Margin trading is one of the most common derivative strategies used in financial markets. It can also be considered tax-efficient as it allows you to choose the size of your wager and exempts profits earned from stamp duties and taxes.
In margin trading, you do not actually own the underlying asset. You can trade with smaller amounts of capital and hold larger positions in the market by speculating on the price movements of the asset.
What is margin trading and how does it work?
Margin trading is a type of trading where traders do not actually buy or sell any assets. Instead, they only speculate on its price movement. Every spread bet includes two prices:
- The bid price at which you buy the asset
- The ask price at which you sell the asset
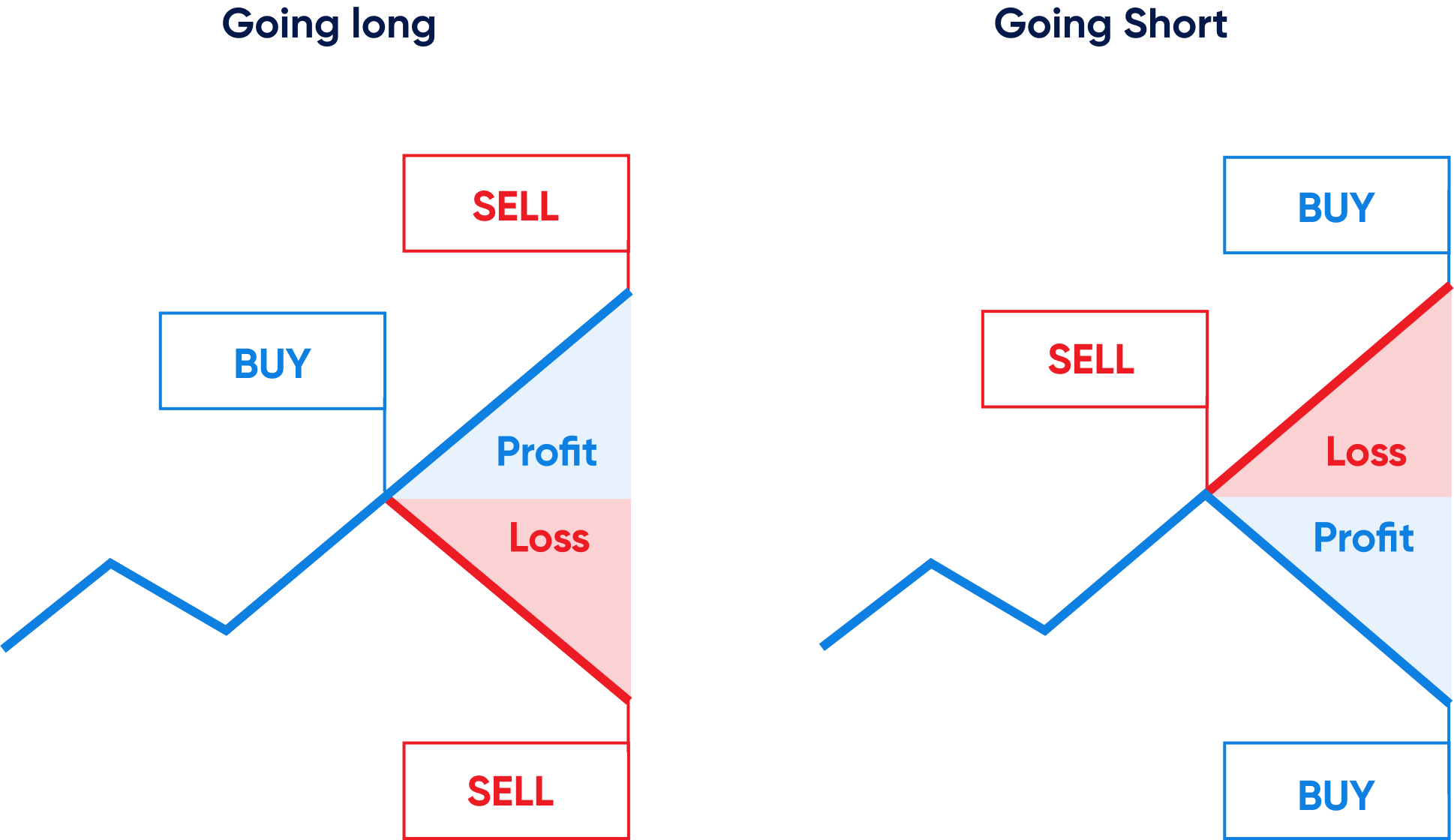
The difference between these two prices is called the spread. Traders who spread bets go long on the asset if they expect the market prices to rise, advice versa.
Top Benefits of Margin Trading
Allows you to go long or short
With margin trading, you can take advantage of both rising and falling markets. Since you only bet on the direction in which the market moves, every price movement in your favor may result in good outcomes for you.
Margin trading
You can get greater exposure in the market by only investing a small percentage of the total trade value through margin trading. For example, if you wish to place a bet worth $1,000, and your broker has a margin of 20%, you will only be required to deposit $200 to hold a $1,000 position.
Multiple market exposure
You can opt for margin trading across several markets, including Forex, Stocks, Commodities, and CFDs. Entering multiple markets may result in a number of accumulated good outcomes at the end of your trading session.
Trading off-hours
Every financial market has different trading hours. However, whenever you opt for margin trading, you can trade beyond the regular hours of trading. This allows you to strategise during the post- and pre-market sessions as well.
Hedge your portfolio
Hedging helps in offsetting risk associated with trading. You can opt to spread bet on an asset you’re expecting to move in a different direction from the Shares you own to hedge your Share portfolio. For instance, if you own Shares in a gold mine company, but its prices have been falling, you can opt to go short and offset incurred losses.
How do you manage risk in margin trading?
Standard stop-loss orders
A stop-loss order is a trade order to sell or buy an asset at a pre-decided price. It limits a trader’s risk by automatically closing a trade as soon as the price passes a certain level. A standard stop loss closes your trade at the best available price after the stop value is reached.
Guaranteed stop-loss orders
A guaranteed stop-loss order is similar to a standard stop-loss order. The only difference is that it closes a trade at the exact price you have specified. This limits losses you may have incurred and mitigates risk.
Start margin trading with Blueberry
Margin trading is an efficient way to earn profits without having to pay for a large sum of money for taxes, commissions, or stamp duties. It allows traders to speculate on the price movement of assets and place trades through margin trading. Blueberry allows you to spread bet a range of markets seamlessly on our industry-standard platform.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you make money from margin trading?
Ideally, yes. You can earn profits from margin trading with proper experience and strategy. A systematic trading plan is needed to place successful spread bets.
Is margin trading better than CFD?
Margin trading is a tax-free trade while CFDs are offset against loss for tax purposes. This makes margin trading a more common option for traders.
What is the difference between margin trading and share dealing?
Margin trading does not involve any ownership of the securities. Hence, the trade is free from taxes, commissions, and stamp duties. On the other hand, shares trading involves having direct ownership of the asset. You are also required to pay taxes, stamp duties, and commissions.




