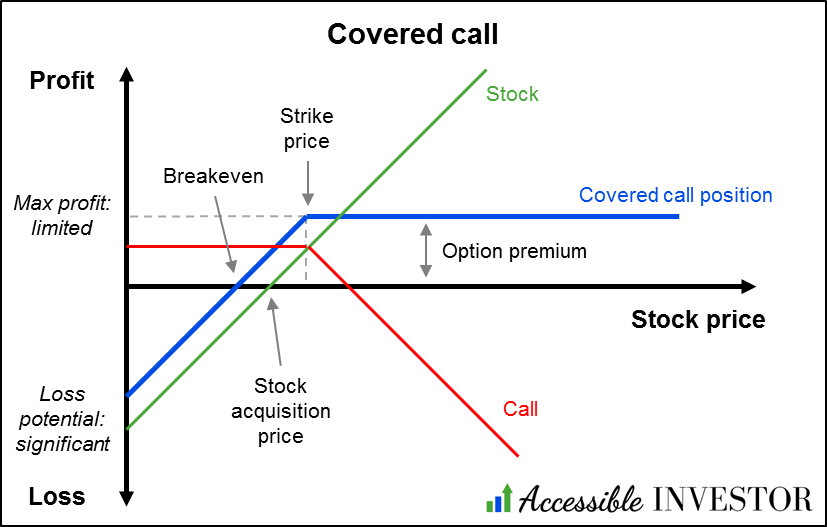
A covered call options strategy allows traders to generate additional income via option premium payments. It acts like a hedge against market price declines by capitalizing on neutral to slightly bullish market trends.
This article will discuss the covered call option strategy in depth.
Define the covered call options trading strategy
The covered call options strategy involves holding a long currency pair position while shorting a covered call option on the same currency pair. This strategy allows traders to generate additional gains from the premiums received from the covered call options. Trades also get downside protection by opening positions in rising and falling markets.
The trader can exercise the option if the currency prices rise more than the covered call option’s strike price. In this case, the trader will have to exit their position at the strike price, missing out on further upside but gaining from the higher price of the currency pair’s appreciation up to the strike price and the premium received.
On the other hand, if the stock price or currency pair price remains below the call options’ strike price, the options contract expires. In this case, the trader can retain the currency pair position and keep the premium received, increasing gains.
Lastly, if the currency pair or stock price enters a downtrend, the premium from the call option acts as protection against the decline, though the trader might still face some losses on the currency pair position.
Advantages and risks of using the call options strategy
Advantages
-
Downside protection: Call options limit traders' risk since the maximum loss is limited to the premium paid. This allows traders to gain from specified price appreciation without exposing themselves to unlimited losses if the market moves against them
-
Flexibility in market conditions: Call options offer flexibility by allowing traders to gain from various market scenarios (bullish, bearish, or neutral)
-
Reduced portfolio volatility: Using call options can help smooth out portfolio volatility by providing leverage and gains without the need to invest a large amount of capital
-
Reduced short-term fluctuation impact: Call options can reduce the impact of short-term price fluctuations on a portfolio
-
Opportunity to adjust position: Options offer the ability to adapt or hedge existing positions without exiting the underlying currency pairs. Traders can write covered calls to modify their additional risk exposure
Risks
-
Limited upside potential: While purchasing call options offers unlimited upside potential, writing call options (covered calls) limits the potential gains to the premium received plus the difference between the exchange rate and the call’s strike price if the option is exercised
-
Opportunity cost: Holding call options involves paying a premium, representing a capital cost that could have been invested elsewhere. If the option expires worthless or underperforms, the opportunity cost can affect overall returns
-
Market risk: covered calls are subject to market risk, including changes in underlying stock price or currency pair prices, interest rates, and volatility
-
Exercise risk: For call options traders, exercise risk occurs when the option holder exercises the option, requiring the trader to deliver the underlying asset at the strike price. This can be problematic if the trader does not own the currency pair (naked call) and must purchase it at a higher market price
-
Overwriting risk: Overwriting occurs when traders frequently exit call options on currencies they own, potentially resulting in excessive transaction costs and increased risk
Stepwise guide to implement the covered call options strategy
Evaluate the position
Before initiating the strategy, traders must evaluate their current forex position price and overall market outlook. Assess the currency holdings, position sizes and analyze the market conditions to ensure that the market is slightly bullish when executing a long order.
For example, if a trader holds a long position of 100,000 units in the EUR/USD currency pair, and the current exchange rate is 1.1200, the trader needs to have a neutral to mildly bullish outlook, expecting the rate to hover around 1.1400 over the next month.
Select the right covered calls option
There are several factors a trader must consider while entering a call option. These factors include –
-
Select a strike price that aligns with the trader’s market outlook. A higher strike price results in more potential upside but a lower premium, and vice versa
-
Expiration date that matches the trader’s investment horizon. Short-term options provide quick gains but need higher management and vice versa
-
The premium that will be received from selling the call option must be aligned with the trader’s income goals
-
Volatility of the currency pair since high volatility leads to higher option premiums but higher risk of the option being exercised and vice versa
Sell the covered calls option
After selecting the appropriate call options, the trader needs to execute the trade. Follow the steps below:
1. Selling the call option using the trading option with the necessary margin and capital required to cover the potential obligations if the option is exercised.
2. Verify that the order is filled out and the premium has been received in the trading account.
3. Check the trade details, such as expiration date, strike price, premium received, etc. If everything is correct, this confirms the transaction.
4. Keep a record of the trade with entry currency or stock price levels, reasons for choosing the option, premiums, and more. This will help the trader evaluate the strategy’s effectiveness.
Manage the position
The trader should then manage the position executed to ensure minimum risks and maximum returns. The trader should monitor the forex market, track the currency pair’s performance, and stay informed about economic releases. The value of the sold covered calls option should also be assessed regularly.
Adjust as needed
If everything goes as planned (or not), traders can adjust the strategy based on changing market conditions. If the option approaches its expiration date and the trader wishes to maintain the strategy, they can use a rollover option and close the current option for a new one with a later expiration date and/or a different strike price.
However, if the market moves against the trader’s expectations, they can close the forex position early to cut losses. This would mean that the trader buys back the option or unwinds the underlying price of the currency pair.
Entering options trading with a covered call strategy
Covered call options can cap forex losses and help traders navigate market volatility by holding opposing positions in a currency pair and trading options. However, they limit upside potential and require careful management to avoid opportunity costs.
Gains are capped at the strike price plus the premium, and option premium costs can impact overall returns. Market, exercise, and overwriting risks are significant, including asset price fluctuations and increased transaction costs. Successful implementation requires careful consideration, regular monitoring, and an understanding of these risks.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.