Sudden price jumps in a forex chart pattern are known as gaps. They often occur due to news events or market sentiment shifts. Identifying different types of gaps (breakaway gaps, exhaustion gaps, common gaps) is crucial since each type offers different market behavior insights. Common gaps are, well, the most common type of gaps.
While common gap signal trend continuations or reversals, they also carry increased risk. Knowledge of gaps helps traders make informed decisions, and that is what we will discuss in this article.
What are common gaps in trading?
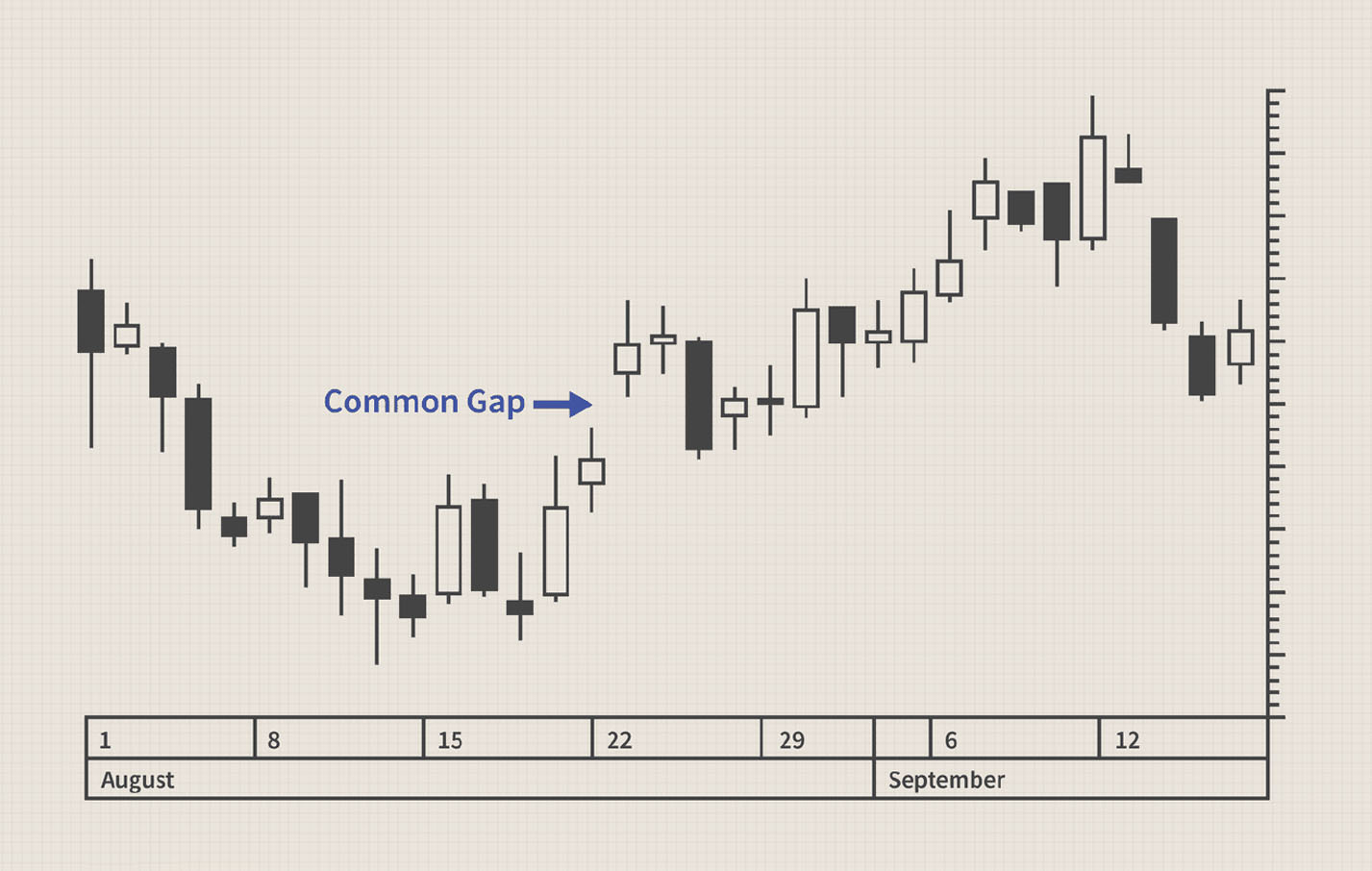
A trading gap occurs when a security's opening price is significantly different from its previous closing price, with no trading activity in between. Common gaps are the most frequent types of gaps to occur which are small in size and caused by normal financial market fluctuations. They tend to fill quickly, meaning that the exchange rate moves to fill the gap relatively soon after it opens.
