Buying the dip is a forex technical analysis strategy which allows you to take advantage of the falling markets. After analyzing the reasons behind the price dip, you can identify the right opportunity to buy and enter either a short trade with a short-term downtrend expectation or long trade with a long-term uptrend expectation.
In our article, let us understand the buying the dip strategy in depth.
What is buying the dip?
Buying the dip refers to purchasing an asset after its prices have dipped. The lower price retracement refers to as a ‘dip’ and is generally short-term, which most likely increases in value with time. At this point, you can buy a new position or add to your existing positions.
A dip in currency pair prices can occur due to a number of factors like a dip in economic reports, a fall in the country’s GDP, fundamental deterioration and more.
For example, you want to trade USD/EUR, which is currently trading at 1.2. Let’s say there is a sudden price dip due to political instability in the US and therefore the exchange rate drops down to 0.7. As a trader, you believe that the dip is going to be temporary, and so you enter a long trade by buying more USD/EUR with an expectation of the prices to increase in the coming few weeks or months.
Now three months have passed and the political situation in the US has improved, which has increased the exchange rate moving past its initial value of 1.2, touching 1.7, therefore providing an upside gains.
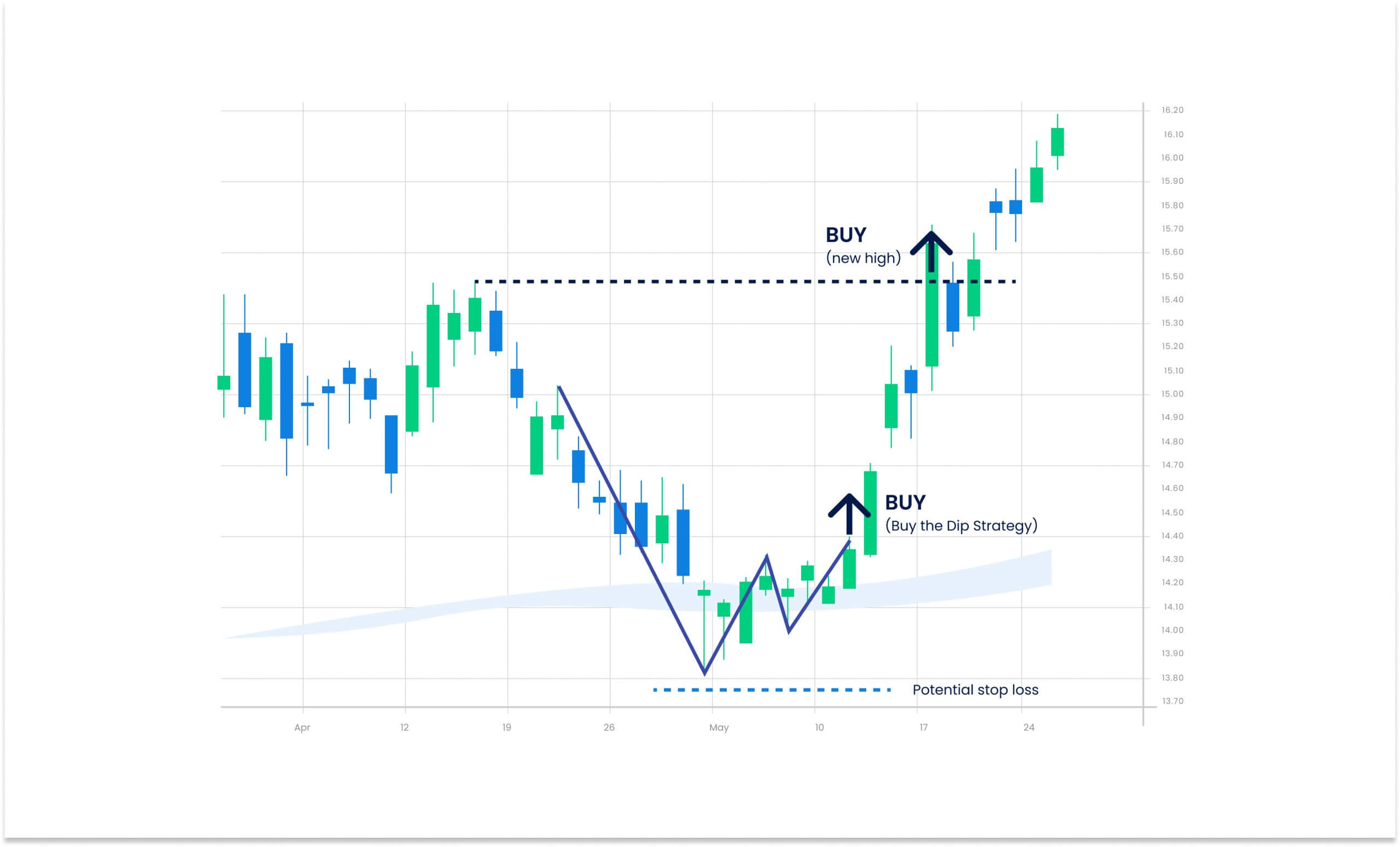
This graph has been recreated from the original source. Please note this image is a representation only and is not provided as general or personal advice.
