Maintaining a trading journal helps traders analyze past performance, identify the strengths and weaknesses of their trading strategies, and make data-driven decisions. A trader can unlock their true trading potential with a trading journal.
In this article, we look into why traders should keep a trading journal and how to use one.
What is a trading journal?
A trading journal is a record-keeping tool that allows traders to document every aspect of their trades. Traders can think of it as their personal trading storybook, where they jot down the details of each trade they make in the financial markets.
Important segments of a trading journal
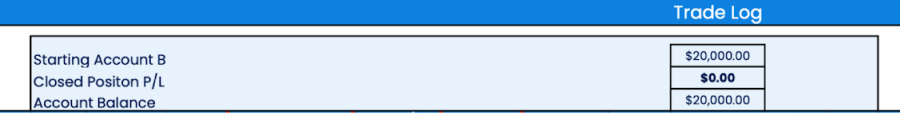
Trade log
A trading log is a detailed record of a trader's individual trades, providing essential information such as trade entry and exit points, dates and times, trade size, direction (long or short), trading strategies, risk management parameters (like stop-loss levels), and any pertinent comments or observations.
It serves as a comprehensive repository of a trader's trading history, enabling them to analyze and review their past performance, identify patterns, assess the effectiveness of their strategies, and learn from both successful trades and mistakes.
It also ensures data accuracy by meticulously recording every trade executed, allowing for precise analysis of trading performance and facilitating necessary adjustments.
A trade log also serves as a valuable tool for performance evaluation, enabling traders to assess their trading strategies objectively and make data-driven decisions.
Additionally, documenting recognizable patterns and technical analysis used in trades helps identify trends and trading behavior. Perhaps most crucially, a trade log helps traders learn from their mistakes by pinpointing where things went wrong when trades did not go as planned, allowing traders to avoid making the same mistakes in the future.
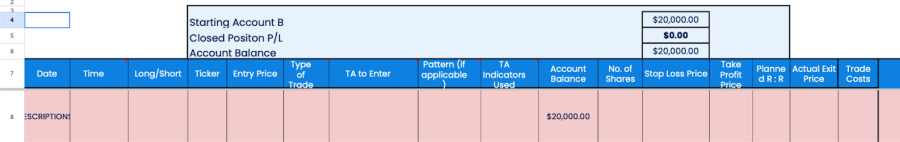
Some of the many parts of a trade log can include:
- Date and time: Tracks trade chronology and time-based patterns.
- Long/short position: Reveals bias and strategy tendencies.
- Ticker symbol: Records specific traded assets for reference.
- Entry price: Critical for gain/loss calculation and entry point assessment.
- Type of trade: Contextualizes trading strategies (e.g., day or swing trade).
- Technical analysis used: Understand decision-making methods.
- Patterns and indicators: Identifies patterns and indicators for refinement.
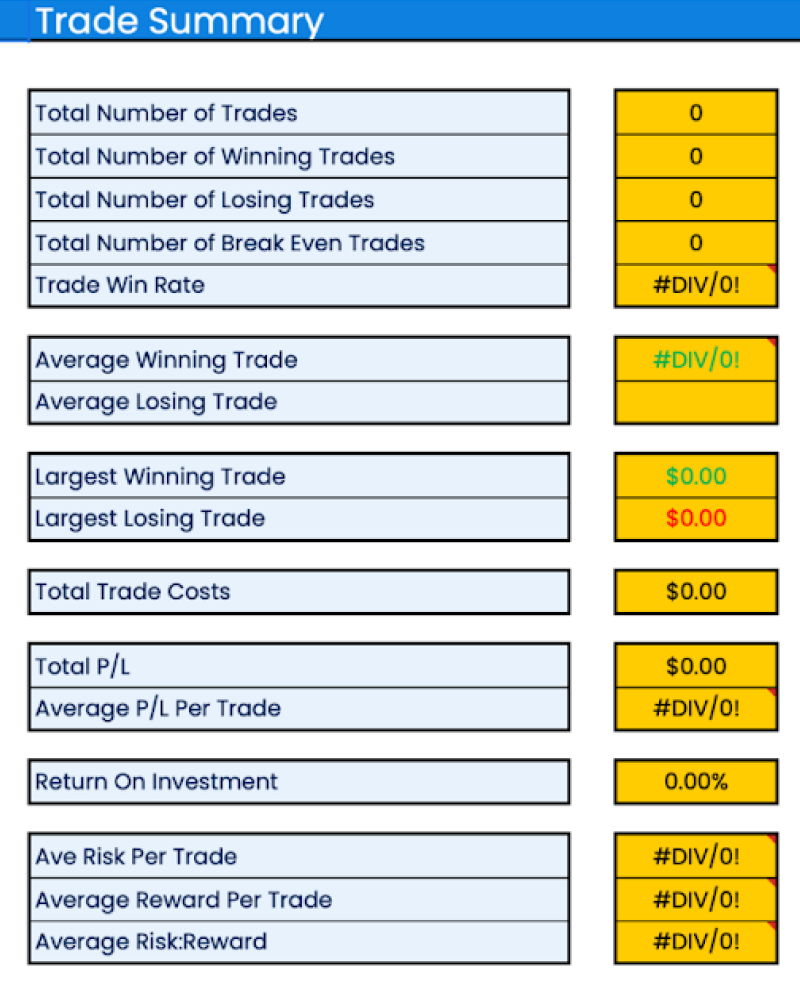
Trading summary
A trading summary concisely summarizes the essential information extracted from the trade log. It provides a high-level overview of the trading performance over a specific period.
While a trading summary is not an absolute requirement for a trading journal, it can prove to be beneficial. Skipping it means missing out on valuable trading opportunities and benefits. While the trade log provides detailed data, a summary offers a condensed overview that is easier to interpret and act upon. It also helps on multiple fronts, such as tracking goals, evaluating trading performance, and identifying current patterns.
A trading summary helps in analyzing future trends in the following ways:
- Performance benchmark: It serves as a benchmark for assessing future performance and helping identify improvements or setbacks.
- Strategy insights: It highlights the effectiveness of trading strategies and enables adjustments for better outcomes.
- Goal refinement: Over time, trading summary aids in refining trading goals, evaluating performance, and optimizing risk management.
- Psychological awareness: It's possible to detect patterns within the summary that can offer insights into emotional and cognitive influences on decision-making.
Timeframe pivots
Timeframe pivots refer to the practice of analyzing trades from different time perspectives. It involves examining the same trade or asset at various timeframes, such as daily, hourly, or even minute-by-minute charts. Each timeframe represents a different lens through which traders can view market data and trends.
Timeframe pivots allow for a comprehensive trade analysis that goes beyond a single timeframe, offering a multi-dimensional view of market behavior. Different timeframes confirm and validate trading signals, enhancing confidence when signals align across multiple periods.
These pivots also aid in risk management by revealing support, resistance, trends, and important price levels that might be missed in a narrow timeframe focus. Additionally, they provide adaptability to swiftly respond to market dynamics, enabling long-term positions with precise entry and exit points on short-term timeframes. Lastly, timeframe pivots help traders refine strategies by identifying the most suitable timeframes for specific approaches.
Important elements of a timeframe pivot are:
- Sum of closed position P/L: Logs the gain or loss from the trades, giving an overview of the trader’s performance.
- Type of trade: Categorizes trades based on strategies (such as day trading and swing trading).
- Win/loss: Indicates whether each trade was a win or a loss, aiding in assessing strategy effectiveness.
- Ticker: Identifies the specific assets or currencies traded.

It may also help traders trade better, here's how:
- Signal confirmation: Multiple timeframes verify trading signals, reducing false signals and enhancing accuracy.
- Entry and exit precision: Different timeframes offer insights for precise entry and exit points, aligning with trend direction.
- Effective risk management: Various timeframes guide stop-loss levels, enabling tailored risk management.
- Trend analysis: Analyzing multiple timeframes helps assess trend strength and duration, informing decisions on holding or capitalizing on trends.
- Diversification: Traders diversify strategies by considering various timeframes and balancing longer-term trends with shorter-term momentum approaches.
Mitigate trading risks with a trading journal
The use of a trading journal presents traders with a powerful tool to manage and mitigate risks while maximizing the benefits of informed decision-making. By diligently maintaining a trading journal, traders can navigate complex financial markets with greater confidence, discipline, and, ultimately, the potential for greater success.
Download the free trading journal template to figure out which trading strategies perfectly fit your trading goals and personality.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.




