The Rate of Change (ROC) indicator measures the speed of price changes, providing insights into momentum and a potential trend reversal. Understanding ROC helps traders identify strong market moves, enhance trading decisions, and improve their overall trading strategies.
In this article, we will discuss the ROC indicator in depth.
What is the Rate of Change indicator?
The ROC indicator is a momentum-based technical analysis tool that measures the percentage change in price over a specific period. It helps traders assess the speed and strength of the price movement.
How the ROC indicator works
The rate of change indicator subtracts the price from ‘n’ periods ago from the current price. It then divides the result by the price ‘n’ periods ago. Finally, the result is multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage.
ROC can be interpreted in the following manner:
-
Positive ROC: Indicates that the price is increasing at an accelerating pace
-
Negative ROC: Suggests that the price is decreasing at an accelerating pace
-
Zero line crossovers: Can signal potential trend reversals
-
Divergence: When the ROC diverges from the price, it can indicate a potential trend reversal
ROC formula: [(Current Price - Price n periods ago) / Price n periods ago)] x 100
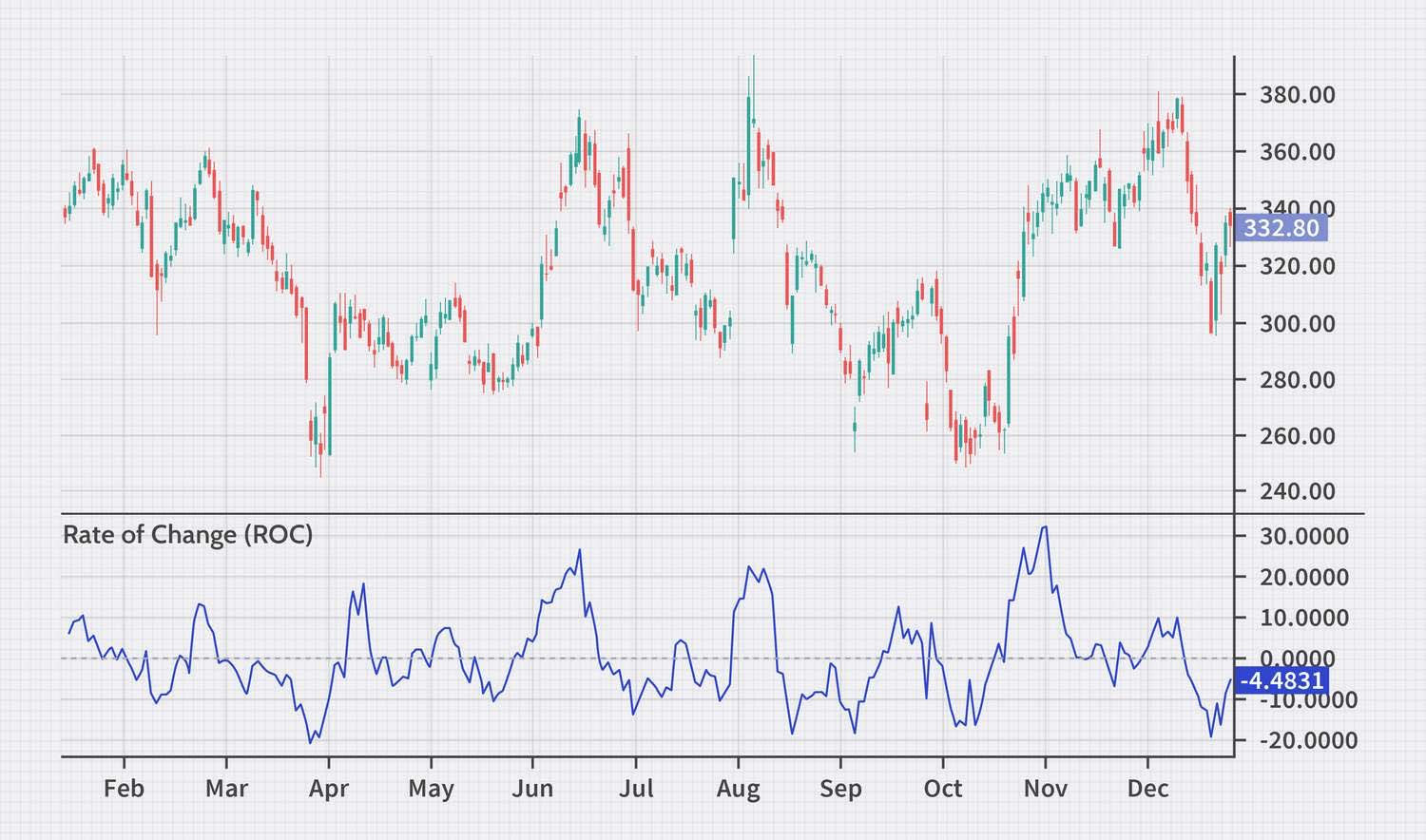
Reading the Rate of Change (ROC) chart
A rate of change indicator is plotted as a line on a chart, usually below the price chart. It fluctuates above and below the zero line.