Technical indicators to use with gaps in forex trading
On balance volume (OBV)
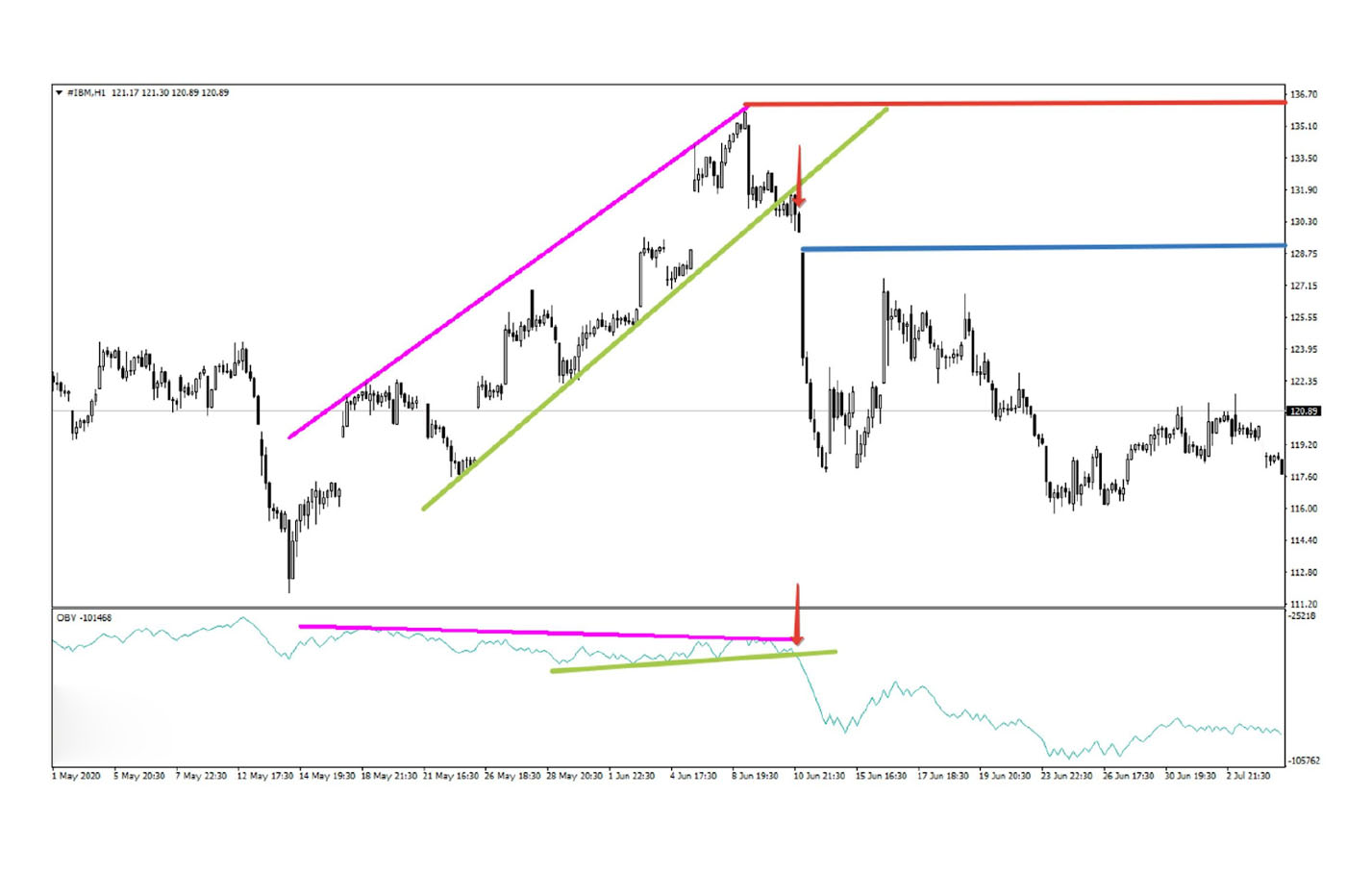
OBV is a cumulative indicator that uses trading volume to predict price changes. It adds volume on up days and subtracts trading volume on down days. OBV can confirm the strength of a trend after a gap. If the trading gaps increase and OBV also increases significantly, it suggests strong long pressure. Conversely, a gap down with a sharp decline in OBV indicates strong short pressure in technical analysis.
