market's historical and current price momentum to derive the future price momentum, enabling traders to take control of their trading analysis and develop benchmarks.
Our article will discuss the top forex forecasting techniques for placing successful trading orders.
What does forex forecast mean?
Forex forecasting refers to predicting the current and future market conditions to trade the currency pairs accordingly. Existing data is utilised and combined with the market sentiment to predict what can happen next. Based on this information, analysts use fundamental and technical methods to predict the economic, financial and market direction.
When traders use the right forex forecasting techniques, they are able to place successful trading orders in the market.
The Top Forex Forecasting Methods
1. Technical Analysis
Technical analysis helps traders study the historical price movement of a currency pair through technical price charts. Traders can identify price patterns and predict the possible future movements of the market to place a buy or sell order accordingly. In technical analysis, indicators, analytical tools, graphical representation, algorithms and mathematical calculations are used to identify the future trend.
It is based on the demand and supply of a currency pair. Studying historical price patterns leads to the same patterns repeating when the market moves similarly. Trends are identified before they occur so that traders can benefit from forex predictions in the short and long term.
The common parameters of technical analysis are –
- Opening price
- Closing price
- Highest price
- Lowest price
When forecasting prices through technical analysis, traders look for uptrends, downtrends and sideways trends.
The top three technical analysis tools are –
- The Relative Strength Index is a momentum indicator that oscillates between 0 to 100.
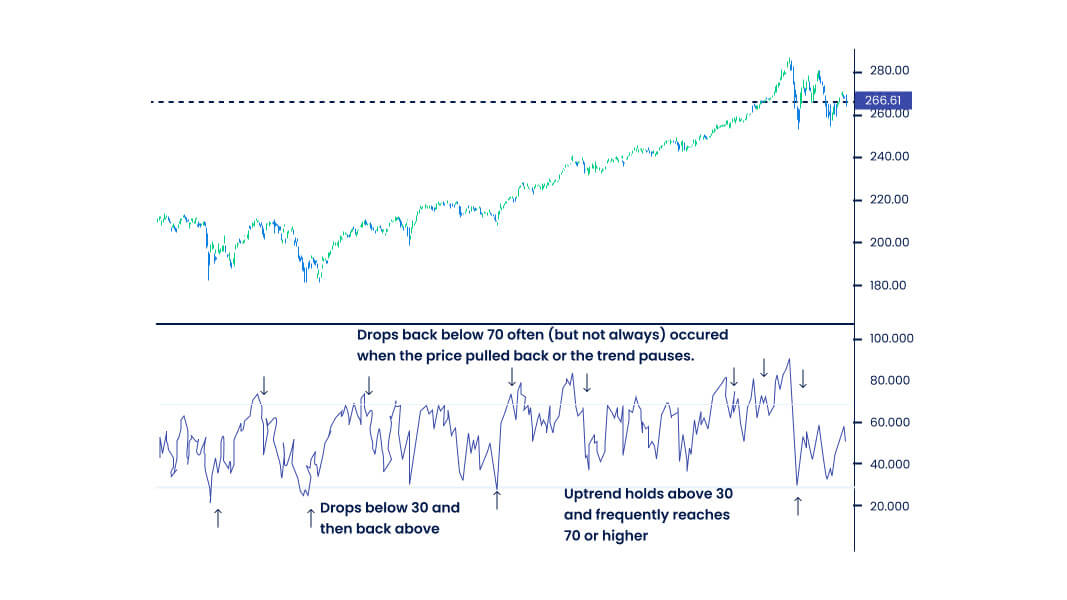
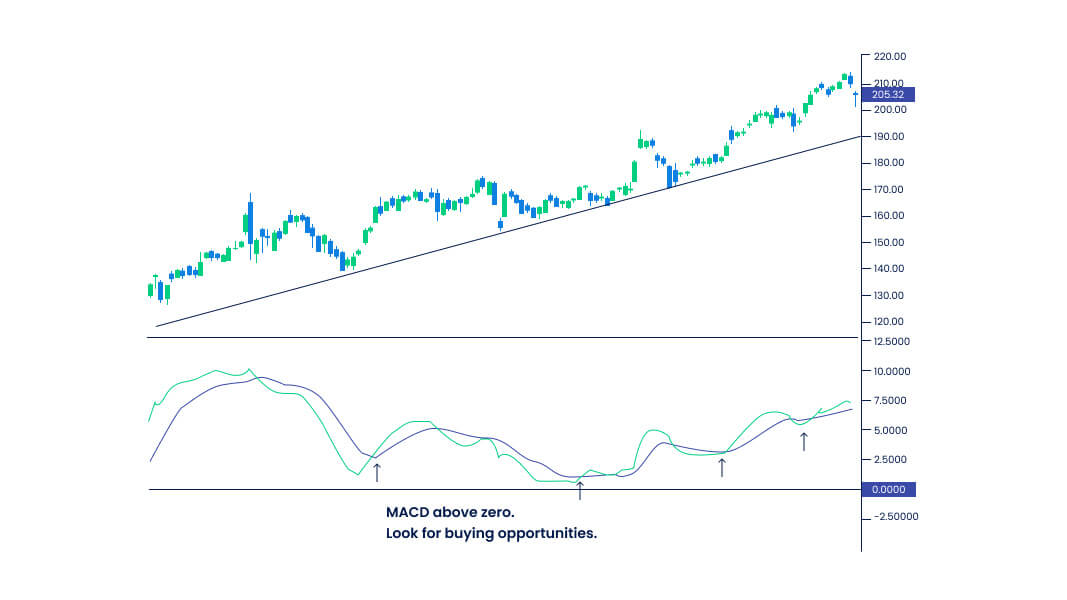
- The Moving Average Convergence Divergence indicator indicates the relationship between a fast-moving average and a slow-moving average.
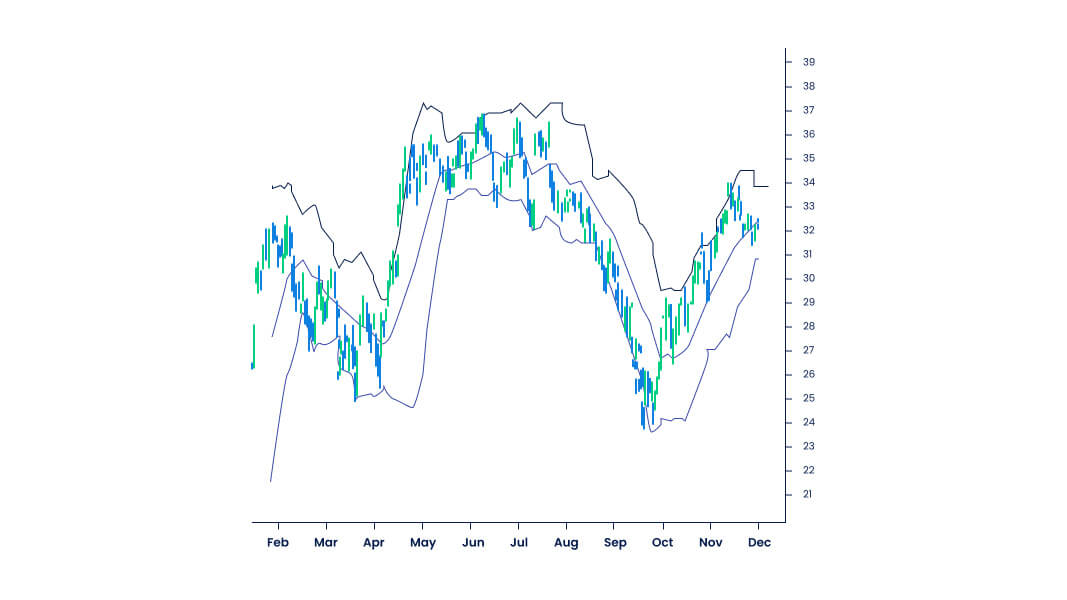
- Bollinger Bands are volatility indicators that identify when a currency pair is overbought or oversold. It enables traders to place entry orders when the market is volatile and touching the lowest levels. Similarly, traders are able to place exit orders in volatile markets when prices touch their highest levels due to an expected reversal.
2. Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on external events impacting the forex market, like the economic condition of a country, war outbreak, monetary policies and more. Through fundamental analysis, traders can identify whether a currency pair is overvalued (overbought) or undervalued (underbought) and help analyse its true value. This type of analysis does not consider the price itself but what impacts the price level at the currency pair is trading.
Fundamental analysis analyses the forex market changes by monitoring the economic interest rates, unemployment level, trade relations between countries, GDP and more. This helps in devising medium to long-term strategies to help place successful forex trading orders.
