Commodity trading is one of the best ways to diversify your portfolio and protect yourself from losses incurred due to inflation. It helps traders take advantage of markets even in volatile conditions. It also allows traders to hedge risk in the Stock market as Commodity prices generally move against it. So, if a particular Stock starts to fall, you can purchase more of the Commodity related to that Stock to potentially make up for your losses.
What is Commodity trading?
Commodity trading is the selling and buying of commodities traded worldwide. The most common Commodities for day traders are gold, oil, natural gas, and copper. While Commodities can be traded in their physical form, they are more popularly traded as Stocks, Futures, Options, ETFs, and CFDs. Commodity trading allows you to make profits through price fluctuations in the market. Fluctuations happen due to a number of factors like demand and supply, seasonal changes, and the global economic state.
Top commodity trading strategies
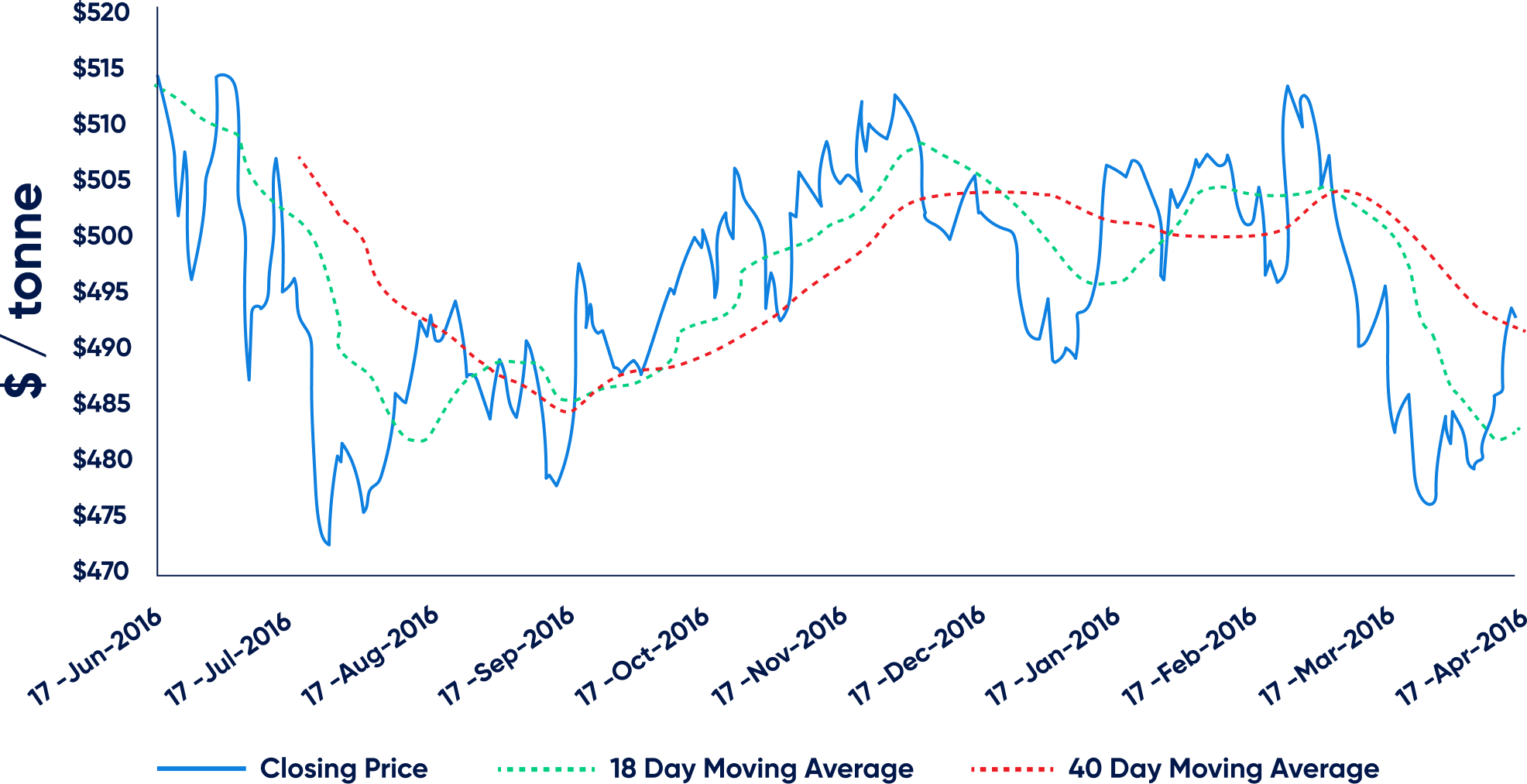
1. Moving averages for commodity
Using moving averages is one of the most common strategies for Commodity trading. It is a technical indicator that takes an asset’s average price for a specific period while smoothing out irrelevant prices by taking an average price. The average is calculated by taking the Commodity’s prices over a specific time, adding them up, then dividing them by the time frame. The average price helps you identify the market trend and place trades accordingly. It also identifies ideal entry and exit points by telling you how near the open and close price of a commodity is to its average price.