Benefits of buying the dip
Rebound potential
Buying the dip allows you to benefit from the rebound potential of currency pairs. This happens because when there is a sudden price dip in a currency pair, you can quickly enter a long position because the prices may increase just as quickly. By buying low, you can benefit when prices increase again. This generally happens when a currency pair price reaches its support level or the market corrects itself after a panic selling situation.
Entry level at a lower price
Buying the dip presents you with an opportunity to buy the currency pair at a lower price than you might have otherwise. This enables you to grab the trading chance that you may have missed during earlier price movements. It is also beneficial for traders who want to enter the market but not at the prevailing high prices and wait for such sudden dips to enter.
Long-term growth potential*
Buying the dip can potentially help in long-term growth potential as it allows you to enter positions that have a strong long-term outlook at a favorable price*. You can benefit from price rebounds and fluctuations in the forex market, contributing to the long-term success* of the trade. You can do this by acquiring forex positions in undervalued currencies and riding long-term trends by holding onto the dip position for long.
*However, do consider that as much as their growth potential, favorable prices, and success, margin trading is high risk and there could also be losses.
Diversification
Buying the dip in forex helps diversify your trading portfolio by allowing you to add positions in currencies with a falling exchange rate. This, in turn, helps you potentially benefit from price fluctuation in currencies that you may not typically consider in a rising market.
Common ways to identify the price dips
Dollar-cost averaging strategy
The dollar-cost averaging strategy focuses on minimizing the impact of volatility from forex price fluctuations. With this strategy, a trader can invest a fixed amount in the currency pair at regular intervals, irrespective of the currency’s price. This helps you acquire higher positions in the market when the price dips and fewer positions when prices are high. Investing at regular intervals smooths out short-term volatility and reduces the impact of emotional trading.
Fibonacci retracements
The Fibonacci retracement strategy identifies the key support and resistance levels based on the Fibonacci ratios (that are derived from the Fibonacci sequence). First, identify the market trend by monitoring the currency pair’s highs and lows and then derive the key support and resistance levels.
When the currency pair goes through a price dip or a temporary downtrend reversal, then use the Fibonacci levels to identify potential buying opportunities.
How to buy the forex dip?*
- Identify the currency pair that you want to trade after analyzing the market and identify key support and resistance levels. Choose a pair showing temporary downtrend reversals.
- Wait for the prices to dip by keeping a close eye on the economic news, market events and similar factors.
- Once the price dip is identified, choose an entry point that could either be a support level or a specific point at which you expect the markets to rebound in the long term.
- Set the stop loss level below the currency pair’s entry point.
- After you have entered the trade, monitor the market closely to ensure the currency pair is moving in the direction you expected.
- Exit the trade in the long term after the prices have moved towards the uptrend.
*Please note this is not personal advice.
Use the dip in a currency pair today*
Buying the dip in forex helps create a high-risk-reward strategy. Focus on the long-term growth potential and adjust entry or exit points based on the current market conditions.
Disclaimer: All material published on our website is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered personal advice or recommendation. As margin FX/CFDs are highly leveraged products, your gains and losses are magnified, and you could lose substantially more than your initial deposit. Investing in margin FX/CFDs does not give you any entitlements or rights to the underlying assets (e.g. the right to receive dividend payments). CFDs carry a high risk of investment loss.