The key drivers of fundamental analysis are –
- Inflation refers to how fast or slow the prices of goods and services in an economy change and affect the country's monetary policy. When the inflation of a particular country is high, the currency of that country is devalued and vice versa, impacting the exchange rate accordingly.
- Economic growth refers to the country's overall economic condition and performance. It calculates the country's GDP, which shows if the economy is growing or sinking and affects the forex rates accordingly. When an economy is growing, it appreciates the country's currency and attracts more traders, whereas a shrinking economy leads to a depreciating currency, pushing traders away.
- Geopolitics refers to the political condition of a country. An unstable political condition of a country devalues the currency of the country, depreciating the exchange rate and vice versa.
- Exports and imports also affect the forex exchange rate. When a country is more dependent on exports, its currency falls in value when exports decrease. On the other hand, a country heavily reliant on imports witnesses an appreciation in its currency value when imports decrease, and they become more self-dependent.
- Interest rates refer to the amount charged or paid by or to the government on obtaining a loan or lending money. If the interest rates in a country are higher, it depicts a stronger currency value, appreciating the forex exchange rates. If the interest rates in a country are low, it depicts a weaker currency value, depreciating the overall exchange rate.
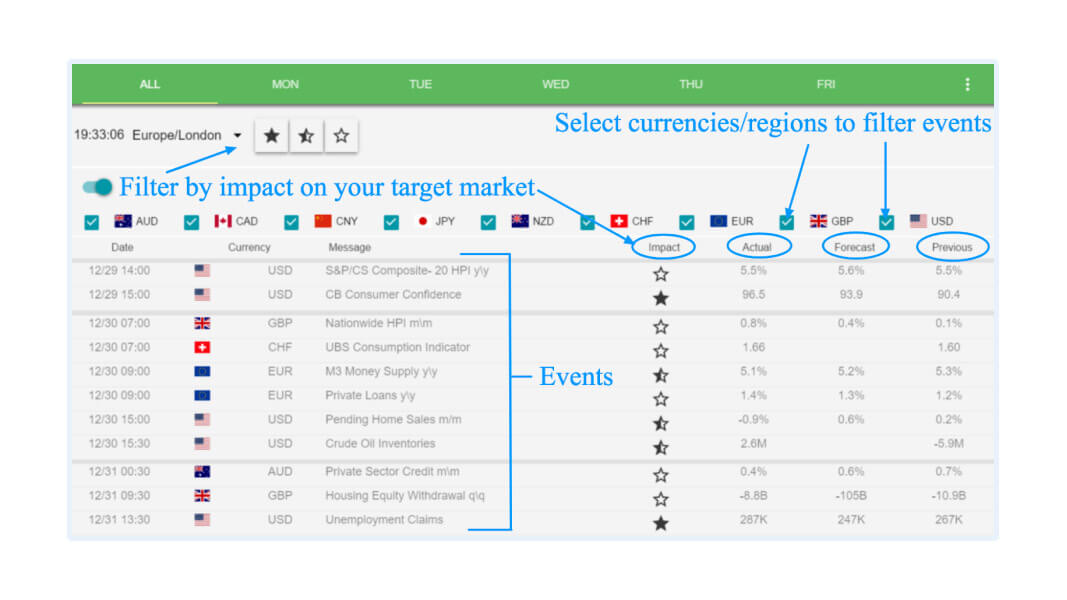
3. Economic calendar
An economic calendar is a pre-decided schedule of dates that indicate significant events and news releases that can impact the forex market. Keeping a close eye on this calendar, forex traders can prepare for a big event before it occurs and place orders accordingly.
For example, if the calendar showcases a scheduled interest rate hike, traders can place buy orders with a prediction of the currency exchange rate appreciating. On the other hand, if a political event is scheduled (like an election result day), traders can either hold their trading orders or place short orders with the expectation of a short-term disturbance that may occur due to the political change.
Using the three forex forecasting techniques to predict prices
In order to predict future forex prices, economic calendar, technical and fundamental analysis can be used together for accurate results. Technical analysis solely relates to the demand and supply of the currency pair, whereas fundamental analysis digs deeper into why the forex prices change.
Start trading with our forex trading platform in Australia to enjoy several technical and fundamental tools, along with a defined economic calendar for successful trading.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.