2. Range trading
Range trading involves trading within a sideways market at which you can buy and sell a Commodity over a period. Most traders buy more of the Commodity at the support level and sell at resistance level. A commodity’s price only fluctuates dramatically when its global demand and supply increases or decreases. Since range trading provides us with a support and resistance price, the commodity prices between this range fluctuate very little, providing traders a stable zone to trade and making it easier for them to identify market entry and exit points.
3. Fundamental trading
Fundamental trading involves trading Commodity-specific or economic events to determine its prices. For example, if the demand for Oil increases in Canada, the price would also increase. This causes traders to take advantage and go long in the market. Fundamental trading is based on trading the news and quantitative and qualitative factors of a particular commodity.
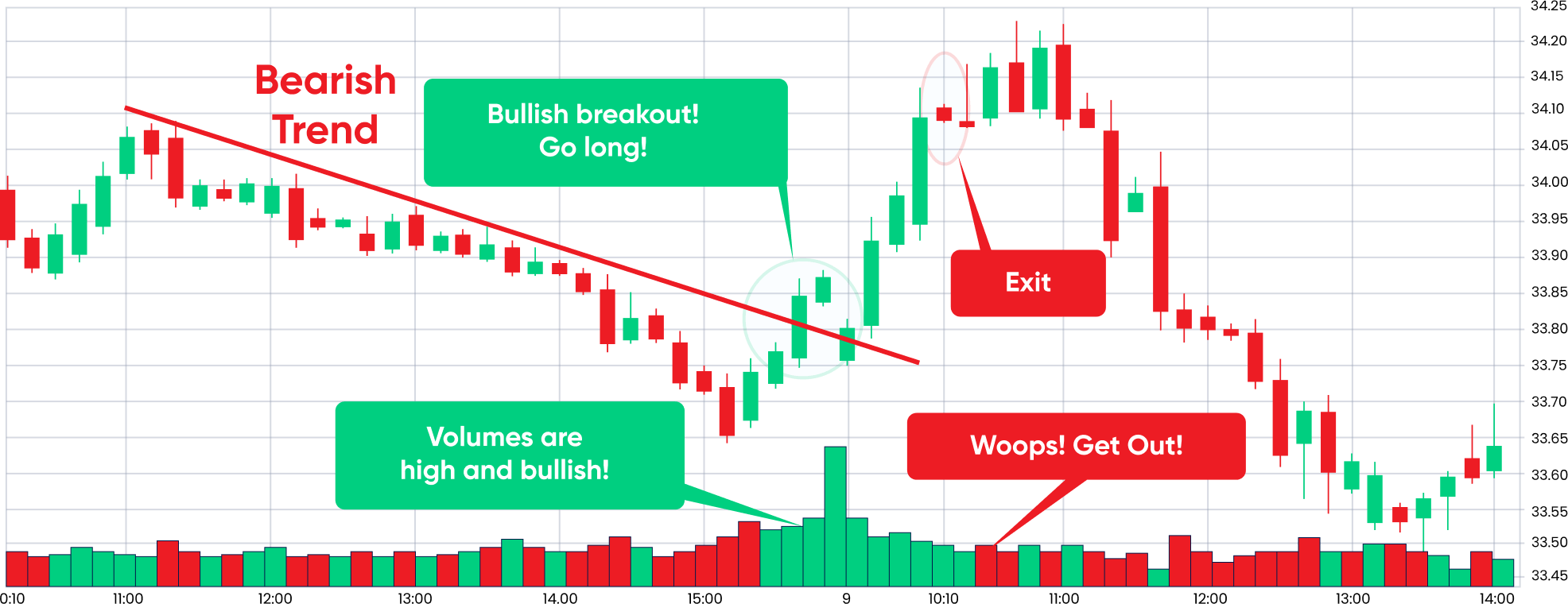
4. Breakout trading
Breakout trading involves traders taking early positions in a commodity’s fluctuating price. It offers traders a potential opportunity as soon as its price goes beyond the resistance level or falls below the support level. By making moves at the early stages of a trend, most traders benefit from major price movements when the market moves in their favor.
- Most breakout traders take a long position when the Commodity price crosses over the highest value of its price range.
- Alternatively, they take the short position if it falls below the lowest value.
