USDX offers insights into the Dollar's strengths or weaknesses, aiding in strategic decision-making. It provides a diversified approach to forex trading, allowing traders to hedge against currency risk or capitalize on trends in the global currency market.
Let’s discuss how to use the USDX for forex trading.
What is the USDX?
The USDX, DXY, and DX, collectively known as US Dollar Index, measures the value of the United States dollar relative to a basket of foreign currencies. It provides a weighted average of the Dollar's exchange rates against major currencies, helping to gauge the Dollar's strength or weakness in global markets.
The currencies included in the USDX basket are:
- Euro (EUR)
- Japanese Yen (JPY)
- British Pound Sterling (GBP)
- Canadian Dollar (CAD)
- Swedish Krona (SEK)
- Swiss Franc (CHF)
If the value of the index rises, it suggests the Dollar is strengthening against the basket of currencies and vice versa.
How is the Dollar Index calculated?
The geometrical average of all the six currencies that form the basket is calculated to compute the value of the Dollar Index. The midpoint value (average) of each currency’s bid and ask price at that point in time is multiplied by its given weightage and divided by six to determine the Index’s value up to three decimal places. The index value is calculated every 15 seconds in real-time.
For example, let us assume the average of bid and ask price of each currency is 1, the value of Index will be calculated as –
1 (57.6%) + 1 (13.6%) + 1 (11.9%) + 1 (9.1%) + 1 (4.2%) + 1 (3.6%) / 6 = 0.167
Factors affecting the US Dollar Index
1. Market supply and demand
The demand for the Dollar increases whenever the US exports its products and services. This is because exporting from a country requires customers to pay in USD. The conversion of local currency into Dollars appreciates the USD in the forex market and the value of the US Dollar Index. However, whenever the US imports products and services, it converts its currency into a foreign currency, which leads to depreciating the value of the Dollar. This leads to a weakening of the US Dollar Index.
2. Economic factors
Economic factors like the GDP of the US, inflation, wage policies, and employment rate, affect the US Dollar Index as well. When the GDP of the country increases or the inflation is stable at a low rate, the US Dollar strengthens in the forex market compared to other currencies, and so does the US Dollar Index.
On the other hand, if the US economic factors are not positive, the value of the currency is negatively impacted in the forex market, decreasing the value of the US Dollar Index.
3. Market sentiment
In situations where the economy of the US weakens due to factors like a decrease in consumption or increase in unemployment, the US economy is forced to sell off the money raised from bonds and government stocks to repay the local currencies. This leads to a decrease in the value of the US Dollar Index. On the contrary, when foreign investors push money back into the economy as the economy flourishes, consumption increases and unemployment decreases, leading to the US Dollar Index strengthening and increasing in value.
How to trade the Dollar Index?
1. Contract for Differences (CFDs)
A Dollar Index CFD allows you to trade the Index without actually owning it. You sign a contract with the broker who enables you to buy as many units of the Dollar Index as you wish and sell them at a later date. The amount paid is the difference between the opening and closing price of the Dollar index.
2. Options
Dollar Index Options can be traded by opening an options trading account. After choosing how many units of the Dollar Index you want to purchase, you predict the future price of the option at which you will buy the options at a predetermined date. With Dollar Index Options trading, you are not obligated to buy the security, and if the expiration date passes, the option becomes invalid.
3. Futures
Dollar Index futures are a type of contract where you predict the future buying price of the Index at a predetermined date. In this contract, you are obligated to execute the buy order at the fixed date. If you wish to exit the contract before the expiration date, you can do so by either selling the contract to someone else or opening an equal-value contract opposite to the original one, at the same predicted price and expiration date.
4. Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs)
Dollar Index ETFs track the Index’s prices from time to time, and hence the price of ETFs fluctuates all the time during a trading day. They are highly liquid due to the high demand and supply of ETFs and can be closed at any point in time. The two most important Dollar Index ETFs to track are UUP and UDN, which consists of several currencies along with the US Dollar.
- UUP ETF longs the US Dollar prices and shorts the other currencies in the Dollar Index basket through US Dollar Index futures
- UDN ETF tracks all value changes in the foreign currencies relative to the USD through US Dollar Index contracts
Top strategies to use with the USDX for trading
Range trading strategy
Range trading involves gaining from price movements within a defined range-bound market. With the USDX, traders can identify periods of consolidation or sideways movement where the index oscillates within a specific price range.
When the currencies are trading in a range, traders can establish long positions near support levels and short positions near resistance levels within the range. Technical indicators such as Bollinger Bands, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Averages applied to the USDX can help identify potential entry and exit points. It helps traders make informed decisions within the range-bound market conditions.
Carry trade strategy
Carry trade is a strategy where traders borrow in a low-interest rate currency and invest in a high-interest rate currency to gain from interest rate differentials. With the USDX, traders can assess the interest rate differentials between the US Dollar and other currencies in the index basket to identify opportunities to enter long positions in high-rate currencies and short low-rate currencies.
By monitoring central bank policies, economic data, and market sentiment, traders can anticipate interest rate changes and execute carry trade positions accordingly. Purchasing the USDX when the Federal Reserve is expected to raise interest rates or when other central banks are expected to lower rates can create a potential yield advantage.
