Recognizing the right forex trend stage helps traders choose the right strategy, manage risks, and capitalize on opportunities. Each stage including accumulation, expansion, and reversal presents unique opportunities and risks.
In this blog, we will discuss the different stages of a forex trend and how to trade them.
What is a forex trend?
A forex trend refers to the general direction in which a currency pair's price moves over time. It can be upward (bullish), downward (bearish), or sideways (neutral). Identifying trends helps traders decide when to enter or exit the market.
3 stages of a forex trend
Trend development (accumulation stage)
The accumulation phase is the initial phase of a forex trend. During this phase, the market moves sideways or consolidates, and institutional traders begin accumulating positions. Price action is typically flat, with no clear direction, as market participants wait to confirm a trend's start.
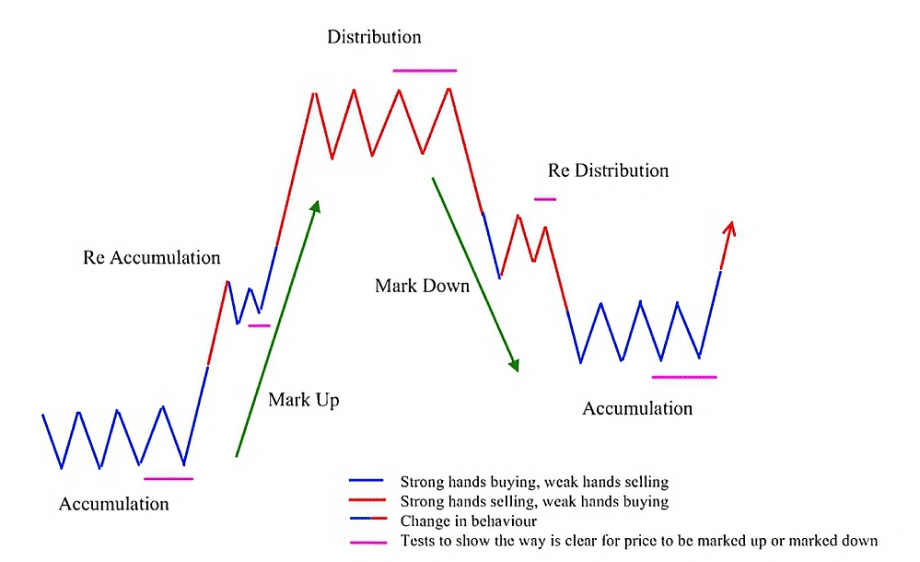
Trend expansion (mark-up/mark-down stage)
In this phase, the trend accelerates. In a bullish trend, prices rise (mark up), while in a bearish trend, prices fall (mark down). This stage is where most retail traders enter as the trend becomes more apparent. Momentum increases with strong price movement, and the market sentiment is in full swing.
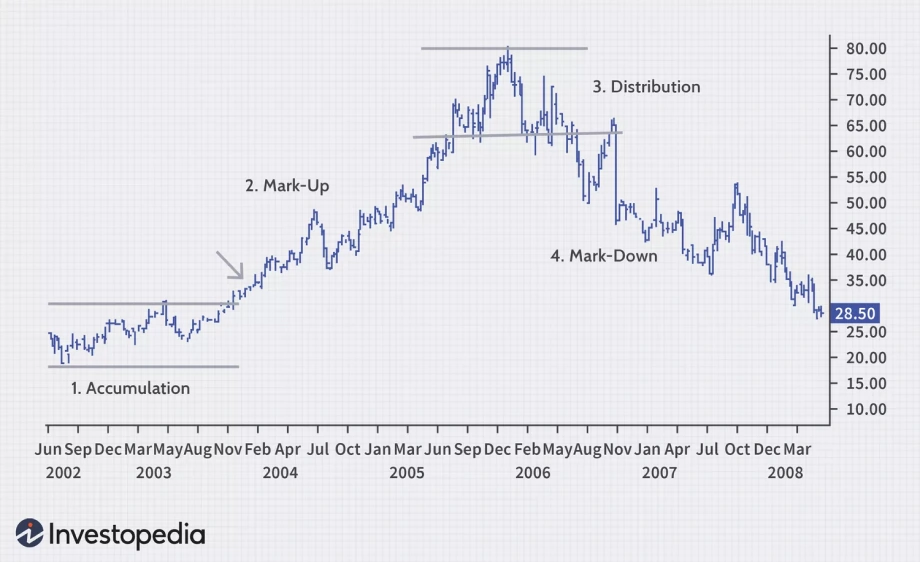
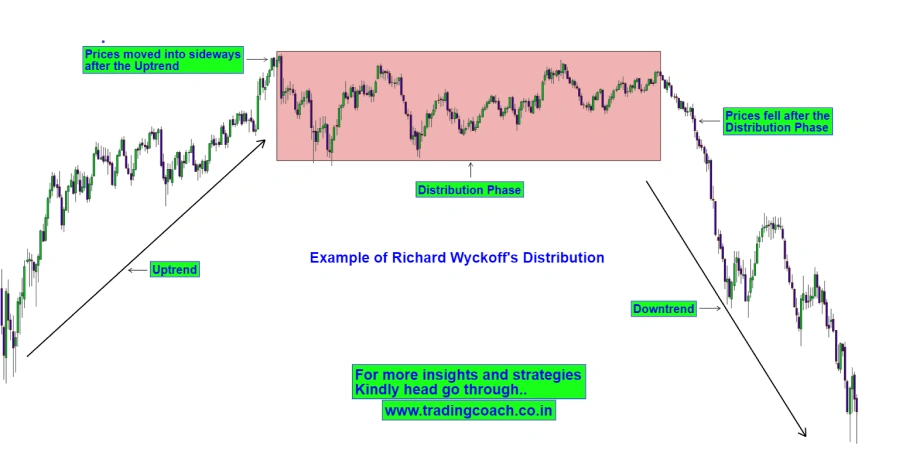
Trend reversal (distribution stage)
In the final stage, the trend starts to lose momentum. This happens when the market reaches a peak or a trough, signaling a potential reversal. During the distribution stage, institutional traders begin to exit their positions (in an uptrend) or purchase back (in a downtrend). Price movement becomes erratic, and a trend reversal is imminent.
