Technical indicators provide traders with the support and resistance price levels that in turn help in placing successful entry and exit orders. By carefully analysing the present and past performance of a currency pair, technical indicators make it easy for you to predict future performance. In this article, we will learn everything about technical indicators:
What are technical indicators?
Technical indicators are a market direction signal based on the current and historical price movement of a currency pair that provides traders with future price expectations. They are pattern-based signals that form different shapes to reflect the open, high, close and low currency pair prices and future market direction.
Types of technical indicator:
-
A leading indicator uses a short-term timeframe to predict future prices and the future market directions. The Stochastic Oscillator, Fibonacci retracement, and Parabolic SAR are some of the most popular leading indicators.
-
A lagging indicator uses the historical price movement to tell traders what the previous market trend has been. It provides reversal signals to determine the next trend. Moving Averages, Bollinger Bands, and MACD are some of the most popular lagging indicators.
How do technical indicators work?
Technical indicators provide traders with a technical analysis of a particular currency pair that evaluates the price movement and identifies successful trading opportunities accordingly. Technical analysis is a methodology to find out future market prices with the help of current and historical market data. Technical indicators put a major focus on current, previous and expected price movements, charting tools, and other trading signals that evaluate the strength or weakness of a currency pair’s trend. It uses mathematical formulas to derive data points that are calculated from the trading volume, historical price and opening price of the currency pair.
Example of a technical indicator
Let us assume that you are trading EUR/USD, and you want to understand the future price direction of the same. Using the Simple Moving Averages will provide you with the expected market movement through current currency pair prices. You will consider one short-term and one long-term moving average to compare and confirm the future trend.
- The 50-day short-term moving average (MA) takes the sum of the currency pair price over the last 50 trading days and divides it by 50
- The 200-day long-term moving average takes the sum of the currency pair price over the last 200 trading days and divides it by 200
When the 50-day MA is more than the 200-day MA, it provides traders with an uptrend signal as it tells them that the currency pair prices in the last 50 days have been strongly trading upwards. If the 50-day MA is less than the 200-day MA, it means that the currency pair prices in the last 200 days have been slightly on the downward side, and hence it signals traders about an expected downtrend.
Top technical indicators you should know
Trend indicators
Trend indicators measure the strength and trend direction of a particular currency pair. It does so by averaging the currency pair prices through the historical prices to establish a single value, based on which current prices can be compared to one another.
- When a trend indicator signals current prices above the moving average price, it indicates an uptrend
- When a trend indicator signals current prices below the moving average price, it indicates a downtrend
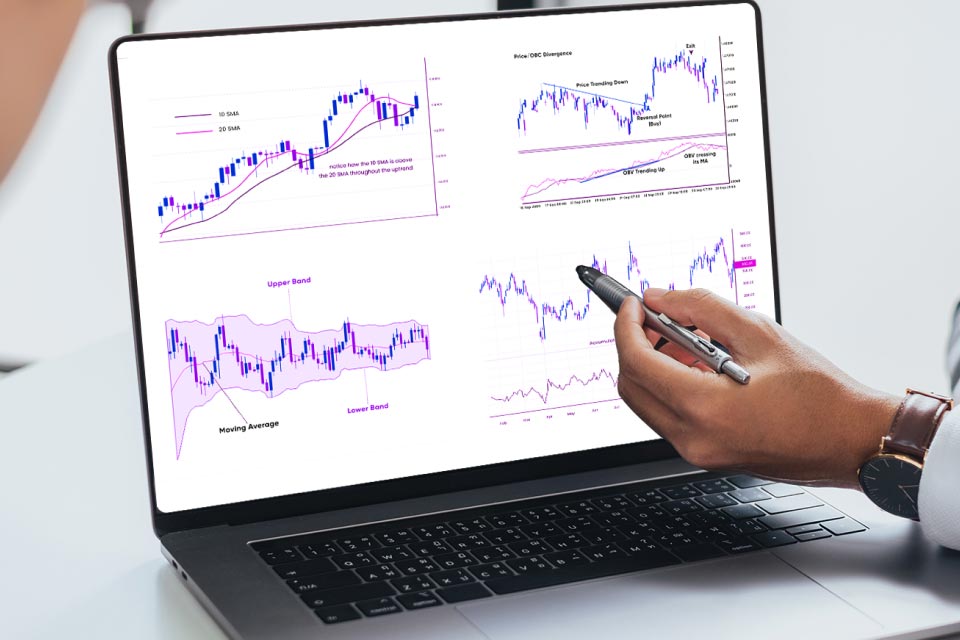
1. Moving Averages (MA)
A Moving Average is one of the most widely used technical indicators that provide traders with an average currency pair price based on the historical price trends of the same. It determines the long-term market movement and helps traders identify future market trends and place trade orders successfully.
- When the Moving Averages signal an uptrend, it provides ideal buy/entry price levels in the market
- When the Moving Averages signal a downtrend, it provides ideal sell/exit price levels in the market
2. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is an indicator that signals future market trends through a crossover. It establishes the relationship between one long-term and one short-term moving average price of a currency pair. This relationship helps traders identify if there is a bullish or bearish trend in the market. It comprises of –
- An MACD line which is calculated as the difference between the 26-period EMA and 12-period EMA
- A signal line which is the 9-day EMA of the currency pair
When the MACD line crosses the signal line from above, it indicates a bullish trend and provides ideal entry levels. When the MACD line crosses the signal line from below, it indicates a bearish trend and provides ideal exit levels.