Counter-trend strategy
Counter-trend trading involves identifying reversals against the prevailing market trend to capitalize on short-term price movements. When using the USDX, traders can look for overextended moves or divergence between the index and underlying currency pairs.
By observing signs of exhaustion or divergence from its trend, traders can anticipate potential reversals and enter counter-trend positions. Technical indicators such as oscillators (such as Stochastic Oscillator, MACD) and candlestick patterns are crucial in identifying potential reversal points. They help traders make informed decisions to gain from short-term price fluctuations.
Step wise guide to place orders using USDX
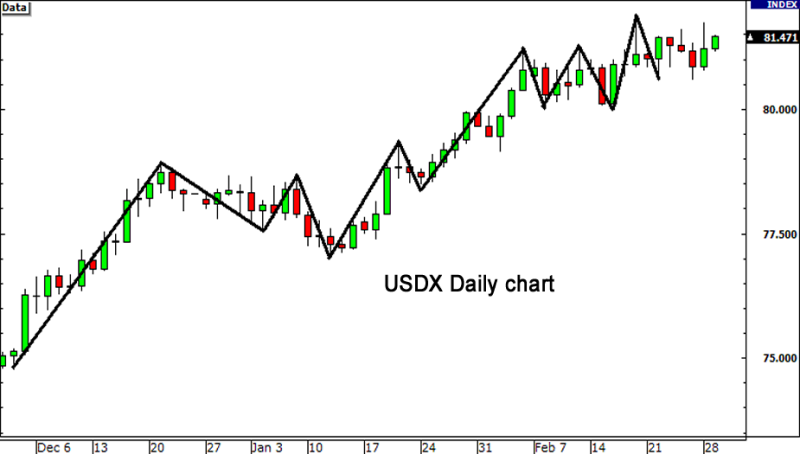
Identify USDX’s direction
Analyze the slope and direction of the USDX chart to identify the prevailing trend.
- An upward trend (with ascending highs and lows) suggests bullish momentum and Dollar strength, signaling traders to enter long trade on the USD.
- A downward trend (with descending highs and lows) indicates bearish momentum and dollar weakness, signaling traders to shorten the USD.
Correlate with forex pairs
USDX is correlated with currency pairs that have USD either as the base or quote currency.
- There is a positive correlation between USDX and currency pairs that have USD as the base currency, as when USDX appreciates, so does USD and, hence, the currency pair.
- There is an inverse correlation between USDX and currency pairs that have USD as the quote currency as when USDX appreciates, the USD depreciates. Hence, the currency pair depreciates as well.
For example, EUR/USD tends to negatively correlate with the USDX. When the USDX strengthens (indicating dollar strength), the EUR/USD pair typically weakens and vice versa.
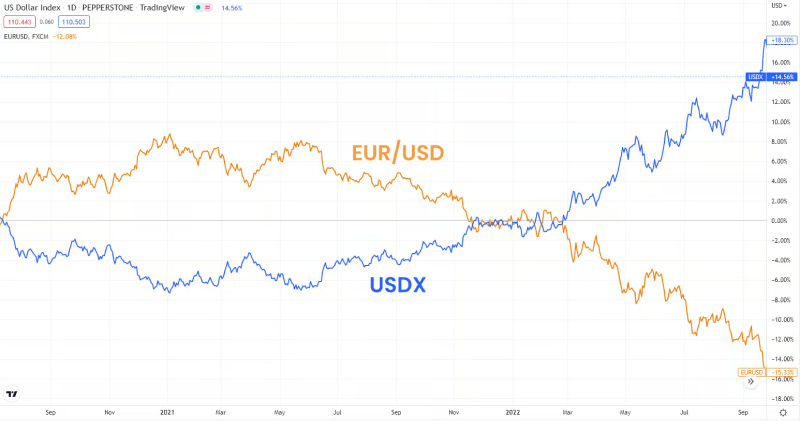
Analyze correlation strength
Use statistical measures like correlation coefficients to quantify the strength between the USDX and forex pairs. A correlation coefficient close to -1 indicates a strong negative correlation, while a coefficient close to +1 indicates a strong positive correlation. A coefficient close to 0 suggests no significant correlation.
Identify the current trend
Analyze the price action of the correlated forex pairs to identify the current trend.
Determine whether the currency pair is trending in the same direction as the USDX (confirming correlation) or exhibiting a divergence.
Confirm trade signals
Look for trade signals that align with both the USDX movement and the trend of the correlated forex pair. For example, if the USDX is trending upwards (indicating dollar strength) and EUR/USD is trending downwards, consider looking for opportunities to shorten EUR/USD and vice versa.
Monitor market sentiment
Stay updated on market sentiment and news events that may impact the USDX and correlated forex pairs. Additionally, monitor economic indicators, central bank decisions, geopolitical events, and other factors influencing market sentiment.
Interpret USDX movements to place forex orders
Trading with the USDX attracts traders seeking reliable instruments for speculation or diversification. However, there are risks, including potential mismatches with specific currency pairs and exposure to market volatility. Traders should weigh these factors carefully to optimize their trading strategies and outcomes.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.