Relative strength index (RSI)
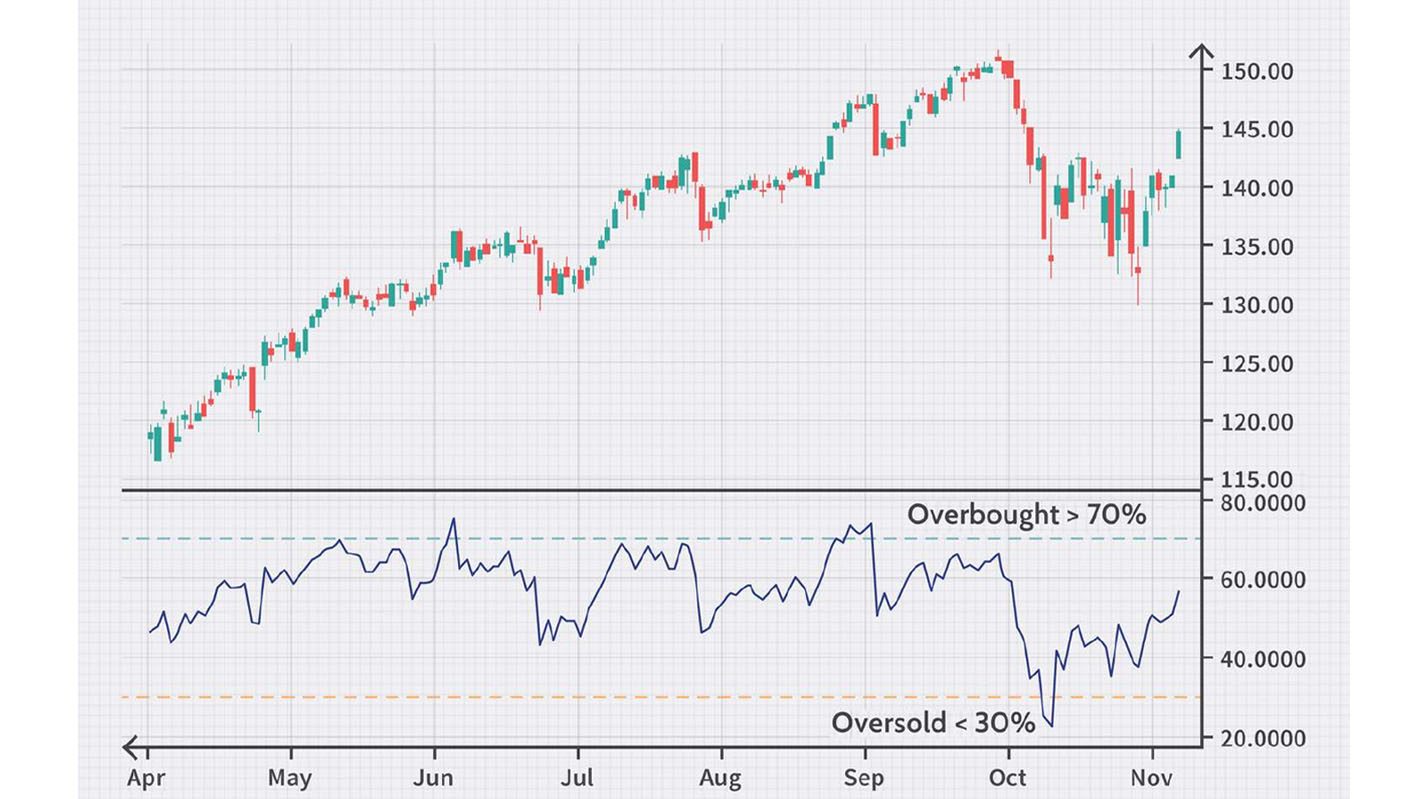
RSI measures the speed and change of price movements. It oscillates between 0 and 100, with readings above 70 generally considered overbought and below 30 oversold. After a gap, RSI can help identify potential overbought or oversold conditions. For example, if a currency pair trading gaps up and RSI is already overbought, it suggests a potential reversal.