-
Above the zero line: Price is increasing compared to the previous period
-
Below the zero line: Price is decreasing compared to the previous period
-
Steep upward slope: Price is increasing rapidly
-
Steep downward slope: Price is decreasing rapidly
-
Divergence: When the ROC line moves in the opposite direction of the price, it can signal a potential trend reversal
Trading with the ROC indicator
1. Choose a timeframe
Select the time period for calculating the rate of change (such as 12, 9, or 6 periods). Shorter periods are more sensitive to price changes.
2. Plot the ROC indicator
Add the rate of change indicator to the forex chart. It will fluctuate around the zero line.
3. Identify positive and negative momentum
Positive ROC values indicate upward price momentum, whereas negative ROC values indicate downward momentum. The further the ROC is from zero, the stronger the momentum.
4. Detect overbought and oversold conditions
When the ROC reaches extremely high positive levels, it may signal an overbought market condition. On the other hand, when the ROC reaches extremely low negative levels, it may signal an oversold condition. These levels can vary depending on the financial markets and time frame.
5. Identify trend reversals
Then, look for bullish or bearish divergence between the price and the ROC. A bullish divergence occurs when the price makes a lower low, but the ROC makes a higher low. This can signal a potential upward trend reversal.
6. Centerline crossovers
Finally, when the rate of change crosses above the zero line, it indicates a potential bullish trend and vice versa.
7. Combine with other technical analysis tools
Use the ROC in conjunction with other technical analysis indicators (such as moving averages and RSI) to confirm and reduce false signals.
