Placing take-profit orders allows traders to lock in gains automatically when the market reaches a desired level. It does not require constant market monitoring and prevents potential losses from market reversals.
In this article, we will discuss everything about take-profit orders in depth.
Understanding take-profit orders
A take-profit order is a forex order that automatically closes a position when the forex pair reaches the specified price level, locking in gains. It protects traders against losing profits and avoids the risk of prices reversing to erase potential gains.
There is no right time to set a take-profit order, as it depends on the trading strategy followed by the trader:
- Trend-following traders can set take-profit orders based on the support and resistance levels.
- Swing traders can identify market reversal points to place the take-profit order.
- Scalpers can place take-profit orders at very short-term targets based on tight spreads and small price movements.
Benefits and risks of using take-profit orders
Benefits
Automatic profit realization
When traders set a take-profit order, they specify the price level at which they want to close the trade to realize gains. This helps traders lock profits without monitoring the market regularly, which is useful in fast-moving markets where prices change rapidly.
Reduced market impacts
If traders manually close a large position, it can impact the market price due to fluctuating prices. A take-profit order ensures the trade is executed at the target price, minimizing this impact.
Time management
Setting up an automatic take-profit doer means traders have more time for other trading activities, such as analyzing markets, using indicators, and placing more trades. This makes it easier for the traders to manage large/multiple trades.
Emotional discipline
Traders are often charged emotionally while trading, which can influence their decisions. Setting a take-profit order reduces the impact of these emotions on trading decisions. By setting a take-profit order, traders can adhere to a predefined exit strategy, helping them avoid impulsive decisions driven by short-term market movements.
Risks
Missed gains
After a take-profit order is executed and the trading position is closed, the market might continue to move in the trader’s favor beyond the target price. The trader would miss out on additional gain opportunities if the order was not filled.
Over-reliance on automation
If traders over-rely on automated take-profit orders, they may lack flexibility in quickly responding to changing market conditions. This can result in missing out on market adjustments based on unexpected market events or new information.
Slippage
In illiquid markets, the execution price of the take-profit order can be different from the specified price due to slippage. This means the trader can end up with a lower profit than anticipated if the market moves quickly and the order is filled at a less favorable price.
Execution delay
There can be a delay between when the market price hits the take-profit point and when the order is executed in a fast market. Execution may be delayed in fast conditions due to market volatility, liquidity changes, venue queuing, and general network/latency conditions across external parties. These factors can lead to fills at the next available price and a different outcome from the requested level. The delay results in the trade being executed at a less favorable price, reducing the realized profit.
How to set take-profit orders
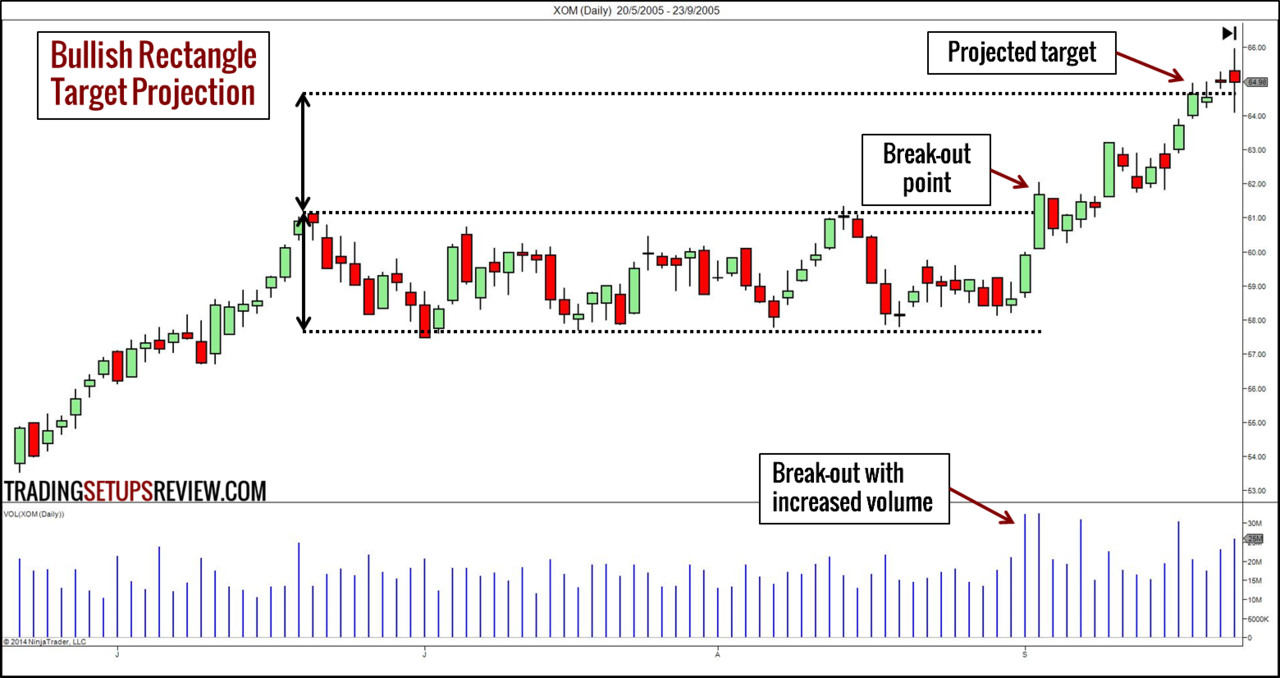
- Analyze the market: First, the trader needs to analyze the market using technical analysis tools such as trendlines, chart patterns, and more. This helps in setting a realistic and achievable profitable position. Combining technical analysis with fundamental analysis provides traders with better market insights.