**This is an example only to enhance a consumer's understanding of the strategy being described above and is not to be taken as Blueberry. providing personal advice.
Average true range (ATR)
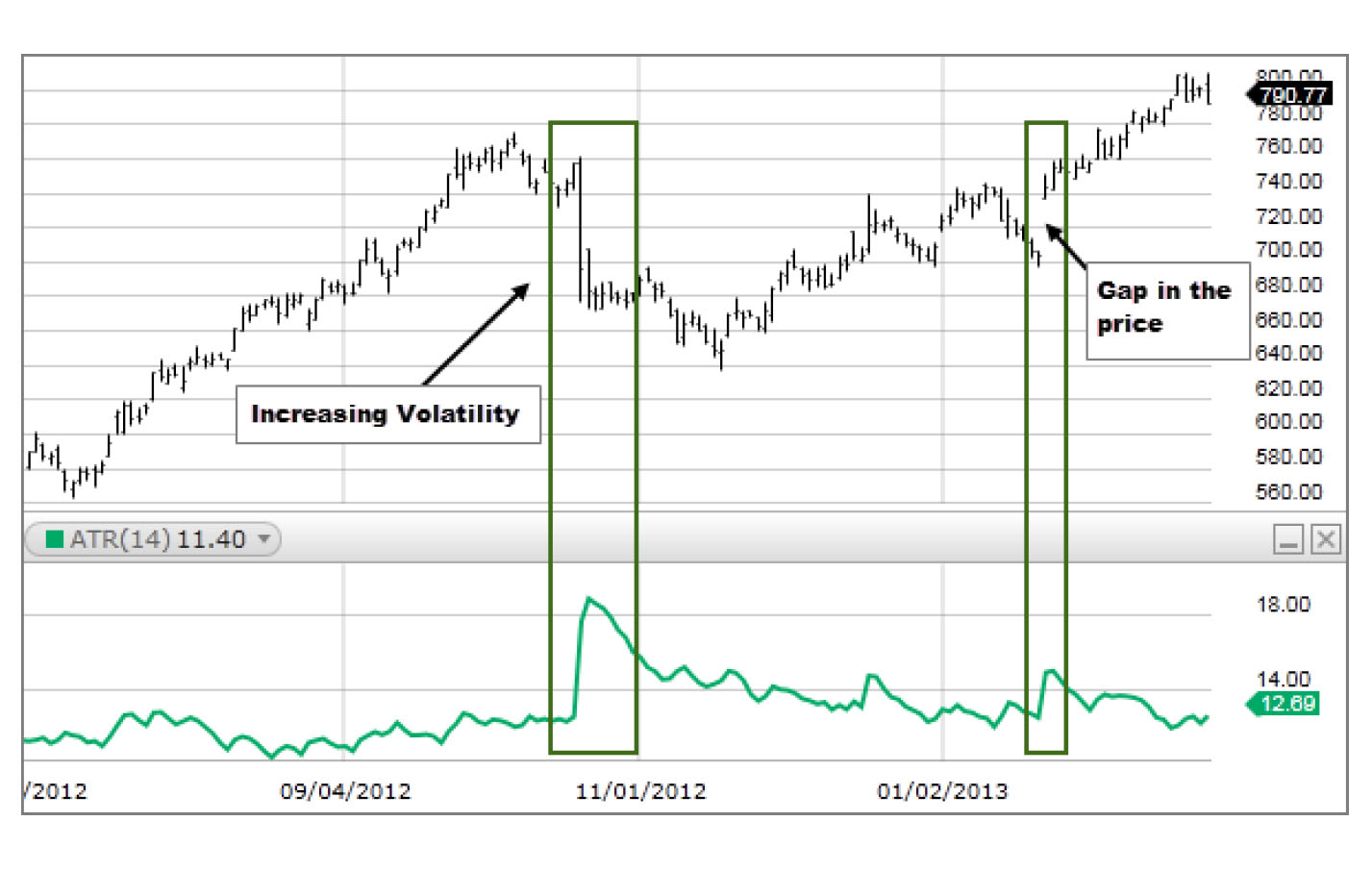
ATR measures market volatility by calculating the average price range over a specific period. ATR can be used to set stop-loss levels. It can help identify potential breakout levels after a gap. A wider ATR indicates higher volatility, which means a higher chance of a breakout gap in technical analysis.
Volume spread analysis (VSA)
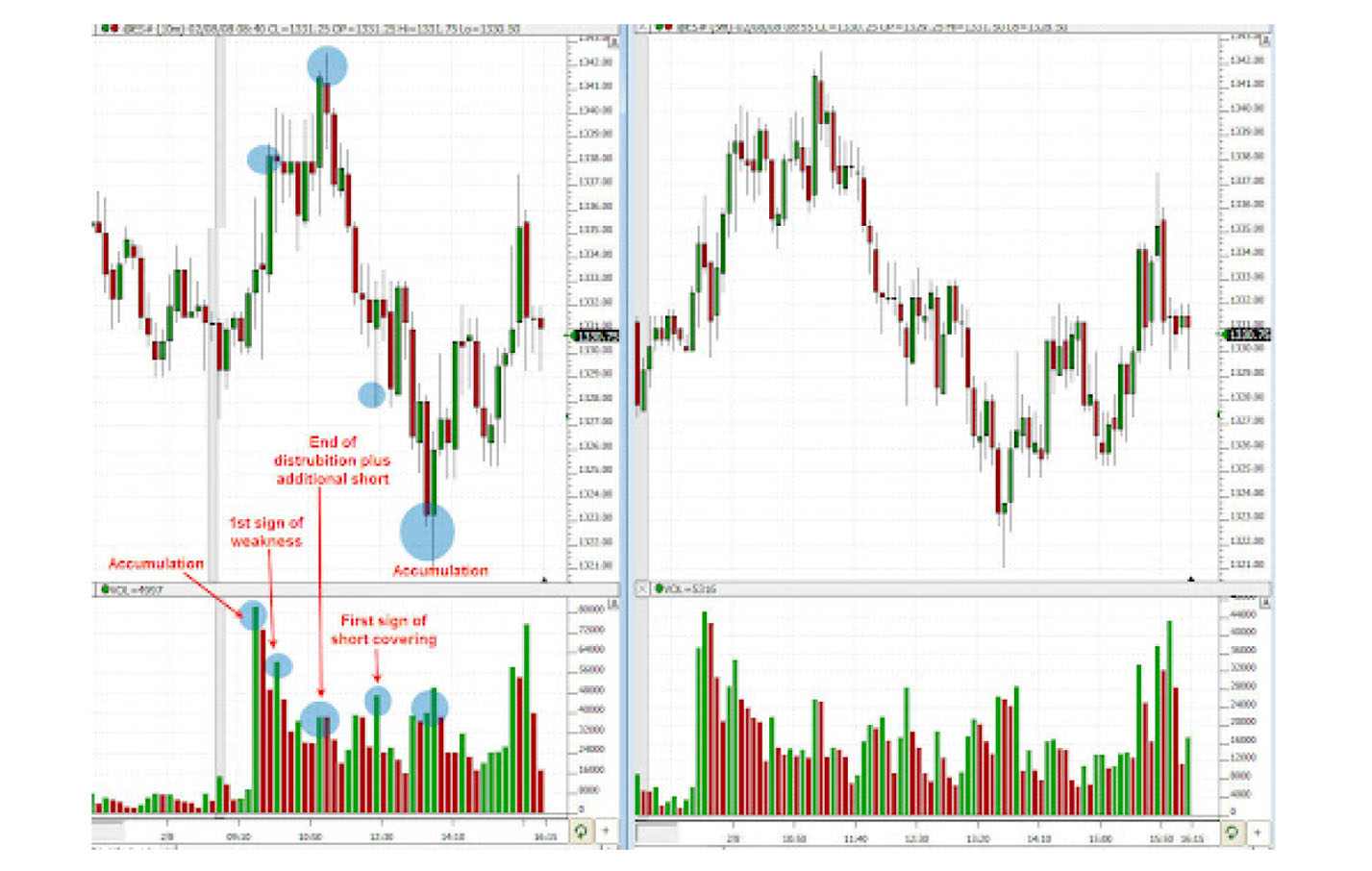
VSA is a method of analyzing price and volume data to understand market behavior.
It involves studying how price and volume interact to identify potential trend reversals or continuations. VSA can provide insights into the strength of a gap and whether it's likely to be filled or extended. By understanding the market's underlying strength, traders can make more informed decisions about entering or exiting a trade.
Top gap trading strategies
Fundamental analysis
A fundamental gap trading strategy helps identify common gaps by correlating them to significant economic or geopolitical events. Major news releases or global crises can trigger unexpected market movements, often resulting in gaps. By closely monitoring economic indicators and global events, traders can anticipate potential gap formations and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