Combining ROC with other indicators
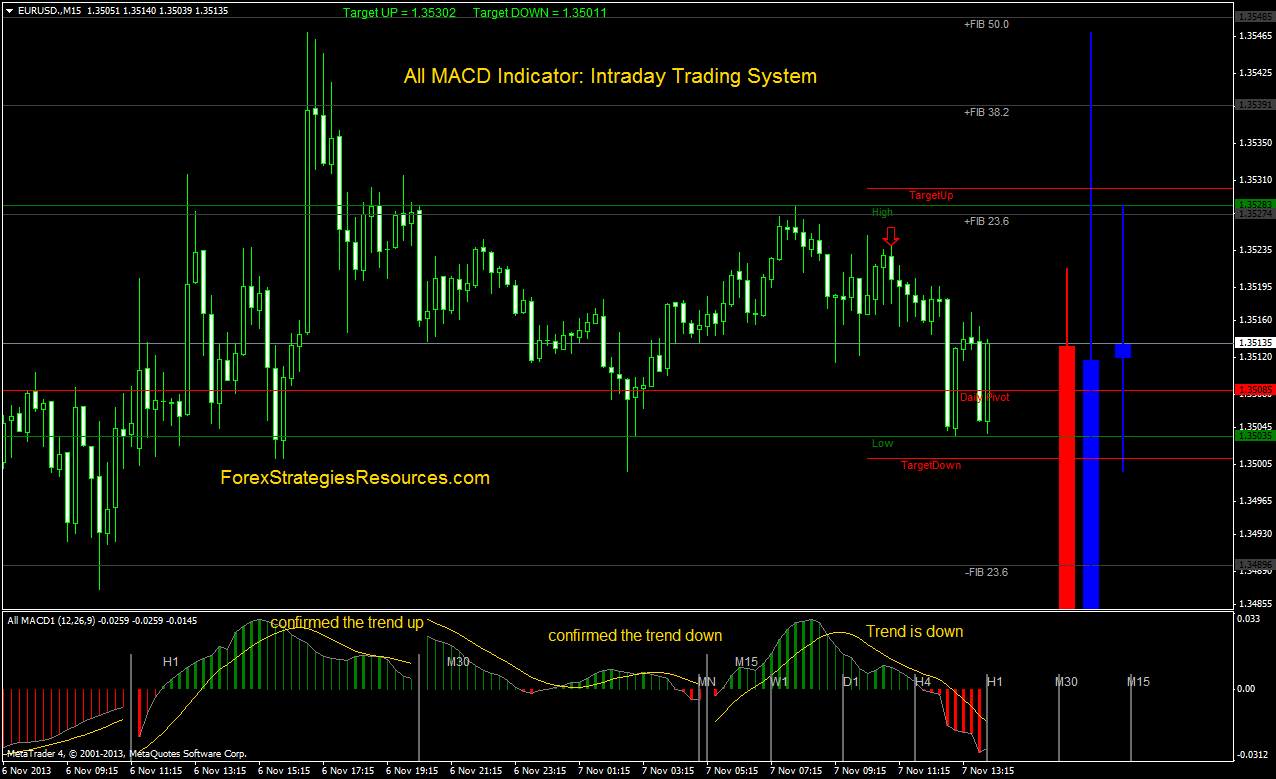
ROC indicator with MACD
The ROC measures the percentage change in the current price over a set period. It highlights the speed of price changes and momentum. The MACD focuses on the relationship between two moving averages to signal changes in trend direction. When combined, the rate of change can confirm MACD signals by providing additional insights into momentum strength.
For instance, a bullish signal is stronger when the MACD line crosses above its signal line and the ROC is positive/rising. This indicates that momentum is strengthening. Conversely, a bearish signal is confirmed when the MACD line crosses below its signal line, and the ROC is negative/falling, suggesting a strengthening downtrend.
Additionally, divergences between the MACD and ROC signals potential trend reversals, such as when the price makes new highs, but the ROC and MACD do not, indicating weakening momentum and a possible reversal.
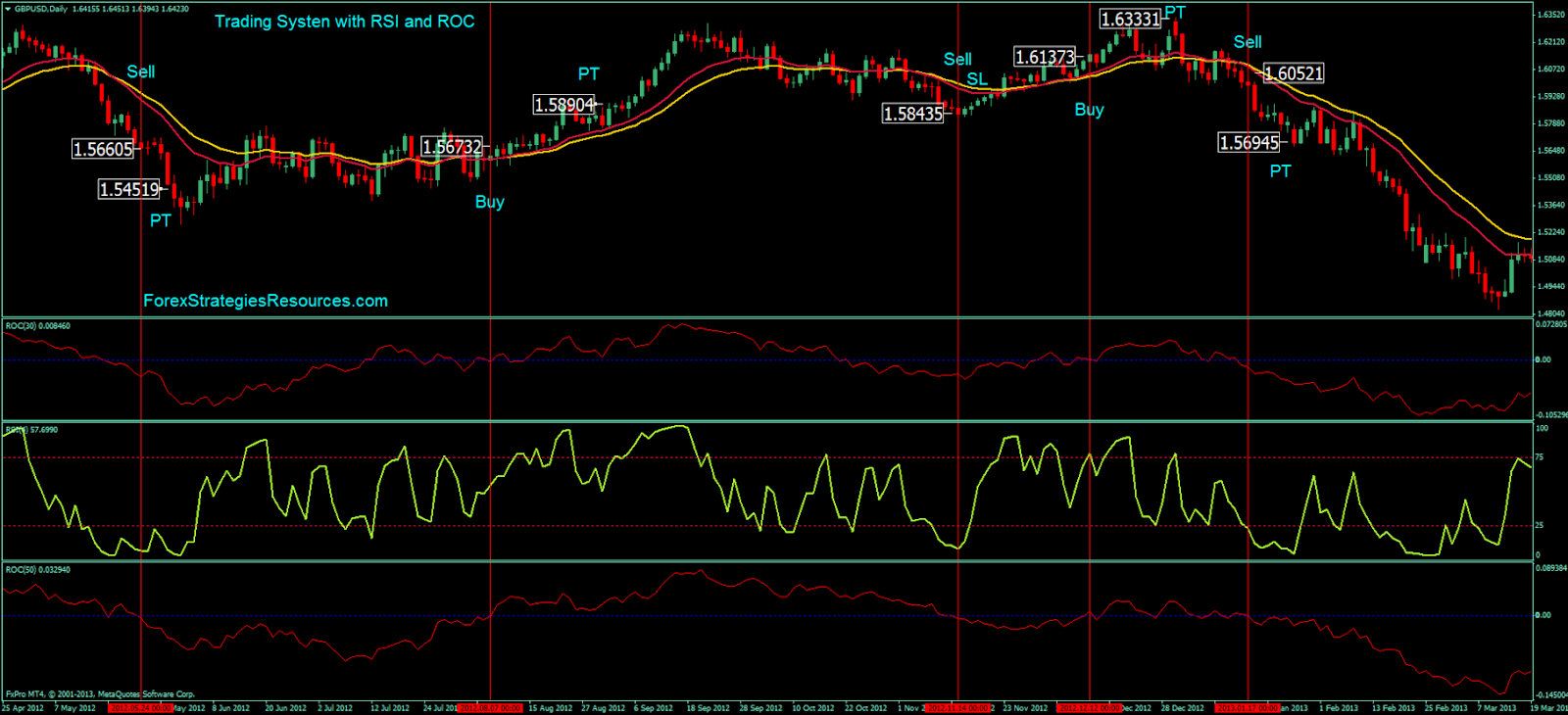
ROC indicator with RSI
Combining the rate of change with the Relative Strength Index (RSI) provides a better view of price momentum and potential reversal points. The ROC indicates the speed of price changes, providing insight into current price momentum, while the RSI identifies overbought or oversold conditions by measuring the magnitude of recent price changes.
When the RSI indicates overbought conditions (above 70), and the ROC shows positive but declining momentum, it may signal that the long pressure is weak, and a reversal could occur. Conversely, if the RSI is in the oversold zone (below 30) and the ROC is negative but increasing, it might suggest that exit pressure is decreasing and there is a possibility of a potential upward reversal.