- Determine profit-target: Decide the profitable position at which the trader wants to lock profits based on the trading strategy. Traders can decide this based on a percentage gain or technical level, such as resistance.
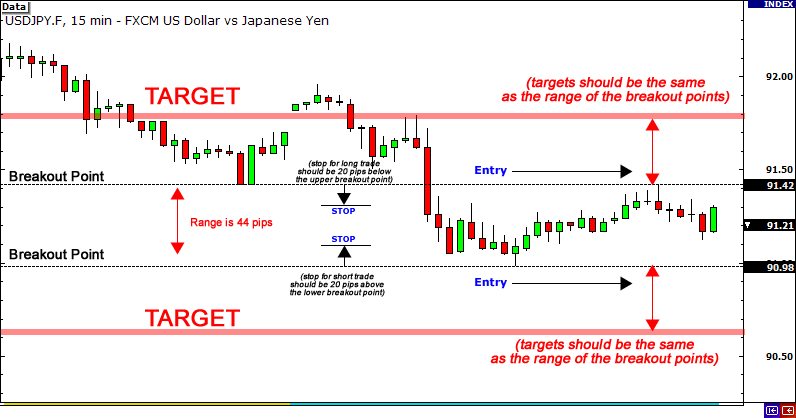
- Set take-profit level: Traders need to choose the specified price at which they want the position to close. A trailing take-profit can also be set to adjust the take-profit levels as the price continues moving in the trader’s favor. For example, if the trailing stop order is placed with a 10% bugger, the take-profit level will move up with the forex price but will not decrease in value.
- Place the take-profit order: Locate the order entry form on the trading platform and specify the type of order. Set the profit price or percentage.
- Monitor/adjust the order: Keep an eye on the trade to ensure that market conditions align continuously with the trading strategy; if the market trend changes, the trade can adjust the take-profit level.
This is an example only to enhance a consumer's understanding of the strategy being described above and is not to be taken as Blueberry providing personal advice.
Managing take-profit orders
- Define clear profit targets: Profit targets should be established based on a trading strategy and thorough market analysis.
- Allow room for fluctuations: Traders can use trailing stops while placing take-profit orders at a level that balances gains and also gives traders some room for price fluctuation. This helps traders not exit a trade prematurely.
- Analyze trade outcomes: After the take-profit order is executed, review the trade’s performance to check if the profit met the trader’s expectations.
Advanced take-profit trading strategies
Multiple take-profit level strategy
The multiple take-profit level strategy allows traders to set the take-profit at multiple levels at different price points instead of a single level. This helps traders to capture gains incrementally as the market moves in their favor. Tiered targets at various levels for the same order can be placed, where only a part of the position at each target level is closed. For example, if one enters a trade at 1.2000, they might set take-profit orders at 1.2050, 1.2100, and 1.2150.