Market sentiment
Gauging market sentiment can provide clues about potential gap occurrences. Social media analysis can reveal prevailing market opinions and expectations, while observing retail trader sentiment can indicate market positioning. Extreme sentiment readings, either overly bullish or bearish, may precede significant price movements and gaps.
Order flow analysis
Order flow gap trading strategy involves studying the underlying market structure to identify large orders and imbalances in supply and demand. Large long or short orders can create significant price impact and potentially lead to gaps. By analyzing market depth, traders can gain insights into order flow dynamics and anticipate potential gap formations.
Algorithmic trading
High-frequency trading algorithms can significantly impact market liquidity and price movements. Understanding how these algorithms operate can help identify potential gap formations caused by rapid order execution and cancellations. Analyzing market microstructure (which focuses on the underlying mechanics of the market) can provide clues about order flow imbalances and potential gaps.
What happens when a gap is filled?
A gap is filled when the price of security retraces back to the price level it was at before the gap occurred. This means the price has returned to its previous trading range. When a gap is filled, it often suggests that the initial price movement was an overreaction to news or other factors. While not confirmed, a filled gap can signal a potential change in market sentiment or trend.
Managing Risk in Gap Trading
Trailing stop-loss orders
In gap trading, price movements can be rapid and unpredictable. A trailing stop-loss allows traders to lock in gains as the price moves in their favor while still protecting against sudden reversals. This approach helps to maximize gains while mitigating potential losses.
Position sizing based on volatility
By reducing position size during high volatility periods, traders can limit potential losses caused by unexpected price gaps. Conversely, increasing position size during low volatility can optimize gain potential.
Psychological preparation
Gap trading can be emotionally challenging due to the high volatility. Traders should develop a strong trading psychology. Techniques like mindfulness, journaling, and seeking professional counseling can help traders manage stress and make rational decisions.
Using gap trading for forex pairs
Gap trading in forex chart patterns offers the potential for significant gains by capitalizing on price dislocations. However, gaps can be unpredictable, and the market may not return to the previous price level. News-driven gaps can be highly volatile, making it difficult to time entries and exits accurately. Hence, it's essential to use stop-loss orders and risk management strategies to mitigate potential losses.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.