Momentum indicators
Momentum indicators determine how strong or weak a trend is. It identifies the speed of currency pair price movements by comparing historical prices with current prices. The more is the momentum of a particular currency pair, the more volatile it is considered to be and vice versa.
1. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Relative Strength Index (RSI) is an indicator that tells about the overbought and oversold levels in the market. It oscillates between 0 to 100, where readings above 70 indicate oversold market conditions and readings below 30 indicate overbought market conditions. It helps understand in which direction the market is going to reverse.
- When the market is oversold, it signals traders to enter the market due to an expected uptrend
- When the market is overbought, it signals traders to enter the market due to an expected downtrend
2. Average Directional Index (ADX)
The Average Directional Index (ADX) indicator is an average of the increasing currency prices in an uptrend and tells the trader how strong a particular market trend is. ADX fluctuates between 0 to 100, and any reading above 50 signals a strong uptrend/downtrend and readings below 20 indicate weak trends. It consists of two direction movement (DM) lines, which indicate where the market is headed. The two DM lines are a positive directional movement line (indicating uptrend) and a negative directional movement line (indicating downtrend).
- When the positive DM line is above the negative DM line, the currency pair is in an uptrend and signals traders to long the trade
- When the negative DM line is above the positive DM line, the currency pair is in a downtrend and signals traders to short the trade
Volatility indicators
Volatility indicators measure how rapidly the currency pair prices change in an uptrend or downtrend. Volatility can be determined by taking the difference between the highest price level and the lowest price level. These indicators provide traders with the ideal range between which the currency pair trades along with reversal points.
1. Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Band is an indicator that helps determine if the currency pair prices are touching their high level or low level compared to the current price trend. It consists of three bands, a middle band which is the average price level, an upper band that is placed two standard deviations above the middle and a lower band that is placed two standard deviations below the middle band.
- When the currency pair prices trade above the middle band and near the upper band, it indicates a downtrend reversal and signals traders to exit the trade
- When the currency pair prices trade below the middle band and near the lower band, it indicates an uptrend reversal and signals traders to enter the trade
2. Average True Range (ATR)
Average True Range is an indicator that provides traders with information about the degree of price volatility of the currency pair. This means it signals to show how much the asset price moves on an average on a particular trading day. With the help of this indicator, traders receive entry or exit signals depending on the market direction. The value of ATR is added or subtracted from the closing price depending on whether the trader wants to enter or exit the trade respectively.
Volume indicators
Volume indicators help measure a trend’s strength and provide them with market trend confirmations. These indicators average out the volume and compare it with price movements to place exit and entry orders. The higher the trade volume in the market, the stronger the existing trend is considered to be.
1. On-balance Volume (OBV)
OBV is the technical analysis indicator that relates the currency pair prices to their volume in order to predict future market prices. It provides traders with a bullish or bearish signal and helps them make buy or sell orders, respectively. Whenever a currency pair closes at a higher price level than its previous day’s closing price, it is considered an up-volume signal and indicates a bullish trend. However, when a currency pair closes at a lower price level than its previous day’s closing price, it is considered a down-volume signal and indicates a bearish trend.
- Up-volume indicates an uptrend continuation and signals traders to place entry/buy orders
- Down-volume indicates a downtrend continuation and signals traders to place exit/sell orders
2. Accumulation Distribution (A/D)
The A/D indicator makes use of the currency pair’s price and volume traded to provide traders with a future market directional signal. The accumulation level signifies the buying pressure, whereas the distribution level signifies the selling pressure in the market.
- When a currency pair is trading at high volumes and is accumulated, it indicates a bullish trend and signals traders to long the trade
- When a currency pair is trading at low volume and is distributed, it indicates a bearish trend and signals traders to short the trade
Tips for trading technical indicators
1. Use more than one indicator for confirmation
A technical indicator indicates the right market direction on its own. However, there are chances of false indications, and that is why it is always advised to use at least two indicators together to confirm the trend direction. You can combine indicators like Moving Averages with RSI, Bollinger Bands and ADX or RSI with MACD. When both indicators provide you with the same market signal, the trend is confirmed.
2. Trade with the trend
Technical indicators suggest traders trade along with the trend and not against it because there is a high chance of the market moving in that particular direction. This means if the technical indicators tell traders there is an uptrend, they should buy it, and if it tells them that there is a downtrend, they should sell it.
3. Use multiple time frames
When you use the technical indicator in more than a single time frame, the possibility of the market signals being true increases. Take a short-term (15-minute), medium-term (one-hour) and long-term (one-week) timeframe to confirm trend directions. If the technical indicator provides the same result in at least two time frames, traders can move forward with placing orders accordingly.
4. Trade according to your pre-defined trading plan
It is essential that, as a trader, you always stick to your trading plan. The market is volatile and may not always trade in the direction you anticipated. However, in the long term, when you stick to your trading plan, your trading goals are fulfilled. If the short-term market direction goes against you, it is advised to hold onto trades for some time and act according to the trading plan instead of the current market situation.
Confirm market directions with technical indicators
Technical indicators help traders establish an uptrend or downtrend in the market that in turn results in making successful buying or selling decisions based on the trader’s trading plan. Start trading with Blueberry for competitive spreads and a seamless trading experience. Sign up for a live trading account or try a demo account.