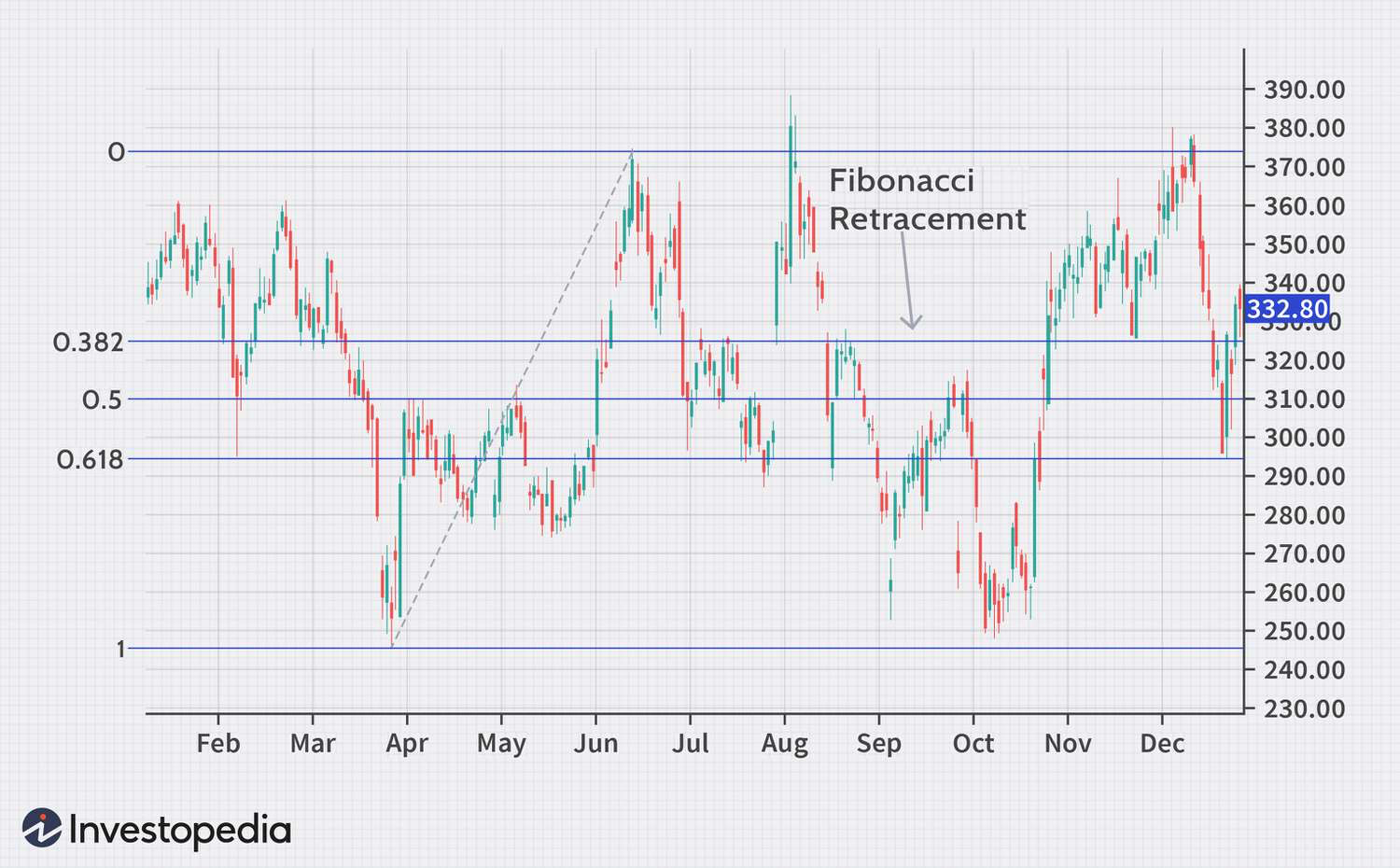
Fibonacci retracement levels
Fibonacci retracement levels can be used to set take-profit targets based on the levels at which the price can be reversed. Traders can analyze historical price moves and place profit targets accordingly to ensure they reap profits before the market reverses. Here is how traders can use Fibonacci retracement levels to set take-profit targets –
- Plot Fibonacci retracement levels from the recent price swing high to the price swing low in an uptrend and vice versa.
- Place the take-profit order at key Fibonacci levels, such as 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8% of the movement.
- Wait for the price to reach this level and for the order to be automatically executed.
Volatility strategy
Traders can adjust the take-profit levels based on market volatility to measure rice fluctuations, which helps them avoid premature exits. Indicators like the average true range enable traders to use this strategy and modify the take-profit level based on any volatility changes during market disruptions.
News trading strategy
Traders should monitor news events and set take-profit based on anticipated market reactions to these news and economic reports. This helps traders manage risk around high-impact news releases by adjusting take-profit levels in advance. Take a look at how the strategy can be implemented:
- Monitor the economic calendar and keep track of scheduled news events that can impact the forex market.
- Modify the take-profit levels before a major news event to anticipate potential price movements.
