The slow stochastic oscillator can identify overbought and oversold conditions, pinpoint potential trend reversals, and improve entry and exit timing. It can provide timely signals to aid traders in navigating volatile intraday price movements, leading to more informed trading decisions and improved gains.
However, like any trading indicator, it comes with its own set of potential drawbacks and risks that traders should be mindful of. One such drawback is its tendency to generate false signals, particularly during choppy or range-bound market conditions. Traders relying solely on stochastic oscillator signals may find themselves entering or exiting trades prematurely, leading to missed opportunities or even losses.
This article will teach us everything about the Slow Stochastic Oscillator for day trading.
What is the slow stochastic oscillator?
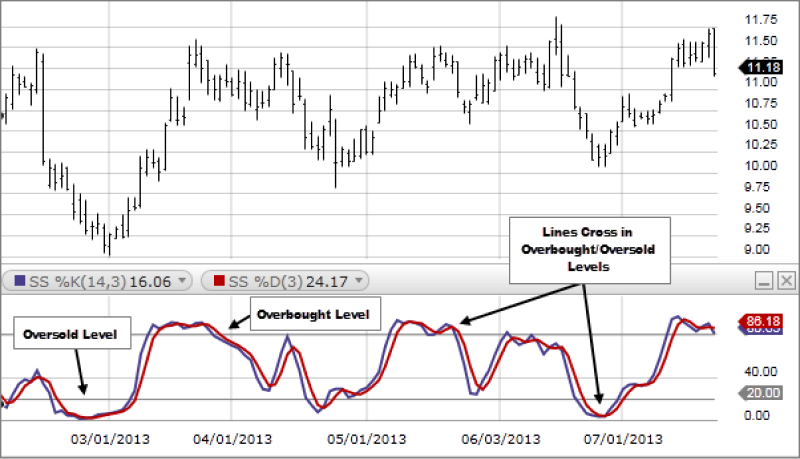
The slow stochastic oscillator is a technical indicator used in trading to measure momentum and identify potential trend reversals in financial markets. It consists of two lines: the %K and %D.
- The %K line represents the current price's position relative to the high and low prices over a specified period, typically 14 periods.
- The %D line is the moving average of the %K line, typically calculated over three periods.
The slow stochastic oscillator oscillates between 0 and 100, with readings above 80 considered overbought and readings below 20 considered oversold.
Advantages and risks of the slow stochastic oscillator
Advantages
- Smoothing effect: The indicator applies a moving average to the %K line, providing a smoother representation of price movements compared to the fast stochastic oscillator. It can filter out short-term fluctuations, making it easier to identify underlying trends.
- Enhanced trend identification: By smoothing out price movements, the indicator can help traders identify trends in the market more accurately.
- Reduced sensitivity to price fluctuations: Using a longer-term moving average reduces its sensitivity to short-term fluctuations. It can help prevent false signals and improve the indicator's reliability.
- Confirmation of trend reversals: It is effective at identifying potential trend reversals. When the oscillator moves back to the neutral range from overbought or oversold levels, it can signal a reversal in the market direction, providing traders with valuable confirmation.
Risks
- Delayed signal generation: Due to its smoothing effect, the indicator may generate signals later than other more responsive indicators. The delay could cause traders to miss early entry or exit opportunities.
- Less responsive to price changes: The indicator's use of longer-term moving averages can make it less responsive to rapid price changes. It may result in missed trading opportunities during periods of high volatility or sudden market movements.
- Increased lag in strong trends: In strong trending markets, the slow stochastic oscillator may lag behind the price action, leading to delayed signals or false readings. Traders should be cautious when using the indicator in such conditions.
- Potential overemphasis on past price data: The indicator's reliance on past price data, particularly its moving averages, may cause traders to overemphasize historical trends at the expense of current market conditions. It could also lead to inaccurate trading decisions.
Tips to use the slow stochastic oscillator in day trading
Combine with trend analysis
Use the slow stochastic oscillator with trend analysis tools, such as moving averages or trendlines, to filter out signals that go against the prevailing trend, increasing the accuracy of trading decisions.
Use overbought/oversold levels
Pay attention to overbought and oversold levels indicated by the indicator to identify potential reversal points in the market.
Adjust settings for market conditions
Adjust the settings of the indicator based on market conditions. For example, in volatile markets, traders may consider using shorter periods for more sensitive readings, while in calmer markets, longer periods may provide more reliable signals.
Consider multiple timeframes
Analyze the indicator over multiple timeframes to get a comprehensive view of the market dynamics. For example, use a longer timeframe (such as daily or weekly) for trend analysis and a shorter timeframe (such as hourly or 15-minute) for entry and exit timing.
Avoid trading during sideways markets
Avoid using the indicator during sideways or range-bound markets, as it may generate false signals. Instead, focus on trading when the market is trending, as the oscillator is more effective in such conditions.
How to trade forex with the slow stochastic oscillator
Confirm market conditions
Assess the overall market conditions to determine if the market is trending or ranging. The indicator is most effective in ranging markets, where prices oscillate between support and resistance levels.
Identify overbought and oversold levels
Use the indicator to identify overbought and oversold conditions. Readings above 80 indicate that the market may be overbought (signaling potential short entries), while readings below 20 suggest oversold conditions (signaling potential long entries).
Look for divergence
Look for divergence between the indicator and price. For example, suppose the price makes a lower low, but the oscillator makes a higher low. In that case, it may indicate weakening bearish momentum and potential for a bullish reversal and vice versa.
Wait for signal confirmation
Wait for the Slow Stochastic Oscillator to cross back below 80 from overbought territory or above 20 from oversold territory to generate a long or short signal, respectively. It confirms that momentum is shifting in the desired direction.
Set entry and exit points
Once a signal is generated, set entry and exit points based on the trading strategy. Consider placing a long order when the Slow Stochastic Oscillator crosses above 20 from oversold territory and a short order when it crosses below 80 from overbought territory.
Implement risk management
Implement risk management techniques such as setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Ensure that the risk-to-reward ratio is favorable for each trade.
Monitor trade
Continuously monitor the trade and adjust the stop-loss levels as the trade progresses. Consider scaling out of the trade partially if the market moves in the trader's favor or closing the trade early if the trend weakens.
Combine the Slow Stochastic Oscillator with other indicators
Employing the Slow Stochastic Oscillator in day trading provides traders with valuable insights into market momentum. It is accurately used in conjunction with other indicators to validate signals and confirm trading decisions.
Combining it with complementary indicators such as moving averages, trendlines, or volume analysis provides a more comprehensive view of market dynamics, reducing the risk of false signals and increasing overall trading accuracy.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.