Strategies for trading in each stage
Trading during the accumulation stage
The accumulation stage occurs when the market consolidates and prices move sideways. This phase is characterized by low volatility, and the trend's direction is unclear. Hence, traders should remain cautious during this stage.
It's important to wait for a clear breakout signal before entering a trade. Identifying key support and resistance levels helps anticipate potential price movements. Traders can also use trendlines or channels to spot breakout opportunities. Indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index) or MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) can confirm momentum changes.
However, traders should avoid chasing false breakouts, which often occur during this phase. Entering too early can result in unnecessary losses. It's also important to avoid committing large capital before confirming the breakout direction.
Once the breakout happens, traders must trade with a smaller position size until the trend gains more strength. At this point, risk management techniques such as tight stop-loss orders can help protect against unexpected reversals.
Entry and exit strategies in the expansion stage
The expansion stage occurs when a trend gains momentum and starts moving decisively in one direction, either up or down. As the trend becomes more obvious, this is the stage where most traders look to enter. For a bullish trend, traders can enter when the price pulls back to a previous support level, which would then act as resistance.
In a bearish trend, entries are made when the price retraces to a previous resistance level. Tools like moving averages, Fibonacci retracements, and trendlines are valuable for identifying entry points during this phase. The strategy involves riding the trend and capitalizing on the momentum.
To maximize gains, traders can use trailing stop-loss orders, which move with the trend and lock in gains as the price continues in the desired direction. Exits should be planned carefully, with gain targets set at key resistance levels or technical indicators signaling a potential reversal.
Risk management remains critical during this stage. Traders should avoid overleveraging and ensure they are not exposed to excessive risk in case of sudden market corrections. Furthermore, it is essential to monitor volume during the expansion stage. A significant increase in volume often confirms the trend's strength and direction.
Risk management in the reversal stage
The reversal stage is the final phase of a trend, during which momentum slows and the market begins to change direction. This is the most challenging stage for traders, as it's difficult to predict when the reversal will occur. Traders should adapt their risk management strategies to account for potential losses.
First and foremost, traders should reduce their position size during the reversal stage. This is because market conditions become more unpredictable. Tight stop-loss orders are crucial for protecting against sharp price movements. Reversal patterns such as head-and-shoulders, double tops, or double bottoms signal that the trend may be losing strength.
Additionally, oscillators like the RSI can help identify overbought or oversold conditions, which indicate a potential reversal. When entering the reversal stage, traders should focus on risk-to-reward ratios to ensure they are not exposed to large potential losses.
A stop-loss can be placed just beyond key support or resistance levels to limit losses if the reversal doesn't materialize. Traders should also monitor price action for signs of weakening momentum. If the market shows signs of indecision or volatility, it may be right to exit early or stay out of the market entirely. Flexibility and constant market monitoring are needed to manage risk during this phase.
Forex trends vs. ranges
Price movement
In a trend, prices move in one direction for an extended period, while in a range, prices move sideways between set levels.
Market sentiment
Trends are driven by strong market sentiment. In contrast, ranges occur when sentiment is neutral or indecisive.
Trading strategy
In trending markets, traders use trend-following strategies. In ranging markets, traders focus on mean-reversion strategies, entering at support and exiting at resistance.
Volatility
Trends tend to be more volatile, as prices move steadily in one direction. Ranges are less volatile, with prices bouncing between the support and resistance levels.
Trade the right forex trend stage at the right time
Trading the right stage of a trend is crucial in forex because it maximizes gain potential and minimizes risk. Entering during the accumulation or expansion stage aligns with market momentum, while trading during a reversal stage can lead to losses. Proper timing ensures more consistent, gainful trades.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.