Price action strategy
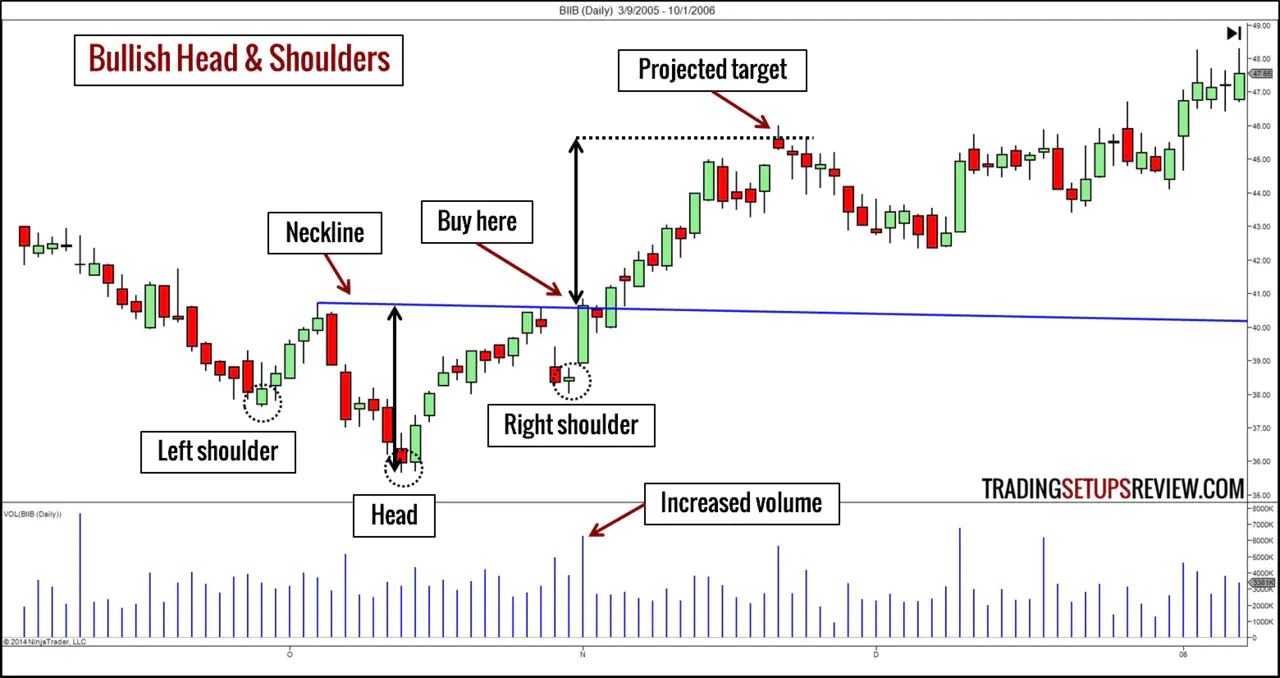
Using price action analysis and chart patterns to set take-profit levels helps traders monitor market behavior and technical formations. Traders can recognize chart patterns such as pennants, tops/bottoms, and more to set take-profit levels.
They can place the order at points where patterns suggest that the market price will likely reverse or strongly continue. Traders can also adjust these orders as new patterns and price actions occur.
Market sentiment analysis
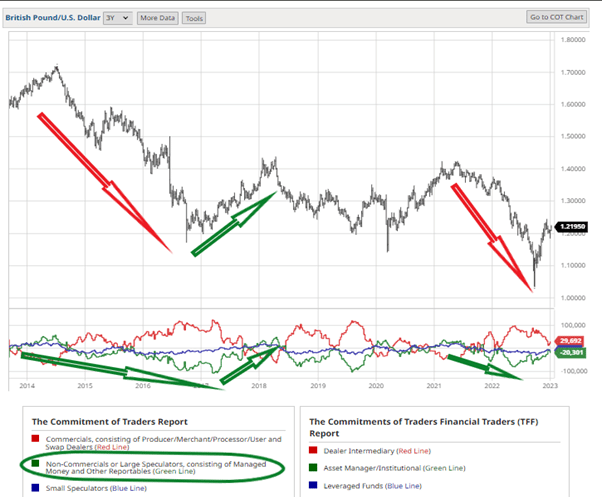
Market sentiment analysis refers to the general market outlook towards different forex pairs. Traders can understand the overall positioning and mood of the market participants to set take-profit orders accordingly.
Using sentiment indicators such as commitment of traders reports, sentiment surveys, and more helps traders set take-profit levels to capture potential gains. Traders can also modify their orders based on shifts in sentiment to align their orders with the prevailing market trend.