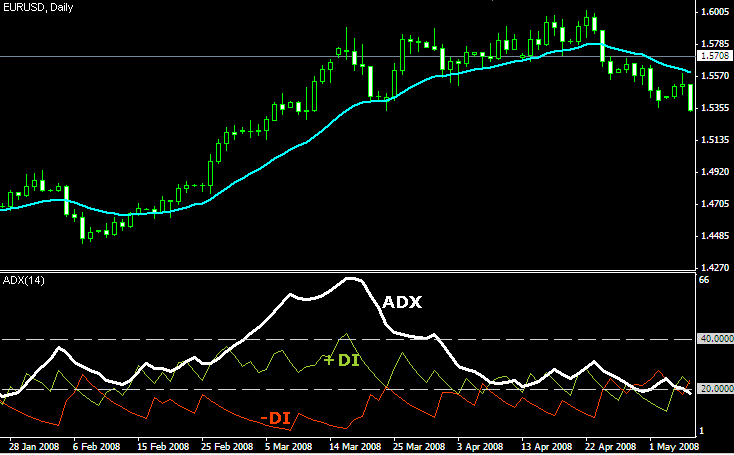
ROC indicator with ADX
The rate of change and the Average Directional Index (ADX) technical indicators help traders in understanding market trends and momentum together. The ROC measures how quickly prices change, indicating the momentum behind price moves, while the ADX assesses the strength of a trend, with values above 25 suggesting a strong trend and values below 20 indicating a weak trend.
When used together, the ROC can validate ADX signals by confirming trend strength with momentum insights. For example, when the ADX is above 25, indicating a strong trend and the ROC is rising, it confirms that the trend is strong and gaining momentum. This leads to a strong trading opportunity depending on the trend direction.
On the other hand, if the ADX is below 20 and the ROC shows declining momentum, it suggests a weak or consolidating trend, signaling that traders might want to be cautious about entering new trades.
Analyze forex prices with the ROC indicator
The rate of change measures the speed and direction of price movements, which helps traders identify potential trend reversals. However, its risks include susceptibility to false signals in volatile or choppy markets, as it may react quickly to short-term price fluctuations without reflecting the overall trend. Additionally, ROC when incorporated with trading strategies can lag behind price movements, potentially delaying signals. Hence, traders should use ROC in conjunction with other indicators to mitigate these risks and enhance decision-making.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.