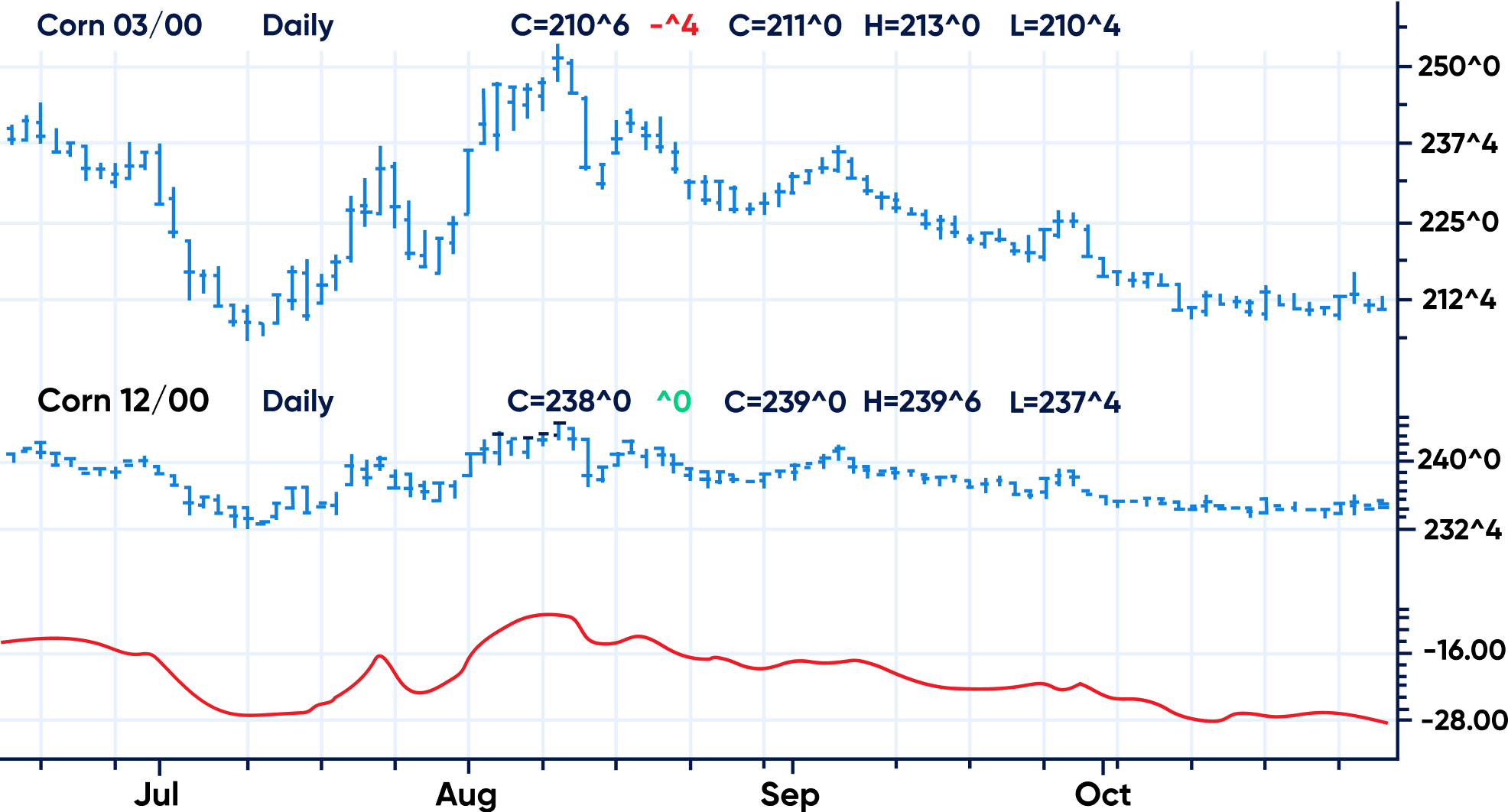
5. Commodity spread trading strategy
You can also trade Commodities by trading their spreads. This strategy involves buying a particular Commodity and selling a similar one simultaneously to earn profits from its spread or the difference in prices. For example, you can buy a Future of a raw commodity when its prices are low and sell the Futures of a finished product as soon as the prices are high, which could reap you profits.
6. Specializing in a single Commodity
Instead of trading multiple Commodities, you can specialize in just one. For example, you can choose Gold to trade as a single Commodity and keep a close eye on its fluctuating prices, place trades accordingly, and profit from the same. When you trade a single Commodity, it gives you more time to analyze it in-depth. It also provides you with better trading prospects by allowing you to focus on just one prime Commodity.
7. Position trading
Position trading allows you to hold a trade for a long time, like months or even years, to benefit from long-term price movements. Position traders ignore all short-term price movements and only rely on fundamental aspects of the market and long-term trends.
8. Season trading
Season traders benefit from the seasonal patterns of a Commodity by taking long and short trade positions. For example, the winter season is best known for wheat worldwide and it is generally harvested in the spring season. Traders holding wheat in the Commodities market can hold larger positions as the spring season approaches as it is expected to rise due to a surge in demand.
Start Commodity trading with Blueberry
Most traders hold positions in the Commodities market through CFDs, Futures, and Options as it allows them to trade without investing the entire trade value. Blueberry Market allows you to trade Oil and Metal Commodities via CFDs on their industry-level platform. Sign up for a live account on Blueberry to start your trading journey.