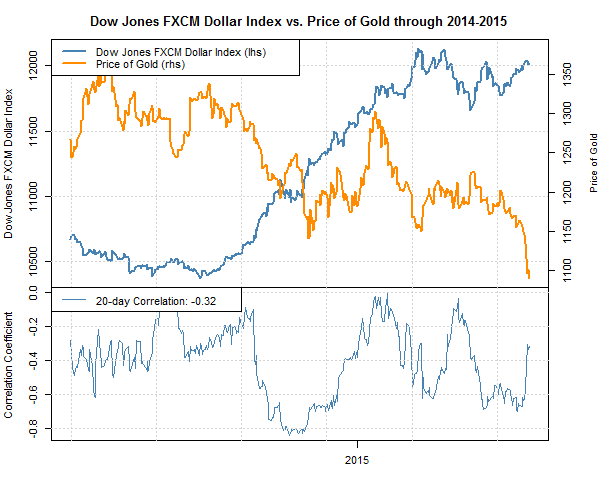
Correlation-based targets
Traders can analyze the correlation between different currency pairs to improve trade precision and place take-profit levels accordingly.
For example, if the EUR/USD is positively correlated with the gold price, traders can use gold price movements to set take-profit levels for EUR/USD trades. This helps traders leverage information from correlated markets to make informed profit decisions.
Example of a take-profit order in trading
Let’s assume a trader trades the EUR/USD currency pair. After performing technical and fundamental analysis, the trader anticipates that the EUR/USD pair will increase based on a positive economic data release.
Assuming the entry price the trade placed the EUR/USD trade at was 1.1200 with 10,000 units, the analysis suggested that the pair could increase to 1.1300 before touching its resistance. Based on this information, the traders set the target price of 1.1300.
As soon as the pair reaches this price level, the take-profit order is automatically executed, and the profit is realized. The total profit in this scenario would be = (1.1300-1.1200)*10,000 = $100
Take-profit vs other order types
Take-profit orders vs stop-loss orders
A take-profit order is designed to automatically close a position once it reaches a specified profit level. This ensures that traders lock in gains without the need for constant monitoring.
Conversely, a stop-loss order limits potential losses by closing a position when the market moves against the trader. This protects the trading capital from significant losses. While take-profit orders focus on securing gains, stop-loss orders focus on risk management and preventing large losses.
Take-profit orders vs limit orders
Take-profit orders are specific limit order used to close a position at a predetermined profit level. They automatically execute when the market price reaches the target the trader sets.
Limit orders, on the other hand, can be employed for both entering and exiting trades at a desired price or better. When traders set a limit order, they specify the exact entry price or exit price, but the order types will only be executed if the market reaches that price. While take-profit orders are placed to finalize trades at a profit, limit orders allow traders to control entry and exit prices based on their preferred price levels.
Take-profit orders vs market orders
Take-profit orders and market orders differ in execution. A take-profit order is set to close a position at a specified take-profit level, locking in profits when that price is reached. This order ensures that the trader exits at a predetermined level.
In contrast, a market order executes immediately at the most reasonable available price. This means that traders prioritize quick execution over precise price control, which can be beneficial in fast-moving markets but may result in slippage, where the execution price differs from the last quoted price. While take-profit orders control the exit price, a market order offers immediate execution with less precision on the exact price.
Take-profit orders vs stop-limit orders
Take-profit orders are intended to close a position at a fixed price once the market reaches the target. Stop-limit orders, however, combine features of both stop orders and limit orders.
They become limit orders once the market price hits a specified stop level, allowing traders to set both a stop and a limit price. This approach provides greater control over the execution price, preventing it from being worse than the limit price.
Take-profit orders vs trailing stop orders
Take-profit orders and trailing stop orders differ in their approach to handling market movements. A take-profit order is set at a fixed price at which the trader wishes to close the position. In contrast, a trailing stop order adjusts dynamically with the market price to protect and lock in profits as the market moves favorably.
It follows the market’s movements and triggers an exit if the price reverses by a specified trailing amount. This allows traders to capture more gains in a trending market while protecting themselves against reversals. While take-profit orders are static and set at a predetermined level, trailing stops adapt to market changes, offering a more flexible approach to profit-taking.
Placing forex trades with take-profit orders
Take-profit orders in forex help traders streamline exit trading strategies and reduce emotional decision-making. However, they may also cap potential gains if the market extends beyond the target, which could lead to missed opportunities if the price briefly surpasses the take-profit level. Hence, traders must analyze the market condition before placing any take-profit order.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.